用來記錄你搜尋過的單字的伺服器
Preparation
- Vapor - 一個後端的Swift框架
- PostgreSQL - 使用的Database
- owlbot dictionary - 一個字典API
- Heroku - 可以發布Server的平台,以及提供Database
Steps
- 建立一個伺服器,在自己電腦上運作
- 處理HTTP請求
- 跟owlbot字典 要查詢單字
- 儲存新增的單字,以及查詢到的單字資訊
Step 1 - 建立一個伺服器,在自己電腦上運作
聽到要用Swift開發資料庫,不用緊張,在我們的這個時代,很多事情都有很好引導,我們重要的是要學會使用現有的工具。跟著我一步一步完成這個伺服器吧。
哦,不只跟著我,在這次關於Vapor的教程中,我會參考Ray Wenderlich的教程,每個影片基本上都在10分鐘之內,快又有內容的教學,值得一看,但我們會做一些修改以符合我們的功能。
介紹Vapor - 讓我們隨著這個影片來開始一個我們的Vapor專案吧!
首先,去到你的Terminal
vapor new LookupWord
去到該目錄
cd LookupWord
用Vapor執行Xcode
vapor xcode
然後稍等一下之後,在對話看選擇y打開Xcode
Select the `App` scheme to run.
Open Xcode project?
y/n> y
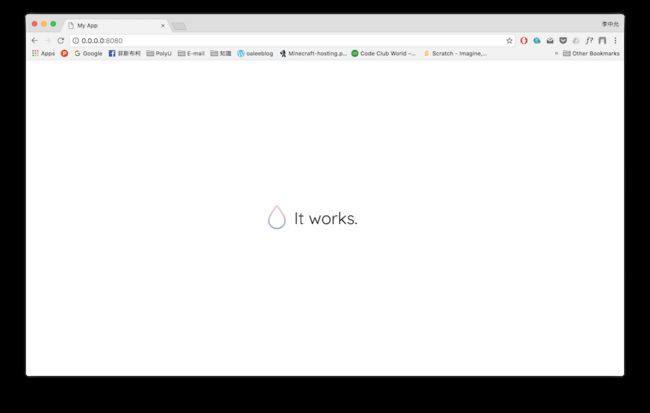
讓我們先來看看這個Xcode的專案是不是正常運作,重新選擇Target之後執行▶️專案。
喔耶!It's works!
Step 2 - 處理HTTP請求*
好了,現在我們需要來寫點程式了,
回到Xocde,然後去到main.swift
你可以按住⇧Shift加上 ⌘Command然後按O來快速打開檔案。
好的,到了main.swift之後,把程式碼變成像下面呈現的一樣。
import Vapor
let drop = Droplet()
drop.get("word", String.self) { req, word in
// We need to add some code later, to get the definition.
// return a json.
return try JSON(node: [
"new word": word
])
}
drop.run()
經過改動之後,讓我們再看看這個程序的功能,在執行▶️ 一次,
這段程式碼會處理送到0.0.0.0:8080/word/[the word you want to search]的請求。
現在這個階段,他會回傳給瀏覽器一個JSON格式的資訊,例如:
現在用你的瀏覽器(Chrome)前往http://0.0.0.0:8080/word/swift
你會看到他回傳{"new word":"swift"},那這樣就,對啦!
太好了,這樣我們第二部也完成了。
Step 3 - 跟owlbot字典 要查詢單字
關於如何在傳送HTTP的請求, 可以參考這裡。
在這裡,我們需要從owlbot dictionary拿到字的定義,所以我們要加一些程式碼來替代// We need to add some code later, to get the definition.,你的main.swfit`會變成:
import Vapor
import Foundation
let drop = Droplet()
drop.get("word", String.self) { req, word in
// get the shared URLSession
let session = URLSession.shared
// define the URL
let wordURLString: String = "https://owlbot.info/api/v1/dictionary/\(word)"
guard let url = URL(string: wordURLString) else {
print("Error: cannot create URL")
return try JSON(node: [
"error": "Error: cannot create URL"
])
}
// create the session task
let task = session.dataTask(with: url, completionHandler: { (data, response, error) in
// check for any errors
guard error == nil else {
print("error calling GET on /todos/1")
print(error!)
return
}
// make sure we got data
guard let responseData = data else {
print("Error: did not receive data")
return
}
// transform to JSON object
let json = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: responseData, options: [])
// cast JSON to Array
guard let jsonArray = json as? [Any] else {
print("Error: wrong data type")
return
}
// get each definition
for jsonDict in jsonArray {
if let wordDict = jsonDict as? [String:String] {
print("\n \(word) \n")
let definition = wordDict["defenition"] ?? "no definition"
let example = wordDict["example"] ?? "no example"
let type = wordDict["type"] ?? "no type"
print("definition : \(definition)")
print("example : \(example)")
print("type : \(type)")
} else {
print("Error: wrong data type")
}
}
})
task.resume()
session.finishTasksAndInvalidate()
return try JSON(node: [
"new word": word
])
}
drop.run()
現在,再回到瀏覽器,前往http://0.0.0.0:8080/word/success,然後你會看到以下的訊息出現在Xcode的Console裡。
GET /word/success
success
definition : the accomplishment of an aim or purpose.
example : "the president had some success in restoring confidence"
type : noun
success
definition : archaic
example : "the good or ill success of their maritime enterprises"
type : noun
Step 4 - 儲存新增的單字,以及查詢到的單字資訊
好了!現在我們到了最後一個步驟了,我們將要在本地建立一個資料庫,先測試,然後再將我們的伺服器發佈至Heroku的平台,一個免費提供空間給限制使用量的平台,他也會提供資料庫給我們使用。
請參考vapor/postgresql
為了要先設定資料庫,這邊有另一個Ray Wenderlich的教學,非常有用也很清楚。
To install database, we need to open the terminal
First, install Homebrew
首先,要安裝資料庫,我們會使用到Homebrew,如果你已經安裝過,可以跳過這個步驟。
先開啟Terminal,並安裝Homebrew:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
接著確保它有最新的內容
brew update
在安裝postgres資料庫
brew postgre
開始postgres的程式
postgres -D /usr/local/var/postgres
再用你自己的使用者名稱建立一個資料庫,whoami是一個指令將會回傳你的使用者名稱
createdb `whoami`
好了,讓我們來看看資料庫建立好了沒
psql
如果你看到以下資訊,那就沒問題啦
psql (9.6.1)
Type "help" for help.
lee=#
輸入\q離開資料庫存取程式。
所以現在,你已經有一個資料庫在你的電腦上工作了,酷吧!
接著要做幾件事情,來設定Vapor去使用這個資料庫:
- Import他的相關程序包
- 設置Droplet使用這個資料庫
- 建立一個配置的檔案
First, check out the provider page
讓我們去看一下Vaporprovider的頁面
複製這個連結加入Package.swift的檔案裡:
.Package(url: "https://github.com/vapor/postgresql-provider", majorVersion: 1, minor: 0)
所以你的Package.swift會看起來像是:
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "LookupWord",
dependencies: [
.Package(url: "https://github.com/vapor/vapor.git", majorVersion: 1, minor: 3),
.Package(url: "https://github.com/vapor/postgresql-provider", majorVersion: 1, minor: 0)
],
exclude: [
"Config",
"Database",
"Localization",
"Public",
"Resources",
"Tests",
]
)
然後我們需要重新生成一次Xcode的相依性,所以在執行一次以下命令
vapor xcode
為了要設定Droplet使用它,我們再一次打開main.swift,然後import VaporPostgreSQL
import VaporPostgreSQL
並且加上一行程式碼在let drop = Droplet()之後
try drop.addProvider(VaporPostgreSQL.Provider)
main.swift會看起來像是:
import Vapor
import VaporPostgreSQL
import Foundation
let drop = Droplet()
try drop.addProvider(VaporPostgreSQL.Provider)
// test the connection of database
drop.get("version") { req in
if let db = drop.database?.driver as? PostgreSQLDriver {
let version = try db.raw("SELECT version()")
return try JSON(node: version)
} else {
return "No db connection"
}
}
drop.get("word", String.self) { req, word in
// get the shared URLSession
let session = URLSession.shared
// define the URL
let wordURLString: String = "https://owlbot.info/api/v1/dictionary/\(word)"
guard let url = URL(string: wordURLString) else {
print("Error: cannot create URL")
return try JSON(node: [
"error": "Error: cannot create URL"
])
}
// create the session task
let task = session.dataTask(with: url, completionHandler: { (data, response, error) in
// check for any errors
guard error == nil else {
print("error calling GET on /todos/1")
print(error!)
return
}
// make sure we got data
guard let responseData = data else {
print("Error: did not receive data")
return
}
// transform to JSON object
let json = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: responseData, options: [])
// cast JSON to Array
guard let jsonArray = json as? [Any] else {
print("Error: wrong data type")
return
}
// get each definition
for jsonDict in jsonArray {
if let wordDict = jsonDict as? [String:String] {
print("\n \(word) \n")
let definition = wordDict["defenition"] ?? "no definition"
let example = wordDict["example"] ?? "no example"
let type = wordDict["type"] ?? "no type"
print("definition : \(definition)")
print("example : \(example)")
print("type : \(type)")
} else {
print("Error: wrong data type")
}
}
})
task.resume()
session.finishTasksAndInvalidate()
return try JSON(node: [
"new word": word
])
}
drop.run()
接下來,要新增一個配置檔案,
先建立在這個專案底下找到config,
並在這個資料夾體下載新增一個叫做secret的資料夾,
接著新增一個檔案叫做postgresql.json,也就是我們的配置檔案。
講你自己的資料替換"user"還有"database"
{
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"user": "Your user name",
"password": "",
"database": "Your user name",
"port": 5432
}
好了,那就讓我們再來執行一次,如果你前往瀏覽器去到以下的網址
http://0.0.0.0:8080/version
你會看到這個資料庫的相關版本資訊,你就可以確定你已經讓Vapor使用這個資料庫了!
[{"version":"PostgreSQL 9.6.1 on x86_64-apple-darwin16.1.0, compiled by Apple LLVM version 8.0.0 (clang-800.0.42.1), 64-bit"}]
現在我們需要加上兩個Model給我們的資料庫,
前往Terminal, 然後去到你的專案的路徑,
接著用以下的指令新增兩個Model:
touch Sources/App/Models/Word.swift
touch Sources/App/Models/Definition.swift
接著再重新生成一次專案的相依性,透過指令:
vapor xcode
然後再把相對應的程式碼,放到該檔案裡面:
Word.swift
import Vapor
import Fluent
import Foundation
final class Word: Model {
var id: Node?
var exists: Bool = false
var word: String
init(word: String) {
self.id = nil
self.word = word
}
init(node: Node, in context: Context) throws {
id = try node.extract("id")
word = try node.extract("word")
}
func makeNode(context: Context) throws -> Node {
return try Node(node: [
"id": id,
"word": word,
])
}
}
extension Word: Preparation {
static func prepare(_ database: Database) throws {
try database.create("words", closure: { words in
words.id()
words.string("word")
})
}
static func revert(_ database: Database) throws {
try database.delete("words")
}
}
extension Word {
func definitions() throws -> Children {
return children()
}
}
Definition.swift
import Vapor
import Fluent
import Foundation
final class Definition: Model {
var id: Node?
var exists: Bool = false
var word_id: Node?
var definition: String
var example: String
var type: String
init(word_id: Node,definition: String, example: String, type: String) {
self.id = nil
self.word_id = word_id
self.definition = definition
self.example = example
self.type = type
}
init(node: Node, in context: Context) throws {
id = try node.extract("id")
word_id = try node.extract("word_id")
definition = try node.extract("definition")
example = try node.extract("example")
type = try node.extract("type")
}
func makeNode(context: Context) throws -> Node {
return try Node(node: [
"id": id,
"word_id": word_id,
"definition": definition,
"example": example,
"type": type,
])
}
}
extension Definition: Preparation {
static func prepare(_ database: Database) throws {
try database.create("definitions", closure: { definitions in
definitions.id()
definitions.parent(Word.self, optional: false, unique: false, default: nil)
definitions.string("definition")
definitions.string("example")
definitions.string("type")
})
}
static func revert(_ database: Database) throws {
try database.delete("definitions")
}
}
extension Definition {
func word() throws -> Parent {
return try parent(word_id)
}
}
最後,讓我們的Droplet使用這兩個Model
let drop = Droplet()
try drop.addProvider(VaporPostgreSQL.Provider)
drop.preparations += Word.self
drop.preparations += Definition.self
這樣就可以了,讓我們來加上一些程式碼來測試一下,把程式碼修改成下的內容:
這邊有做一些修改,相較於前面的程式碼,這邊使用
drop.client去跟字典要資料
import Vapor
import VaporPostgreSQL
import HTTP
let drop = Droplet()
try drop.addProvider(VaporPostgreSQL.Provider)
drop.preparations += Word.self
drop.preparations += Definition.self
// test the connection of database
drop.get("version") { req in
if let db = drop.database?.driver as? PostgreSQLDriver {
let version = try db.raw("SELECT version()")
return try JSON(node: version)
} else {
return "No db connection"
}
}
//Redirect to word
drop.get() { req in
// change to your URL
return Response(redirect: req.uri.appendingPathComponent("word").path)
}
// Show all the words
drop.get("word") { req in
return try JSON(node: Word.all().makeNode())
}
// Show single word
drop.get("word", String.self) { req, wordString in
// Check if the word exist
if let word = try Word.query().filter("word", wordString).first() {
// if exist, show all the definition
return try JSON(node: word.definitions().all().makeNode())
} else {
// create a new word and save
var word = Word(word: wordString)
try word.save()
let wordDictResponse = try drop.client.get("https://owlbot.info/api/v1/dictionary/\(wordString)")
print(wordDictResponse.json?.array ?? "no response")
if let jsonArray = wordDictResponse.json?.array {
for jsonDict in jsonArray {
print(jsonDict)
if let jsonDefinition = jsonDict as? JSON {
let definition = jsonDefinition["defenition"]?.string ?? "no definition"
let example = jsonDefinition["example"]?.string ?? " "
let type = jsonDefinition["type"]?.string ?? "no type"
//create Definition
var newDefinition = Definition(word_id: word.id!, definition: definition, example: example, type: type)
try! newDefinition.save()
}
}
}
return try JSON(node: word.definitions().all().makeNode())
}
}
drop.run()
為了從我們的Server發出HTTP請求,我們需要做一些小調整,前往
Config/clients.json,然後將verifyHost以及verifyCertificates改成false
Warning Note: Use extreme caution when modifying these settings.
Config/clients.json
{
"tls": {
"verifyHost": false,
"verifyCertificates": false,
"certificates": "mozilla"
}
}
Hurrah!! now go test the application again by run it and use browser the lookup a word.
好的,讓我們再一次測試一下我們的伺服器,重新執行▶️,並且前往瀏覽器:
輸入例如http://0.0.0.0:8080/word/happy
如果一切都正確,他將會回傳:
[{"definition":"feeling or showing pleasure or contentment.","example":"\"Melissa came in looking happy and excited\"","id":1,"type":"adjective","word_id":1},
{"definition":"fortunate and convenient.","example":"\"he had the happy knack of making people like him\"","id":2,"type":"adjective","word_id":1},
{"definition":"informal","example":"\"they tended to be grenade-happy\"","id":3,"type":"adjective","word_id":1}]
恭喜你!!代表你成功啦!
現在我們擁有我們所需要的功能了:
- 透過對我們的伺服器發送HTTP請求,查詢字的定義
- 我們的伺服器從owlbot dictionary拿到定義
- 伺服器將新的單字以及定義儲存在資料庫
發佈至Heroku
不過,雖然功能都有了,但現在都還是在本地端執行,在我們自己的電腦裡,這樣子的話沒有辦法讓我們用手機來拿到資料,
所以我們要把它發佈到雲端,
再次借用Ray Wenderlich的發佈教學
首先,先建立Git的repository(讓我們可以記錄開發檔案的任何變動)
git init
依照Git的運作,新增所有檔案,
git add .
並且commit確認發送。
git commit -m "init"
最後,透過Vapor的指令,上傳到Heroku
vapor heroku init
維持一切預設的設定,所以被詢問是否要修改都回答N
Would you like to provide a custom Heroku app name?
y/n>n
https://boiling-ocean-81373.herokuapp.com/ | https://git.heroku.com/boiling-ocean-81373.git
Would you like to provide a custom Heroku buildpack?
y/n>n
Setting buildpack...
Are you using a custom Executable name?
y/n>n
Setting procfile...
Committing procfile...
Would you like to push to Heroku now?
y/n>n
You may push to Heroku later using:
git push heroku master
Don't forget to scale up dynos:
heroku ps:scale web=1
接著,建立雲端的資料庫
heroku addons:create heroku-postgresql:hobby-dev
執行以下指令:
heroku config
會按看到資料庫的相關地址,待會會用到這個地址。
DATABASE_URL: postgres://yfghktvrmwrael:6e48ccb331711093e9ee11bc89d2ef49db4d2bde8a9b596f7b5275e8fb2c3bfc@ec2-107-20-149-243.compute-1.amazonaws.com:5432/d5cds2laqgtqqu
接著,設定Procfile檔案裡面,
vi Procfile
按i來插入編輯
新增這些資訊在最後
--config:servers.default.port=$PORT --config:postgresql.url=$DATABASE_URL
整個檔案會看起來像是這樣:
web: App --env=production --workdir="./"
web: App --env=production --workdir=./ --config:servers.default.port=$PORT --config:postgresql.url=$DATABASE_URL
最後回到Xcode
編輯Config/secret/postgresql.json如下:
根據你拿到的地址,
{
"url": "postgres://yfghktvrmwrael:6e48ccb331711093e9ee11bc89d2ef49db4d2bde8a9b596f7b5275e8fb2c3bfc@ec2-107-20-149-243.compute-1.amazonaws.com:5432/d5cds2laqgtqqu"
}
然後回到Terminal
commit所以變動:
git add .
git commit -m "modified Procfile"
最後的最後,發佈至Heroku
git push heroku master
接著,等待...
經過一段漫長時間等待之後,讓我們來測試一下!
remote: -----> Compressing...
remote: Done: 64.2M
remote: -----> Launching...
remote: Released v10
remote: https://[your app].herokuapp.com/ deployed to Heroku
remote:
remote: Verifying deploy... done.
To https://git.heroku.com/[your app].git
1b544e4..6a8e4df master -> master
前往你拿到的網址https://[your app].herokuapp.com/
恭喜你!!!你現在有一個自己的伺服器,會記錄所有你問他的單字,
感謝你,和我一起Swift。
更多相關資訊,請前往我的Blog