0. summary
1. MySQL的连接登录
. 1.1 登录的几种方式
. 1.2 免密码登录
. 1.2.1 my.cnf增加[client]标签
. 1.2.2 login-path
. 1.2.3 ~/.my.cnf
2. 使用mysqlworkbench
. 2.1 下载地址
. 2.2 连接登录
1. MySQL的连接登录
1.1 登录的几种方式
- mysql -p
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
......
mysql> select user();
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| root@localhost |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
- mysql -S /tmp/mysql.sock -u root -p
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql -S /tmp/mysql.sock -u root -p
Enter password:
......
mysql> select user();
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| root@localhost |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
该方法适用于在安装MySQL主机上进行本地登录,和第一种其实是一样的。因为默认的socket文件就是/tmp/mysql.sock, 如下:
mysql> show variables like 'socket%';
+---------------+-----------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------+
| socket | /tmp/mysql.sock |
+---------------+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p
Enter password:
......
mysql> select user();
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| [email protected] |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- mysql -h localhost -u root -p
[root@lab11g mysql]# mysql -h localhost -u root -p
Enter password:
......
mysql> select user();
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| root@localhost |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
该方式等价于2), 且和3)属于两个不同的"用户"
1.2 免密码登录
1.2.1 my.cnf增加[client]标签
[client]
user=root
password=mysql
#### 针对定义不同的客户端 ####
[mysql] ---- 这个是给/usr/loca/mysql/bin/mysql 使用的
user=root
password=mysql
[mysqladmin] ---- 这个是给/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqladmin使用的
user=root
password=mysql
每个不同的客户端需要定义不同的标签,使用[client]可以统一。这个方法有个不好,是明文的。
1.2.2 login-path
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql_config_editor
mysql_config_editor Ver 1.0 Distrib 5.7.13, for linux-glibc2.5 on x86_64
Copyright (c) 2012, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
MySQL Configuration Utility.
Usage: mysql_config_editor [program options] [command [command options]]
-#, --debug[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
-?, --help Display this help and exit.
-v, --verbose Write more information.
-V, --version Output version information and exit.
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
verbose FALSE
Where command can be any one of the following :
set [command options] Sets user name/password/host name/socket/port
for a given login path (section).
remove [command options] Remove a login path from the login file.
print [command options] Print all the options for a specified
login path.
reset [command options] Deletes the contents of the login file.
help Display this usage/help information.
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql_config_editor set --help
mysql_config_editor Ver 1.0 Distrib 5.7.13, for linux-glibc2.5 on x86_64
Copyright (c) 2012, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
MySQL Configuration Utility.
Description: Write a login path to the login file.
Usage: mysql_config_editor [program options] [set [command options]]
-?, --help Display this help and exit.
-h, --host=name Host name to be entered into the login file.
-G, --login-path=name
Name of the login path to use in the login file. (Default
: client)
-p, --password Prompt for password to be entered into the login file.
-u, --user=name User name to be entered into the login file.
-S, --socket=name Socket path to be entered into login file.
-P, --port=name Port number to be entered into login file.
-w, --warn Warn and ask for confirmation if set command attempts to
overwrite an existing login path (enabled by default).
(Defaults to on; use --skip-warn to disable.)
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
host (No default value)
login-path client
user (No default value)
socket (No default value)
port (No default value)
warn TRUE
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql_config_editor set -G panda -S /tmp/mysql.sock -u root -p
Enter password:
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql_config_editor print --all
[client]
[panda]
user = root
password = *****
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
[root@lab11g mysql_data]# mysql --login-path=panda ---- 这样登录就不需要密码,且文件二进制存储,位置是 ~/.mylogin.cnf, 打开可以发现其实是二进制文件。
该方式相对安全。如果server被黑了,也没什么用。不需要看明码。
MySQL其他客户端工具也都支持login-path
root@codelab:~# mysqladmin --help | grep login
-u, --user=name User for login if not current user.
except for login file.
--login-path=# Read this path from the login file.
1.2.3 ~/.my.cnf
[client]
user=root
password=mysql
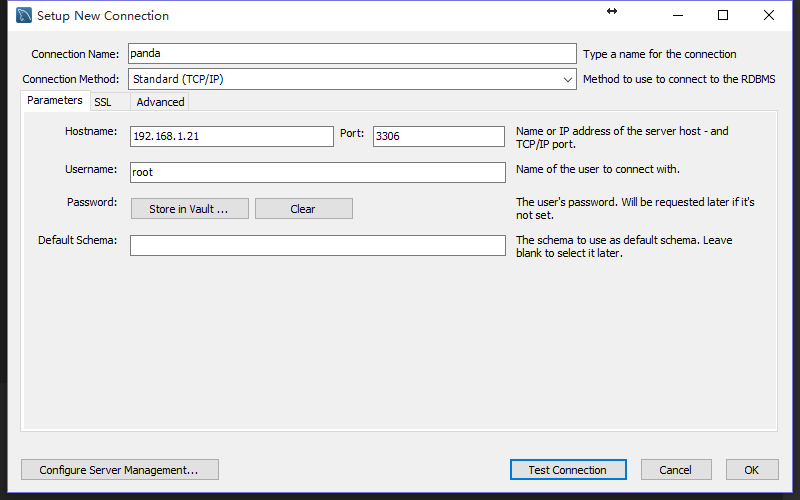
2. 使用mysqlworkbench
2.1 下载地址
http://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQLGUITools/mysql-workbench-community-6.3.7-winx64.msi