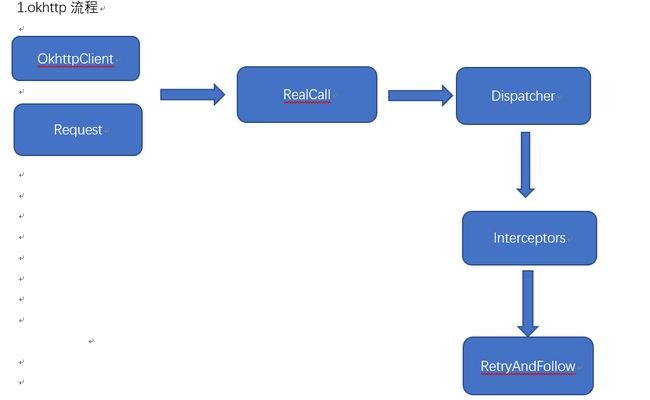
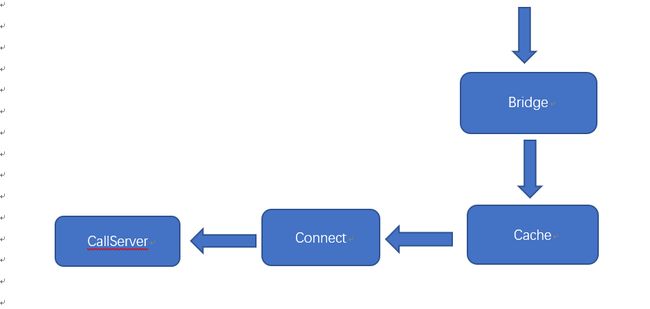
下面介绍下流程图中用到的类的主要作用
OkhttpClient:所有请求的客户端类,一般只创建一次作为全局实例保存
Request:主要是封装请求报文信息url,请求方法,各种请求头等。
RealCall:代表一个实际的http请求,是链接request和respone的桥梁
Despatcher:决定了同步或者异步请求,它的内部维护了一个线程池用来执行网络请求,内部有三个队列维护同步或者异步请求,despatcher不 断的从request队列中获取Realcall,然后通过拦截器连是否复用缓存,如果不复用就从服务器获取数据
Interceptors:拦截器连依次执行拦截器连中的每个拦截器将服务器的数据返回。
RetryAndFollow:网络连接失败后重连,重定向。
Bridge:主要是设置内容长度,编码,压缩格式,添加cookies,设置报头等主要是请求前的操作。
Cache:主要负责缓存的管理,当网络请求有符合的缓存请求,直接返回cache给客户端,不用经过网络端。
Connect;为当前的请求找到一个合适的链接,有可能复用已有的链接,如果链接可以复用就不用重新创建,还涉及到连接池的概念
CallServer:向服务器发起真的网络请求然后返回
public void synRequest(){
OkHttpClient client =
new OkHttpClient.Builder().connectTimeout(60,TimeUnit.SECONDS).build();
Request request =
new Request.Builder().url("http://www.baidu.com").get().build();
Call call = client.newCall(request);
try {
Response response =call.execute();
System.
out.print(response.body().string());
}
catch (IOExceptione) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
接下来我们分析OkHttpClient.Builder()内部类
public Builder() {
dispatcher = new Dispatcher();
protocols = DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS;
connectionSpecs = DEFAULT_CONNECTION_SPECS;
eventListenerFactory = EventListener.factory(EventListener.NONE);
proxySelector = ProxySelector.getDefault();
cookieJar = CookieJar.NO_COOKIES;
socketFactory = SocketFactory.getDefault();
hostnameVerifier = OkHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE;
certificatePinner = CertificatePinner.DEFAULT;
proxyAuthenticator = Authenticator.NONE;
authenticator = Authenticator.NONE;
connectionPool = new ConnectionPool();
dns = Dns.SYSTEM;
followSslRedirects = true;
followRedirects = true;
retryOnConnectionFailure = true;
connectTimeout = 10_000;
readTimeout = 10_000;
writeTimeout = 10_000;
pingInterval = 0;
}
从内部类的构造方法中可以看出创建了Dispatcher,ConnectionPool两个重要的类
接下来我们分析Request的创建
public final class Request {
final HttpUrl url;
final String method;
final Headers headers;
final @Nullable RequestBody body;
final Object tag;
private volatile CacheControl cacheControl; // Lazily initialized.
Request(Builder builder) {
this.url = builder.url;
this.method = builder.method;
this.headers = builder.headers.build();
this.body = builder.body;
this.tag = builder.tag != null ? builder.tag : this;
}
public HttpUrl url() {
return url;
}
public String method() {
return method;
}
public Headers headers() {
return headers;
}
public String header(String name) {
return headers.get(name);
}
public List headers(String name) {
return headers.values(name);
}
public @Nullable RequestBody body() {
return body;
}
public Object tag() {
return tag;
}
public Builder newBuilder() {
return new Builder(this);
}
/**
* Returns the cache control directives for this response. This is never null, even if this
* response contains no {@code Cache-Control} header.
*/
public CacheControl cacheControl() {
CacheControl result =
cacheControl;
return result != null ? result : (cacheControl = CacheControl.parse(headers));
}
public boolean isHttps() {
return url.isHttps();
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Request{method="
+ method
+ ", url="
+ url
+ ", tag="
+ (tag != this ? tag : null)
+
'}';
}
public static class Builder {
HttpUrl
url;
String
method;
Headers.Builder
headers;
RequestBody
body;
Object
tag;
public Builder() {
this.method = "GET";
this.headers = new Headers.Builder();
}
Builder(Request request) {
this.url = request.url;
this.method = request.method;
this.body = request.body;
this.tag = request.tag;
this.headers = request.headers.newBuilder();
}
public Builder url(HttpUrl url) {
if (url == null) throw new NullPointerException("url == null");
this.url = url;
return this;
}
/**
* Sets the URL target of this request.
*
*@throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code url} is not a valid HTTP or HTTPS URL. Avoid this
* exception by calling {@link HttpUrl#parse}; it returns null for invalid URLs.
*/
public Builder url(String url) {
if (url == null) throw new NullPointerException("url == null");
// Silently replace web socket URLs with HTTP URLs.
if (url.regionMatches(true, 0, "ws:", 0, 3)) {
url =
"http:" + url.substring(3);
}
else if (url.regionMatches(true, 0, "wss:", 0, 4)) {
url =
"https:" + url.substring(4);
}
HttpUrl parsed = HttpUrl.parse(url);
if (parsed == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("unexpected url: " + url);
return url(parsed);
}
/**
* Sets the URL target of this request.
*
*@throws IllegalArgumentException if the scheme of {@code url} is not {@code http} or {@code
* https}.
*/
public Builder url(URL url) {
if (url == null) throw new NullPointerException("url == null");
HttpUrl parsed = HttpUrl.get(url);
if (parsed == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("unexpected url: " + url);
return url(parsed);
}
/**
* Sets the header named {@code name} to {@code value}. If this request already has any headers
* with that name, they are all replaced.
*/
public Builder header(String name, String value) {
headers.set(name, value);
return this;
}
/**
* Adds a header with {@code name} and {@code value}. Prefer this method for multiply-valued
* headers like "Cookie".
*
*
Note that for some headers including {@code Content-Length} and {@code Content-Encoding},
* OkHttp may replace {@code value} with a header derived from the request body.
*/
public Builder addHeader(String name, String value) {
headers.add(name, value);
return this;
}
public Builder removeHeader(String name) {
headers.removeAll(name);
return this;
}
/** Removes all headers on this builder and adds {@code headers}. */
public Builder headers(Headers headers) {
this.headers = headers.newBuilder();
return this;
}
/**
* Sets this request's {@code Cache-Control} header, replacing any cache control headers already
* present. If {@code cacheControl} doesn't define any directives, this clears this request's
* cache-control headers.
*/
public Builder cacheControl(CacheControl cacheControl) {
String value = cacheControl.toString();
if (value.isEmpty()) return removeHeader("Cache-Control");
return header("Cache-Control", value);
}
public Builder get() {
return method("GET", null);
}
public Builder head() {
return method("HEAD", null);
}
public Builder post(RequestBody body) {
return method("POST", body);
}
public Builder delete(@Nullable RequestBody body) {
return method("DELETE", body);
}
public Builder delete() {
return delete(Util.EMPTY_REQUEST);
}
public Builder put(RequestBody body) {
return method("PUT", body);
}
public Builder patch(RequestBody body) {
return method("PATCH", body);
}
public Builder method(String method, @Nullable RequestBody body) {
if (method == null) throw new NullPointerException("method == null");
if (method.length() == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("method.length() == 0");
if (body != null && !HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(method)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("method " + method + " must not have a request body.");
}
if (body == null && HttpMethod.requiresRequestBody(method)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("method " + method + " must have a request body.");
}
this.method = method;
this.body = body;
return this;
}
/**
* Attaches {@code tag} to the request. It can be used later to cancel the request. If the tag
* is unspecified or null, the request is canceled by using the request itself as the tag.
*/
public Builder tag(Object tag) {
this.tag = tag;
return this;
}
public Request build() {
if (url == null) throw new IllegalStateException("url == null");
return new Request(this);
}
}
}
从中我们可以看出Request主要是一些请求前的信息设置如url,请求方式,请求头等的设置
接下来我们分析
Callcall = client.newCall(request);
Call是链接request和response的桥梁
Okhttpclient类中
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);
}
RealCall类中
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.
eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}
主要是创建RealCall
接下来我们分析
Response response = call.execute();
RealCall类中
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
//保证每个call只能执行一次
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
//通过连接器连里面的拦截器依次执行
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
}
catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
}
finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
[if !supportLineBreakNewLine]
[endif]
我们分析
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Dispatcher类中
private final Deque runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** Used by {@code Call#execute} to signal it is in-flight. */
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
我们从中可以看出同步请求就是将call添加到同步队列中
接下来我们分析
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
private void finished(Deque calls, T call, boolean promoteCalls) {
int runningCallsCount;
Runnable idleCallback;
synchronized (this) {
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");
if (promoteCalls) promoteCalls();
runningCallsCount = runningCallsCount();
idleCallback =
this.idleCallback;
}
if (runningCallsCount == 0 && idleCallback != null) {
idleCallback.run();
}
}
public synchronized int runningCallsCount() {
return runningAsyncCalls.size() + runningSyncCalls.size();
}
从中我们可以看出主要是重新计算请求的数量
接下来我们分析RealCall中
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(
client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(
retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(
new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(
new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(
new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(
client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(
new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain =
new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
主要是依次执行拦截器连中不同功能的拦截器来获取数据,后续的章节我们会介绍每个拦截器的作用。