Python数据可视化
写得比较粗浅,后面会对数据分析专题进行深入。
安装环境matplotlib
个人前面也说了强烈建议使用Pycharm作为Python初学者的首选IDE,主要还是因为其强大的插件功能,很多环境都能一键安装完成,像本文的matplotlib,numpy,requests等。
下面直接上效果图:
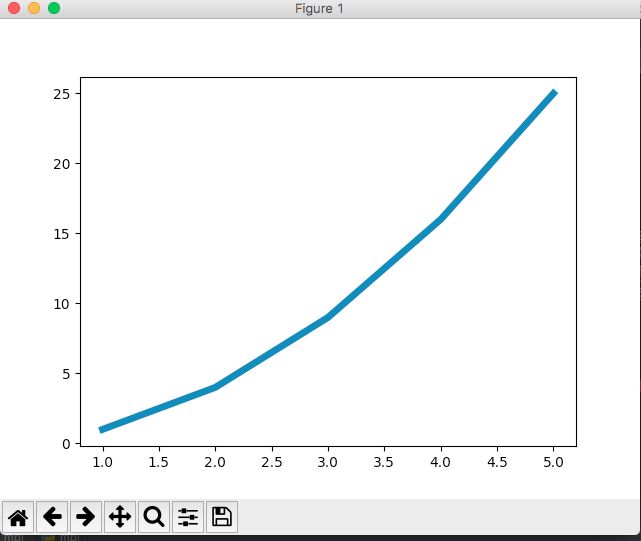
绘制简单的折丝图
使用plot来绘制折线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制折线图
squares = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
# plt.plot(squares, linewidth=5) # 指定折线粗细,
# #plt.show();
#
# #修改标签文字和线条粗细
# plt.title("squre number", fontsize=24)
# plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
# plt.ylabel("square of value", fontsize=14)
# plt.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=14)
# plt.show()
# 校正图形
input_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
plt.plot(input_values, squares, linewidth=5)
plt.show()
生成的效果图:
使用scatter绘制散点图并设置样式
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 简单的点
# plt.scatter(2, 4)
# plt.show()
#
# # 修改标签文字和线条粗细
plt.title("squre number", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("square of value", fontsize=14)
#设置刻度标记大小
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=14)
# 绘制散点
x_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y_values = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, s=100)
plt.show()
自动计算数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_values = list(range(1, 1001))
y_values = [x ** 2 for x in x_values]
# y_values = [x * x for x in x_values]
# y_values = [x ^ 2 for x in x_values]
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, s=40)
# 坐标轴的取值范围
# plt.axis(0, 1100, 0, 1100000) # 依次是xmin xmax,ymin,ymax
plt.show()
随机漫步
import matplotlib.pyplot as ply
from random import choice
class RandomWalk():
def __init__(self, num_points=5000):
self.num_points = num_points
self.x_values = [0]
self.y_values = [0]
def fill_walk(self):
# 不断走,直到达到指定步数
while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points:
# 决定前进方向以及沿这个方向前进的距离
x_direction = choice([1, -1])
x_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
x_step = x_direction * x_distance
y_direction = choice([1, -1])
y_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
y_step = y_direction * y_distance
# 不能原地踏步
if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0:
continue
next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step
next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step
self.x_values.append(next_x)
self.y_values.append(next_y)
rw = RandomWalk()
rw.fill_walk()
ply.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, s=15)
ply.show()
效果图
使用Pygal模拟掷骰子
pygal能够绘制的图形可以访问pygal介绍
环境安装,直接在Pycharm上安装插件。
import pygal
from random import randint
class Die():
def __init__(self, num_sides=6):
self.num_sides = num_sides;
def roll(self):
# 返回一个位于1和骰子面数之间的随机值
return randint(1, self.num_sides)
die = Die()
results = []
# 掷100次骰子,并将结果放在列表中。
for roll_num in range(10):
result = die.roll()
results.append(str(result))
print(results)
# 分析结果
frequencies = []
for value in range(1, die.num_sides + 1):
frequency = results.count(value)
frequencies.append(frequency)
print(frequencies)
# 对结果进行可视化
hist = pygal.Box()
hist.title = "result of rolling one D6 1000 times"
hist.x_labels = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6']
hist.x_title = "Result"
hist.y_title = "frequency of result"
hist.add('D6', frequencies)
hist.render_to_file('die_visual.svg')
使用Web API
1.1安装requests
这个可以直接在Pycharm中安装插件,非常方便。
1.2处理API响应
import requests
# 执行api调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
r = requests.get(url)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
# 将api响应存储在一个变量中
response_dic = r.json()
# 处理结果
print(response_dic.keys())
得到结果:
Status code: 200
dict_keys(['total_count', 'incomplete_results', 'items'])
1.3处理响应字典
# 将api响应存储在一个变量中
response_dic = r.json()
# 处理结果
print(response_dic.keys())
print("Total repositories:", response_dic['total_count'])
repo_dics = response_dic['items']
print("repositories returned:" + str(len(repo_dics)))
# 研究一个仓库
repo_dic = repo_dics[0]
print("\nKeys:", str(len(repo_dic)))
# for key in sorted(repo_dic.keys()):
# print(key)
print("Name:", repo_dic['name'])
print("Owner:", repo_dic['owner']['login'])
print("Starts:", repo_dic['stargazers_count'])
print("Repository:", repo_dic['html_url'])
print("Created:", repo_dic['created_at'])
print("Updated:", repo_dic['updated_at'])
print("Description:", repo_dic['description'])
得到结果:
Total repositories: 2061622
repositories returned:30
Keys: 71
Name: awesome-python
Owner: vinta
Starts: 40294
Repository: https://github.com/vinta/awesome-python
Created: 2014-06-27T21:00:06Z
Updated: 2017-10-29T00:50:49Z
Description: A curated list of awesome Python frameworks, libraries, software and resources