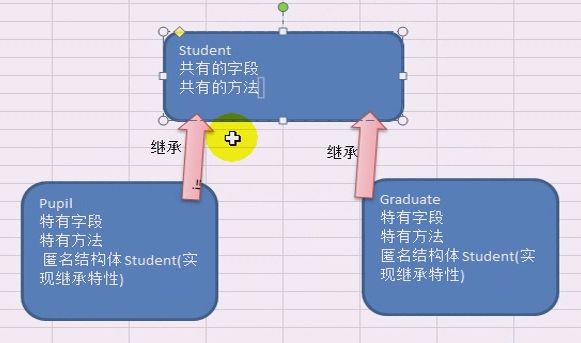
快速入门应用案例
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int
Scores float64
}
//将Pupil和Graduate共有方法绑定到Student结构体
func (stu *Student) ShowInfo () {
fmt.Printf("学生名=%v 年龄=%v 成绩=%v\n",stu.Name,stu.Age,stu.Scores)
}
func (stu *Student)GetSum( n1 float64,n2 float64) float64{
//业务判断
return n1 + n2
}
func (stu *Student)SetScores(scope float64){
//业务判断
stu.Scores = scope
}
//小学生
type Pupil struct {
Student //嵌入Student匿名结构体
}
//小学生独有的方法
func (p *Pupil) Testing(){
fmt.Println("小学生正在考试")
}
//大学生
type Graduate struct {
Student //嵌入Student匿名结构体
}
//大学生独有方法
func (gra *Graduate) Testing(){
fmt.Println("大学生正在考试")
}
func main() {
//小学生
pupil :=&Pupil{}
pupil.Student.Name="tome"
pupil.Student.Age=10
pupil.Testing()
pupil.Student.SetScores(70.1)
pupil.Student.ShowInfo()
//大学生
graduate :=&Graduate{}
graduate.Student.Name="mary"
graduate.Student.Age=22
graduate.Testing()
graduate.Student.SetScores(90.1)
graduate.Student.ShowInfo()
fmt.Println(graduate.GetSum(21.1,25.0))
}
深入讨论
package main
import "fmt"
type A struct {
Name string
age int
}
func (a *A)SayOk() {
fmt.Println("A SayOk",a.Name)
}
func (a *A)hello() {
fmt.Println("A hello",a.Name)
}
type B struct {
A
}
func main() {
var b B
b.A.Name="tom"
b.A.age=20
b.A.SayOk()
b.A.hello()
}
简写
func main() {
var b B
b.A.Name="tom"
b.A.age=20
b.A.SayOk()
b.A.hello()
//上面的写法可以简化
b.Name="jack"
b.age= 34
b.SayOk()
b.hello()
}
package main
import "fmt"
type A struct {
Name string
age int
}
type B struct {
Name string
Score float64
}
type C struct {
A
B
Name string
}
func main() {
var c C
//如果c没有Name字段,而A和B有Name,
//这时就必须通赤指定的匿名结构体的名字来访问(区分)
c.Name="tom"
fmt.Println("c=",c.Name)
}
package main
import "fmt"
type Goods struct {
Name string
Price float64
}
type Brand struct {
Name string
Address string
}
type TV struct {
Goods
Brand
}
func main() {
tv := TV{Goods{"电视机001", 3999.99}, Brand{"小米", "北京"}}
fmt.Println("TV:", tv)
tv2 :=TV{
Goods: Goods{
Price:8999.9,
Name:"sony",
},
Brand: Brand{
"海尔",
"山东",
},
}
fmt.Println(tv2)
}
指针的方式
package main
import "fmt"
type Goods struct {
Name string
Price float64
}
type Brand struct {
Name string
Address string
}
type TV struct {
*Goods //用指针的方式,效率高
*Brand
}
func main() {
tv := TV{&Goods{"电视机001", 3999.99}, &Brand{"小米", "北京"}}
fmt.Println("TV:", *tv.Goods,*tv.Brand)
tv2 :=TV{
Goods: &Goods{
Price:8999.9,
Name:"sony",
},
Brand: &Brand{
"海尔",
"山东",
},
}
fmt.Println(*tv2.Goods,*tv2.Brand)
}
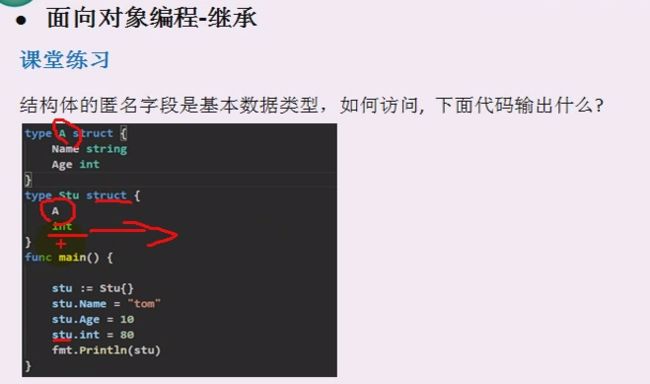
package main
import "fmt"
type Monster struct {
Name string
Age int
}
type E struct {
Monster
int
n int
}
func main() {
//匿名字段是基本数据类型的例子
var e E
e.Name = "孙悟空"
e.Age = 500
e.int = 20
e.n = 30
fmt.Println("E = ",e)
}
多重继承
type Goods struct {
Name string
Price float64
}
type Brand struct {
Name string
Address string
}
type TV struct {
*Goods //用指针的方式,效率高
*Brand
}