本文会介绍怎么用python解决线性规划问题,为什么要用python而不是matlab和lingo呢?因为matlab的函数写法不太符合正常的思维方式,编起来很复杂。而lingo虽然编写容易,但报错不详细,一旦有错很难查出来。而python就没有这些问题。
关于python的语法就不再介绍了,主要介绍pulp库的用法。
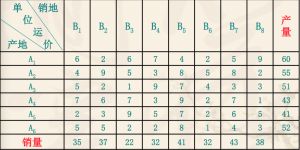
以此题为例:计算6个生产点8个销售点的最小费用运输问题。产销单位运价如下表。
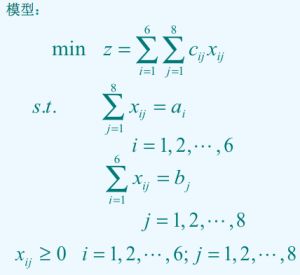
先建模,很容易得到以下模型:
现在开始编程:
引入头文件是必须的:
#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
importnumpyasnp
frompulpimport*
step1先新建一个问题,随便取名为prob:
prob = LpProblem("test1", LpMinimize)
step2然后定义变量为x,每个x代表了对应的A点卖到B点的数量:
foriinrange(1, 49, 1):
exec('x%s= LpVariable("x%s", 0, None, LpInteger,[])'%(i,i))
x = [[x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6,x7,x8],[x9,x10,x11,x12,x13,x14,x15,x16],
[x17,x18,x19,x20,x21,x22,x23,x24],[x25,x26,x27,x28,x29,x30,x31,x32],
[x33,x34,x35,x36,x37,x38,x39,x40],[x41,x42,x43,x44,x45,x46,x47,x48]]
对于LpVariable函数包含的参数,一次为 变量名,变量值的最小值,变量值的最大值,变量类型。
这里LpInteger表示变量的类型是int型,根据题目的需要还可以改成LpContinuous(实数型)和LpBinary(二值型,即0或1)。
step3开始写入数据:
cost = np.array([[6,2,6,7,4,2,9,5],[4,9,5,3,8,5,8,2],[5,2,1,9,7,4,3,3],
[7,6,7,3,9,2,7,1],[2,3,9,5,7,2,6,5],[5,5,2,2,8,1,4,3]])
capacity = np.array([60,55,51,43,41,52])
demand = np.array([35,37,22,32,41,32,43,38])
产地的产量为capacity,销地的销量为demand,单位运价为cost
step4设定目标函数:
result = 0
foriinrange(0, 6):
forjinrange(0, 8):
result += x[i][j]*cost[i][j]
prob += result, "obj"
是以result最小为目标的,如果要求结果最大为目标的题目可在result前面加上负号。
step5还要设置约束:
产量的约束:
foriinrange(1,7,1):#设置产量的约束
exec('prob += sum(x[%s]) <= capacity[%s]' % (i - 1, i - 1))
销量的约束:
foriinrange( 1 , 9 , 1):#设置销量的约束
z=0
forjinrange( 1 , 7 , 1):
z+=x[j-1][i-1]
exec('prob += z >= demand[%s]'%(i-1))
step6需要编写的部分就已经完成了,只需要输出结果就行了
# Solve the problem using the default solver
prob.solve()
# Print the status of the solved LP
print ( "Status:", LpStatus[prob.status] )
# Print the value of the variables at the optimum
forvinprob.variables():
print (v.name, "=", v.varValue)
# Print the value of the objective
print ( "objective=", value(prob.objective) )
输出的内容分别是计算状态(optimal时就说明结果正常),变量值,和目标函数值。
这题就做完啦~
最后把代码汇总一下:
#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from pulp import *
# A new LP problem
prob = LpProblem("test1", LpMinimize)
cost = np.array([[6,2,6,7,4,2,9,5],[4,9,5,3,8,5,8,2],[5,2,1,9,7,4,3,3],
[7,6,7,3,9,2,7,1],[2,3,9,5,7,2,6,5],[5,5,2,2,8,1,4,3]])
capacity = np.array([60,55,51,43,41,52])
demand = np.array([35,37,22,32,41,32,43,38])
# Variables
for i in range(1, 49, 1):
exec('x%s= LpVariable("x%s", 0, None, LpInteger,[])'%(i,i))
x = [[x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6,x7,x8],[x9,x10,x11,x12,x13,x14,x15,x16],
[x17,x18,x19,x20,x21,x22,x23,x24],[x25,x26,x27,x28,x29,x30,x31,x32],
[x33,x34,x35,x36,x37,x38,x39,x40],[x41,x42,x43,x44,x45,x46,x47,x48]]
# Objective
result = 0
for i in range(0, 6):
for j in range(0, 8):
result += x[i][j]*cost[i][j]
prob += result, "obj"
# (the name at the end is facultative)
# Constraints
# for i in range(1,7,1):#先对y赋值
for i in range(1,7,1):#设置产量的约束
exec('prob += sum(x[%s]) <= capacity[%s]' % (i - 1, i - 1))
for i in range( 1 , 9 , 1):#设置销量的约束
z=0
for j in range( 1 , 7 , 1):
z+=x[j-1][i-1]
exec('prob += z >= demand[%s]'%(i-1))
# Solve the problem using the default solver
prob.solve()
# Print the status of the solved LP
print ( "Status:", LpStatus[prob.status] )
# Print the value of the variables at the optimum
for v in prob.variables():
print (v.name, "=", v.varValue)
# Print the value of the objective
print ( "objective=", value(prob.objective) )