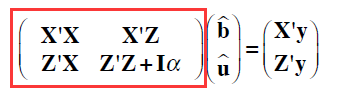王金玉, 陈国宏. 数量遗传与动物育种[M]. 东南大学出版社, 2004.
第十六章: BLUP育种值估计
用矩阵混合线性方程组计算:方差组分已知
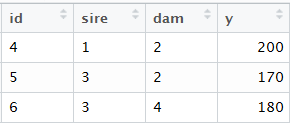
数据
Y = Xb + Za + e
> dat <- data.frame(id=c(4,5,6),sire = c(1,3,3),dam=c(2,2,4),y=c(200,170,180))
> dat
id sire dam y
1 4 1 2 200
2 5 3 2 170
3 6 3 4 180
> for( i in 1:3) dat[,i] <- as.factor(dat[,i])
> str(dat)
'data.frame': 3 obs. of 4 variables:
$ id : Factor w/ 3 levels "4","5","6": 1 2 3
$ sire: Factor w/ 2 levels "1","3": 1 2 2
$ dam : Factor w/ 2 levels "2","4": 1 1 2
$ y : num 200 170 180
> dat
id sire dam y
1 4 1 2 200
2 5 3 2 170
3 6 3 4 180
A-1
> Ainv <- makeAinv(pped)$Ainv;Ainv
6 x 6 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1 1.5 . 0.5 -1.0 . .
3 . 2.0 0.5 0.5 -1 -1
2 0.5 0.5 2.0 -1.0 -1 .
4 -1.0 0.5 -1.0 2.5 . -1
5 . -1.0 -1.0 . 2 .
6 . -1.0 . -1.0 . 2
> cbind(XpX,XpZ)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7]
[1,] 3 0 0 0 1 1 1
> cbind(ZpX,ZpZ+Ainv*alpha)
6 x 7 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1 . 3 . 1 -2 . .
3 . . 4 1 1 -2 -2
2 . 1 1 4 -2 -2 .
4 1 -2 1 -2 6 . -2
5 1 . -2 -2 . 5 .
6 1 . -2 . -2 . 5
混合线性方程组:LHS
> LHS=rbind(cbind(XpX,XpZ),cbind(ZpX,ZpZ+Ainv*alpha)) #LHS
> LHS
7 x 7 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
3 . . . 1 1 1
1 . 3 . 1 -2 . .
3 . . 4 1 1 -2 -2
2 . 1 1 4 -2 -2 .
4 1 -2 1 -2 6 . -2
5 1 . -2 -2 . 5 .
6 1 . -2 . -2 . 5
混合线性方程组:RHS
> RHS=rbind(Xpy,Zpy) #RHS
> RHS
[,1]
[1,] 550
[2,] 0
[3,] 0
[4,] 0
[5,] 200
[6,] 170
[7,] 180
求解方差
> sol=solve(LHS)%*%RHS #
> sol
7 x 1 Matrix of class "dgeMatrix"
[,1]
[1,] 183.1993935
[2,] 2.7445034
[3,] -3.1235785
[4,] 0.3790751
[5,] 4.3062926
[6,] -3.7376801
[7,] -0.1667930
用asreml计算BLUP值,方差组分定义
计算逆矩阵
ainv <- asreml.Ainverse(dat[,1:3])$ginv
定义方差组分,为固定的值
Va <- (1/2)*Ve;names(Va) <- c("F")
Ve <- 6666.67;names(Ve) <- c("F")
拟合模型
mode <- asreml(y ~ 1, random=~ ped(id,init=Va),
family=asreml.gaussian(dispersion = Ve),
ginverse =list(id=ainv),data=dat)
结果查看
> summary(mode)$varcomp
gamma component std.error z.ratio constraint
ped(id)!ped 3333.335 3333.335 NA NA Fixed
R!variance 6666.670 6666.670 NA NA Fixed
> coef(mode)$random
effect
ped(id)_1 2.7445034
ped(id)_3 -3.1235785
ped(id)_2 0.3790751
ped(id)_4 4.3062926
ped(id)_5 -3.7376801
ped(id)_6 -0.1667930
> summary(mode,all=T)$coef.random
solution std error z ratio
ped(id)_1 2.7445034 56.40660 0.048655711
ped(id)_3 -3.1235785 55.86638 -0.055911592
ped(id)_2 0.3790751 57.25153 0.006621222
ped(id)_4 4.3062926 54.53877 0.078958379
ped(id)_5 -3.7376801 54.26003 -0.068884590
ped(id)_6 -0.1667930 55.18367 -0.003022507
注意,这里blup值的标准误,它的计算方法是Ve*diag(solve(LHS))计算出来的。
所有R语言的代码
# data
y=c(110,100,110,100,100,110,110,100,100)
Herd <- c(1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,3)
Sire <- c("ZA","AD","BB","AD","AD","CC","CC","AD","AD")
dat <- data.frame(Herd,Sire,y)
dat
X = matrix(c(1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1),9, byrow=F)
X
Z = matrix(c(1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,
0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1),9, byrow=F)
Z
I1=diag(4)
I2=diag(9)
# 方差组分固定值
se=1
su=0.1
G=I1*su
R=I2*se
V = Z%*%G%*%t(Z) + R
V
Vinv <- solve(V)
blue <- solve(t(X)%*%Vinv%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Vinv%*%y
blue
blup <- G%*%t(Z)%*%Vinv%*%(y - X%*%blue)
blup
# 用混合线性方程组
alpha <- se/su
XpX=crossprod(X) #X’X
XpZ=crossprod(X,Z) #X’Z
ZpX=crossprod(Z,X) #Z’X
ZpZ=crossprod(Z) #Z’Z
Xpy=crossprod(X,y) #X’y
Zpy=crossprod(Z,y) #Z'y
LHS=rbind(cbind(XpX,XpZ),cbind(ZpX,ZpZ+diag(4)*alpha)) #LHS
LHS
RHS=rbind(Xpy,Zpy) #RHS
RHS
sol=solve(LHS)%*%RHS #
sol
# 用asreml进行处理
Ve = 0.1; Va = 1
names(Ve) <- c("F")
names(Va) <- c("F")
dat$Herd <- as.factor(dat$Herd)
mod <- asreml(y ~ Herd-1,random = ~ Sire,data=dat)
model <- asreml(y ~ Herd-1, random = ~ id(Sire,init=Va),
family=asreml.gaussian(dispersion = Ve), data=dat)
model <- update(model)
coef(model)
summary(model)$varcomp
dat
write.csv(dat,"d:/dat.csv")
# have pedigree information
dat <- data.frame(id=c(4,5,6),sire = c(1,3,3),dam=c(2,2,4),y=c(200,170,180))
dat
for( i in 1:3) dat[,i] <- as.factor(dat[,i])
str(dat)
dat
ped <- dat[,1:3]
library(nadiv)
pped <- prepPed(ped)
pped
makeA(pped)
Ainv <- makeAinv(pped)$Ainv;Ainv
library(asreml)
library(Matrix)
y <- matrix(c(200,170,180),3,1)
X <- matrix(c(1,1,1),3,1);X
Z <- matrix(c(0,0,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1),byrow = T,3,6);Z
alpha = 2
XpX <- crossprod(X);XpX
XpZ <- crossprod(X,Z);XpZ
ZpX <- crossprod(Z,X);ZpX
ZpZ <- crossprod(Z);ZpZ
Xpy <- crossprod(X,y);Xpy
Zpy <- crossprod(Z,y);Zpy
cbind(XpX,XpZ)
cbind(ZpX,ZpZ+Ainv*alpha)
LHS=rbind(cbind(XpX,XpZ),cbind(ZpX,ZpZ+Ainv*alpha)) #LHS
LHS
RHS=rbind(Xpy,Zpy) #RHS
RHS
# result
sol=solve(LHS)%*%RHS #
sol
ainv <- asreml.Ainverse(dat[,1:3])$ginv
ainv
Va <- (1/2)*Ve;names(Va) <- c("F")
Ve <- 6666.67;names(Ve) <- c("F")
mode <- asreml(y ~ 1, random=~ ped(id,init=Va),
family=asreml.gaussian(dispersion = Ve),
ginverse =list(id=ainv),data=dat)
summary(mode)$varcomp
coef(mode)$random
summary(mode,all=T)$coef.random