1.请描述你所了解的设计模式.举例并描述其使用场景
单例模式
iOS生命周期中,有时我们只需要某个类的一个实例.
应用案例
UIApplication,UIAccelerometer,NSUserDefaults,NSNotificationCenter,NSFileManager,NSBundle,NSWorkspace,NSApplication
实现代码
//
// Singleton.h
//
@interface Singleton : NSObject
(Singleton *)sharedManager;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *singletonData;
@end
//
// Singleton.m
//
#import “Singleton.h”
@implementation Singleton
static Singleton *sharedManager = nil;
+ (Singleton *)sharedManager {
static dispatch_once_t once;
dispatch_once(&once, ^{
sharedManager = [[self alloc] init];
});
return sharedManager;
}
委托模式
委托是为了降低一个对象的复杂度和耦合度,使其能够更具通用性而将其中一些处理置于委托对象的编码方式.通用类因为通用性(与具体应用的无关性)而变为框架类,框架类保存委托对象的指针,并在特定时刻向委托对象发送消息.
应用案例
UITextFieldDelegate
textFieldShouldBeginEditing:
textFieldDidBeginEditing:
textFieldShouldEndEditing:
textFieldDidEndEditing:
委托消息的命名有一定的定性:使用Should时,应该返回一个布尔值;使用Will时,没有返回值,表示改变之前要做的事情;使用Did时,没有返回值,表示改变之后要做的事情.
UITableView:委托对象主要对控件对象的事件和状态变化做出响应,而数据源对象是为控件对象提供数据.委托中的方法在实现时是可选的,而数据源中的方法一般必须实现
观察者模式
一个对象状态改变也会连带影响其他很多对象的状态发生改变.观察者模式复用性强且对象之间匿名通信.
应用案例
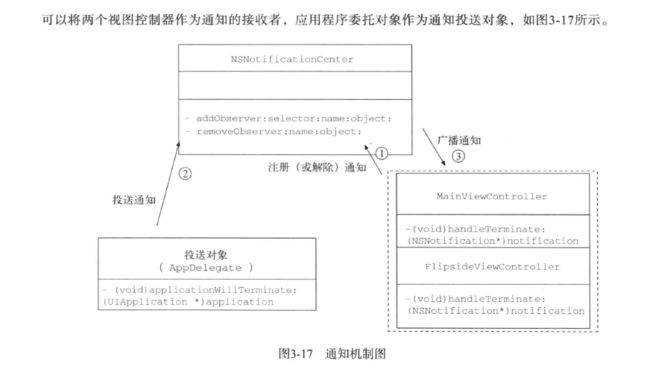
通知机制和KVO机制
通知机制
通知机制与委托机制不同的是,前者是”一对多”的对象之间的通信,后者是”一对一”的对象之间的通信
使用Utility Application工程模板,这个模板有主界面控制器(MainViewController)和翻转界面控制器(FlipsideViewController),还有应用程序委托对象AppDelegate
在MainViewController和FlipsideViewController这两个视图控制器中,注册通知者
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@selector(handleTerminate:)
name:@“AppWillTerminateNotification”
object:nil];
}
解除通知
- (void)dealloc {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserve:self];
}
MainViewConrtroler和FilpsideViewController的处理通知方法
- (void)handleTerminate:(NSNotification *)notification {
NSDictionary *theData = [notification userInfo];
if (theData != nil) {
NSDate *date = [theData objectForKey:@"TerminateDate"];
NSLog(@"FlipsideViewController App Terminate Date: %@", date);
}
}
如果我们想在应用终止时投送通知,需要重写AppDelegate中的方法
- (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
NSDate *date = [NSDate date];
NSDictionary *dataDict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:date forKey:@"TermineDate"];
[[NSNotificationCenter default] postNotificationName:@"AppWillTerminateNotification" object:self userInfo:DateDict];
// 除了上面代码中所示之外,还有另外一个重载方法:
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@"AppWillTerminateNotification" object:self];
}
// 事实上,Cocoa Touch框架该通知,当应用事件发生时,由iOS系统自动投送
// so, 删除上面的代码并修改MainViewController和FlipsideViewController中注册接收通知者的代码
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserve:self
selector:@selector(handleTerminate:)
name:UIApplicationWillTerminateNotification
object:nil];
}
除了应用生命周期的不同阶段有不同的通知外,很多控件也会在某些事件发生时投送通知,例如UITextField控件.在编辑过程的不同阶段会分别发出如下通知:UITextFieldTextDidBeginEditingNotification, UITextFieldTextDidChangeNotification, UITextFieldTextDidEndEditingNotification
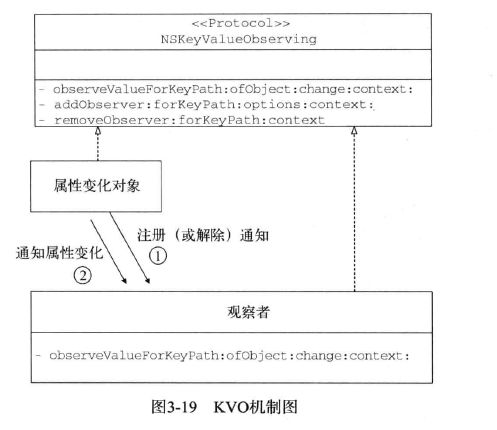
KVO机制
KVO不像通知机制那样通过一个通知中心通知所有观察者对象,而是在对象属性变化时通知会被直接发送给观察者对象
应用程序委托对象的AppDelegate.h
@interface AppDelegate : UIResponder
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIWindow *window;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *appStatus; // 记录应用程序状态的变化
@property (strong, nonatomic) AppStatusWatcher *watcher; // 定义ppStatusWatcher类型的观察者对象属性
AppDelegate.m
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
self.watcher = [AppStatusWatcher new];
// addObserver是要要被关注的对象
// forKeyPath是要被关注对象的属性
// options是为属性变化设置的选项,NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionOld意味着把新旧两个值都传递给观察者
// context上下文内容,类型为(void*),如果传递"空",应是"NULL",而非"nil"
[self addObserver:self.watcher forKeyPath:@"appStatus" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionOld context:@"Pass Context"];
self.appStatus = @"launch";
return YES;
}
- (void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application {
self.appStatus = @"inactive";
}
- (void)applicationDidEnterBackground:(UIApplication *)application {
self.appStatus = @"background";
}
- (void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application {
self.appStatus = @"inactive";
}
- (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application {
self.appStatus = @"active";
}
- (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
self.appStatus = @"terminate";
}
观察者AppStatusWatcher的代码
@interface AppStatusWatcher : NSObject
@end
@implementation AppStatusWatcher
- (void)observeValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath ofObject:(id)object change:(NSDictionary *)change context:(void *)context {
NSLog(@"Property '%@' of object '%@' changed: %@ context: %@", keyPath, object, change, context);
}
@end
因为NSbject类实现了NSKeyValueObserving协议,所以只需声明AppStatusWatcher继承NSObject类,无需实现NSKeyValueObserving协议.
observeValueForKeyPath:ofObject:change:context:方法中的
observeValueForKeyPath参数是被关注的属性
ofObject是被关注的对象
change是字典类型,包含了属性变化的内容,这些内容与注册时属性设置的选项(options参数)有关
context是注册时传递的上下文
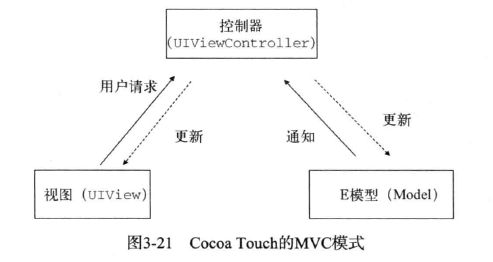
MVC模式
Model-ViewController,模型-视图-控制器 模式
模型:保存应用数据的状态,回应视图对状态的查询,处理应用业务逻辑,完成应用的功能,将状态的变化通知视图.
视图:为用户展示信息并提供接口,用户通过视图想控制器发出动作请求,然后再向模型发出查询状态的申请,而模型状态的变化会通知给视图
控制器:接收用户请求,根据请求更新模型.另外,控制器还会更新所选择的视图作为对用户请求的回应.控制器是视图和模型的媒介,可以降低视图和模型的耦合度,是视图和模型的权责更加清晰,从而提高开发效率.
2.不手动指定autoreleasepool的前提下,一个autorelease对象在什么时刻释放?
在MRR(Manual Retain Release, 手动保持释放), 也称为MRC(Manual Reference Counting, 手动引用计数)中,释放对象通过release或autorelease消息实现,其中release消息会立刻使引用计数减1,autorelease消息会使对象放入内存释放池中延迟释放,对象的引用计数并不变化,而是向内存释放池中添加一条记录,直到池被销毁前通知池中的所有对象全部发送release消息才真正将引用计数减少.
在iOS程序中,默认内存释放池的释放在程序结束
注意
int main(int argh, char *argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
return UIApplicationMain(argh, argue, nil, NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]));
}
}
代码被包裹在@autoreleasepool{...}之间,这是池的作用范围,默认是整个应用.如果产生大量对象,采用autorelease释放也会导致内存泄漏.
什么时候必须使用autorelease?
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
static NSString *CellIdentifier = @"CellIdentifier";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
if (cell == nil) {
cell = [[[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier] autorelease];
}
NSUInteger row = [indexPath row];
NSDictionary *rowDic = [self.listTeams objectAtIndex:row];
cell.textLabel.text = [rowDict objectForKey:@"name"];
NSString *imagePath = [rowDict objectForKey:@"image"];
imagePath = [imagePath stringByAppendingString:@".png"];
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:imagePath];
cell.accessoryType = UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator;
return cell;
}
1> 上述代码中,cell对象不能马上释放,我们需要使用它设置表视图界面.autorelease一般用在为其他调用者提供对象的方法中,对象在该方法不能马上释放,而需要延迟释放.
2> 此外,还有一种情况需要使用autorelease,即"类级构造方法":
NSString *message = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"您选择了%@队", rowValue];
该对象的所有权虽然不是当前调用者,但它是由iOS系统通过发送autorelease消息放入到池中的.当然,这一切对于开发者都是不可见的,我们也要注意减少使用这样的语句
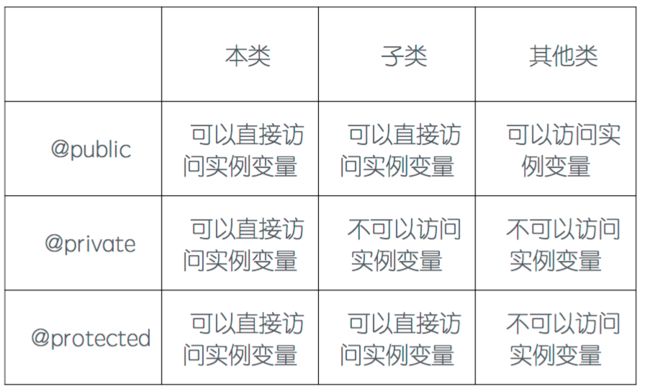
3.分别描述Swift和OC中的访问限制有哪些?
Swift
略
OC
4.简述KVC和KVO
KVC(Key Value Coding)
键值编码是Cocoa的标准组件,允许开发者通过名字(键)访问属性,而无需调用显式的存取方法.由此,系统的某些部分就可以动态访问属性,即使在编译的时候不知道属性的键是什么.这种动态访问对于nib文件的加载和Core Data尤其重要.在Mac系统上,KVC是AppleScript接口的基础部分.
valueForKeyPath:会自动把数字类型(int,float等)转换成NSNumber对象,而其他的非对象类型(结构体,指针)会转换成NSValue对象.
KVC方法有key和keyPath两个版本.键和键路径的区别在于,后者可以包含嵌套关系,用句点分开.��
用KVC实现高阶消息传递
valueForKey:有很对有用的特例,比如说NSArray和NSSet这样的容器类都覆盖了这个方法.valueForKey:被传递给容器中的每个对象,而不是对容器本身进行操作.结果会被添加进返回的容器中.这样可以很方便的用一个容器对象创建另一个容器对象.
NSArray *array = @[@"foo", @"bar", @"baz"];
NSArray *capitals = [array valueForKey:@"capitalizedString"];
方法capitalizedString被传递给NSArray中的每一项,并返回一个包含结果的新NSArray,把消息(capitalizedString)作为参数传递称为高阶消息传递(Higher Order Messaging).多个消息可以用键路径传递:
NSArray *array = @[@"foo", @"bar", @"baz"];
NSArray *capitalLengths = [array valueForKey:@"capitalizedString.length"];
以上代码对array的每一个元素调用capitalizedString,然后调用length,再把返回值封装进NSNumber对象.结果被收集进名为capitalLengths的新数组
KVO(Key Value Observing)键值观察
键值观察是就对象对象属性变化透明地通知观察者的一种机制.
实现功能:无论对象什么时候发生变化,都可以让表格单元自动更新.
KVO用addObserver:forKeyPath:options:context:开始观察,用removeObserver:forKeyPath:context:停止观察.回调总是observeValueForKeyPath:ofObject:change:context:
// KVCTableViewCell.m
- (void)removeObservation {
if (self.isReady) {
[self.object removeObserver:self forKeyPath:self.property];
}
}
- (void)addObservation {
if (self.isReady) {
[self.object addObserver:self forKeyPath:self.property options:0 context:(void *)self];
}
}
- (void)observeValueForKeyPat:(NSString *)keyPath ofObject:(id)object change:(NSDictionary *)change {
if ((__bridge id)context == self) {
[self update];
}
else {
[super observeValueForKeyPath:keyPath ofObject:object change:change context:context];
}
}
- (void)dealloc {
if (__object && [_property length] > 0) {
[_object removeObserver:self forKeyPath:_property context:(void *)self];
}
}
- (void)setObject:(id)anObject {
[self removeObservation];
_object = anObject;
[self addObservation];
[self update];
}
- (void)setProperty:(NSString *)aProperty {
[self removeObservation];
_property = aProperty;
[self addObservation];
[self update];
}
// KVCTableViewController.m
#import "RNTimer.h"
@interface KVCTableViewController ()
@property (readwrite, retain) RNTimer *timer;
@property (readwrite, retain) NSDate *now;
@end
@implementation KVCTableViewController
- (void)updateNow {
self.now = [NSDate date];
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[self updateNow];
__weak id weakSelf = self;
self.timer = [RNTimer repeatingTimerWithInterval:1 block:^{
[weakSelf updateNow];
}];
}
- (void)viewDidUnload {
self.timer = nil;
self.now = nil;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
static NSString *CellIdentifier = @"KVCTableViewCell";
id cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
if (cell == nil) {
cell = [[[KVCTableView alloc] initWithReusableIdentifier:CellIdentifier] autorelease];
[cell setProperty:@"now"];
[cell setObject:self];
}
return cell;
}
@end
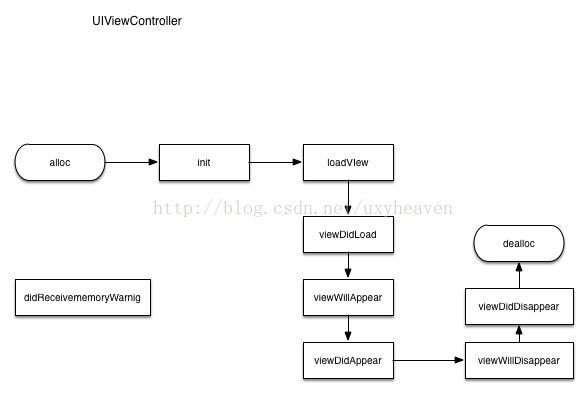
5.简述视图控制器的生命周期
loadView中的三个方法
createFields 接受参数,初始化变量
createViews 创建视图
createEvents 绑定事件.如按钮的点击,NotificationCenter,KVO
viewDidLoad
loadData 加载数据,调用一些api
dealloc
destroyEvents 取消事件绑定
destroyViews 释放,销毁视图
destroyFields 释放,销毁引用的变量
didReceiveMemoryWarning
cleanData 释放一些可以释放的资源
额外
enterForeground 进入前台时调用
enterBackground 进入后台时调用