- Adobe Animate(常简称为 AN)多媒体创作工具绿色下载安装
sdiSONG
adobe
AdobeAN软件简介AdobeAnimate(常简称为AN)是Adobe公司开发的一款强大的多媒体创作工具。它主要用于制作动画、互动内容以及游戏。AdobeAnimate的前身是FlashProfessional,经过多次版本迭代后,现已成为一款功能丰富、界面友好的专业设计软件。它支持多种平台,包括桌面、移动设备和网页,因而广受动画师和设计师的喜爱。一、软件简介1.1什么是AdobeAnimat
- transformer编码器解码器图解
Ai玩家hly
人工智能transformernlp
这张图展示了Transformer模型的架构,包含编码器(左边)和解码器(右边)两部分。以下是对图中每个步骤的详细解释,结合生活场景来说明每一步的意义和推理过程。编码器部分(左边)输入嵌入(InputEmbedding):步骤:将输入序列中的每个单词转换为固定维度的向量表示。生活场景:想象你在学习一种新的语言,每个单词都有一个独特的代号或符号。这一步就像是给每个单词分配一个独特的代码,以便计算机能
- C语言-堆(heap)的详解与实现
CodeNest
C语言算法数据结构c语言
1.什么是堆?堆(Heap)是一种特殊的树形数据结构,通常用于实现优先队列。它分为最大堆(MaxHeap)和最小堆(MinHeap),具有以下特性:最大堆:父节点的值大于或等于任何一个子节点的值。最小堆:父节点的值小于或等于任何一个子节点的值。在堆中,树的每个节点的值都必须满足堆的性质。2.堆的结构和性质堆通常是一棵完全二叉树,其特性决定了它的用途和性能:完全二叉树:除了最底层,其他每一层的节点都
- 【Android】安卓开源项目(AOSP)
守月满空山雪照窗
Androidandroid
安卓开源项目(AndroidOpenSourceProject,AOSP)是由谷歌主导的一个开放源代码项目,旨在为移动设备提供一个可定制的操作系统。AOSP的源码库包含了构建安卓操作系统的所有必要组件,开发者可以利用这些源码进行定制和开发。以下是关于安卓开源项目的详细介绍:AOSP的组成部分源码库:包含安卓操作系统的完整源代码,包括系统核心、库、服务、应用程序和工具。构建系统:AOSP使用Soon
- Git配置SSH及通过IDEA连接GitLab方法总结
小鹿的周先生
gitsshintellij-idea
写在前面:还记得大学毕业来到公司那一阵子,老大叫我配置Git环境,并且通过SSH连接GitLab来上传和拉取代码。当时我整了一个下午还是没能配置好。一个方面是自己能力实在是太差了,另一个方面是网上有些方法都比较乱、不够详细。前几天我的Git工具出现了莫名其妙的错误(能够拉取新代码、当时上传代码却失败了),于是我重新配置了SSH。后面决定写一篇博客来记录一下。开始配置1、下载并且安装git2、第一次
- mysql之group by语句
程序研
mysqlmysql数据库
MySQL的GROUPBY语句详细介绍在MySQL数据库中,GROUPBY子句用于将查询结果按照一个或多个列进行分组。这在数据分析和报表生成中非常有用,因为它允许我们对数据进行汇总和聚合,从而提取有价值的信息。本文将详细介绍GROUPBY语句的用法、注意事项以及通过多个代码例子来演示其功能。1.基本概念GROUPBY子句通常与聚合函数(如COUNT、SUM、AVG、MAX、MIN等)一起使用,以便
- 66道软件工程面试八股文(答案、分析和深入提问)整理
ocean2103
面试题软件工程面试职场和发展
1.软件测试的策略是什么?回答软件测试的策略是确保软件产品的质量和稳定性,以便满足用户需求和期望。下面是一些常见的软件测试策略:手动测试与自动化测试:手动测试:测试人员手动执行测试用例,以发现软件缺陷。自动化测试:使用自动化工具执行测试,提高效率和可重复性,尤其适用于回归测试。黑盒测试与白盒测试:黑盒测试:关注于软件的功能和输出,不考虑内部实现细节。白盒测试:关注软件内部的逻辑结构,测试代码的每个
- 10道计算机组成原理面试八股文(答案、分析和深入提问)整理
ocean2103
面试题面试javaspringboot
1.解释缓存(Cache)的工作原理及其类型。回答缓存(Cache)是计算机系统中用于提高数据访问速度的一种临时存储器。它位于中央处理器(CPU)与主存(RAM)之间,旨在减少CPU对主存的访问延迟,从而加速程序运行。缓存的工作原理局部性原理:时间局部性:如果某个数据被访问,那么它在近期内很可能会再次被访问。空间局部性:如果某个数据被访问,那么它附近的数据也很可能在不久的将来被访问。存储结构:缓存
- 关于银联支付交易状态码的一些分析
初九之潜龙勿用
数据库大数据microsoft金融c#
目录关于银联支付一些准备交易状态码的一些分析小结关于银联支付目前B2C购物支付场景下,支付宝和微信的在线支付已经成为我们经常遇到的支付方式。另外,银联支付也是我们日常的一种支付方式,本文所指的银联支付即指中国银联网关支付产品,主要适用于持卡人在商户网站B2C购物支付场景,持卡人通过点击银联在线支付图标(可选择支付类型),并在银联在线支付网关完成支付信息录入,最终完成支付。银联在线支付支持输入卡号付
- 高校物品捐赠管理系统(11291)
codercode2022
java后端springboottypescriptspringjavascriptactionscript
有需要的同学,源代码和配套文档领取,加文章最下方的名片哦一、项目演示项目演示视频二、资料介绍完整源代码(前后端源代码+SQL脚本)配套文档(LW+PPT+开题报告)远程调试控屏包运行三、技术介绍Java语言SSM框架SpringBoot框架Vue框架JSP页面Mysql数据库IDEA/Eclipse开发
- python笔记(3)(re库和pandas库)
Techer_Y
笔记
参考链接:Python正则表达式|菜鸟教程(runoob.com)1、re库,python正则表达式正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列它能帮助你检查一个字符串是否与某种模式匹配。re模块使python语言拥有全部的正则表达式功能。re.match尝试从字符串起始位置匹配一个模式,如果不是起始位置匹配成功的话,match()就返回none。re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
- ✨探究✨进程最大可以打开多少个文件
linuxlinux运维运维
大家好,我是半夏之沫一名金融科技领域的JAVA系统研发我希望将自己工作和学习中的经验以最朴实,最严谨的方式分享给大家,共同进步写作不易,期待大家的关注和点赞关注微信公众号【技术探界】前言原本是想搞清楚一台服务器最多能建立多少个连接,在学习的过程中,发现能建立多少个连接受多个因素影响,其中一个因素就是进程最大可打开文件数,我在自行查阅资料加请教专门搞容器的同事后,感觉这个知识点有点意思,故撰写此文以
- 【Linux】20.基础IO(2)
流星白龙
Linuxlinux服务器性能优化
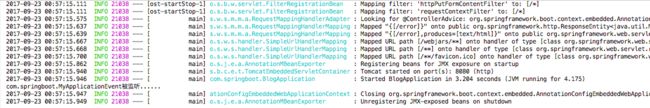
文章目录2.理解文件系统2.1inode2.2如何理解目录2.3硬链接2.4软链接2.5硬链接和软链接的区别2.理解文件系统2.1inode我们使用ls-l的时候看到的除了看到文件名,还看到了文件元数据。ydk_108@iZuf68hz06p6s2809gl3i1Z:~/108/lesson20$lltotal8drwxrwxr-x2ydk_108ydk_1084096Jan2317:05./dr
- arm-trusted-firmware (ATF介绍)
赢在拼搏中
1.大致描述ATF提供了安全世界的参考实现软件[ARMv8-A],包括执行的[SecureMonitor][TEE-SMC]异常级别3(EL3)。它实现了各种ARM接口标准,如电源状态协调接口([PSCI]),可信板启动要求(TBBR,ARMDEN0006C-1)和[SMC呼叫公约][SMCCC]。尽可能代码旨在重用或移植到其他ARMv8-A型号和硬件平台。2.功能◆初始化安全世界(例如,异常向量
- Transformer的linear和softmax
编码浪子
AItransformer机器学习人工智能
线性层(LinearLayer)场景假设我们现在有一个包含许多特征的向量,比如描述一本书的内容、风格、作者、逻辑等信息。你想要根据这些特征预测这本书属于哪个类别,如小说、科幻、历史等。线性层的作用就是帮助你将这些特征转换成一个更简单的形式,使得你可以更容易地做出分类决策。解释特征组合:线性层接收来自解码器最后一层的输出,这个输出是一个高维向量,包含了关于输入序列的丰富信息。权重矩阵:线性层内部有一
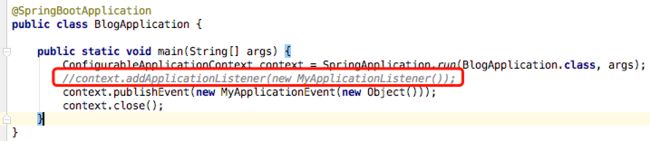
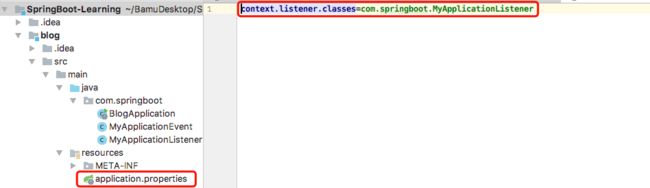
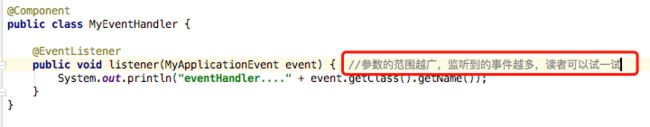
- 构建一个rust生产应用读书笔记6-拒绝无效订阅者02
编码浪子
Rust学习rust开发语言后端
打破域子模块通常指的是对应用程序的某个特定业务领域进行重构或重新组织。这可能包括拆分、合并或重组代码结构以更好地反映业务规则和逻辑。下面是一些关于如何处理这种情况的建议:1.理解当前状态首先,确保你完全理解现有系统的工作方式。这包括:阅读文档:如果有任何现有的文档,请先阅读。代码审查:深入研究代码库,了解各个部分的功能和相互之间的关系。与团队沟通:与熟悉系统的同事讨论,获取他们的见解和经验。2.定
- 构建一个rust生产应用读书笔记四(实战6)
编码浪子
Rust学习rust网络oracle
本节我们开始使用tracing来记录日志,实际上在生产环境中,更推荐使用tracing作为日志记录的首先,它提供了更丰富的上下文信息和结构化日志记录功能。tracing不仅可以记录日志信息,还可以跟踪函数调用、异步任务等,适用于复杂的分布式系统和微服务架构。添加配置依赖#Cargo.tomltracing="0.1.19"tracing-subscriber={version="0.3",feat
- 构建一个rust生产应用读书笔记6-拒绝无效订阅者01
编码浪子
Rust学习rustoracle数据库
为了增强您的POST/subscriptions端点的安全性和可靠性,确保输入数据的质量和有效性是非常重要的。当前的实现似乎只做了最基础的验证——即检查name和email字段是否存在。这样的做法可能会让系统暴露于各种潜在的问题之下,例如恶意用户提交无效或格式不正确的数据,或者导致数据库中存储了低质量的数据。改进输入验证验证数据类型:确保name和email字段是字符串类型。验证长度:为name和
- 融云IM干货丨uni-app 生命周期有哪些?
融云即时通讯imuni-app
uni-app的生命周期分为应用生命周期、页面生命周期和组件生命周期三类:应用生命周期应用生命周期函数需要在App.vue中声明,主要包含以下函数:onLaunch:当uni-app初始化完成时触发(全局只触发一次)。onShow:当uni-app启动,或从后台进入前台显示时触发。onHide:当uni-app从前台进入后台时触发。onError:当uni-app报错时触发。onPageNotFo
- 六个步骤学会CNAS软件检测机构的不确定度评定
daopuyun
CNAS\CMA专栏不确定度CNAS检测机构
测量不确定度是CNAS软件检测机构过程要求中非常重要的一个部分。测量不确定度作为测量结果的一部分,合理表征了被测量量值的分散性,对测量结果的可信性、可比性和可接受性都有重要影响,是评价测量活动质量的重要指标。CNAS软件检测机构在软件检测过程中应识别测量不确定度的贡献,评定测量不确定度。当软件检测项目中有测量不确定度要求时,应建立相应的数学模型,给出相应的测评不确定度案例。当软件检测出现临界值、内
- ATF(ARM Trusted firmware)完成启动流程
cpj123cpj
linuxkernelatf
历经一年多时间的系统整理合补充,《手机安全和可信应用开发指南:TrustZone与OP-TEE技术详解》一书得以出版,书中详细介绍了TEE以及系统安全中的所有内容,全书按照从硬件到软件,从用户空间到内核空间的顺序对TEE技术详细阐述,读者可从用户空间到TEE内核一步一步了解系统安全的所有内容,同时书中也提供了相关的示例代码,读者可根据自身实际需求开发TA。目前该书已在天猫、京东、当当同步上线,链接
- 开放创新,释放云上生产力 | 2024华为云开源开发者论坛盛大开启,邀您相约上海
论坛开源开发者生态云原生前端
12月7日,首届华为云开源开发者论坛将于上海静安香格里拉酒店举行。论坛主题为“开放创新,释放云上数字生产力”,面向生态合作伙伴、企业、个人和高校开发者。论坛将围绕当前热门的开源话题,如“开源生态前景剖析”、“开源技术解读”、“开源开发者支持与实践”等进行分享和讨论,旨在帮助开发者利用开源链接鲲鹏、昇腾根生态和华为云生态,实现高效创新和价值裂变。开源,是一种开放共享的协作模式,为全球数字经济注入活力
- MySQL、PostgreSQL 和 Microsoft SQL Server:谁是王者?
cda2024
mysqlpostgresqlmicrosoft
在当今数据驱动的时代,选择合适的数据库系统对于企业的成功至关重要。MySQL、PostgreSQL和MicrosoftSQLServer是目前市场上最受欢迎的三种关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS)。每种数据库都有其独特的优势和适用场景,但究竟哪一种更适合你的业务需求呢?本文将从多个维度对这三种数据库进行对比,帮助你做出明智的选择。1.性能1.1MySQLMySQL是一款开源数据库,以其高性能和易用
- openGemini v1.2.0版本正式发布,IoT 场景性能大幅提升!
开源时序数据库云原生版本发布
在openGeminiv1.2.0版本中,我们为您带来了一系列令人振奋的内核优化,将您的体验提升到新的高度,这包括针对IoT场景的性能优化,查询效率有极大的提升。针对数据存储的优化,进一步节约磁盘空间,降低数据存储成本。针对部分功能的优化,比如showtagkeys,stream等,使得功能更加丰富。新增了一部分内核的监控指标,进一步清楚了解内核的运行状态、行为和性能,帮助分析、定位和优化数据库性
- Redis-主从同步原理
redis主从复制
大家好,我是半夏之沫一名金融科技领域的JAVA系统研发我希望将自己工作和学习中的经验以最朴实,最严谨的方式分享给大家,共同进步写作不易,期待大家的关注和点赞关注微信公众号【技术探界】前言Redis为了保证服务高可用,其中一种实现就是主从模式,即一个Redis服务端作为主节点,若干个Redis服务端作为主节点的从节点,从而实现即使某个服务端不可用时,也不会影响Redis服务的正常使用。本篇文章将对主
- Redis-内存机制
redismemory内存管理
大家好,我是半夏之沫一名金融科技领域的JAVA系统研发我希望将自己工作和学习中的经验以最朴实,最严谨的方式分享给大家,共同进步写作不易,期待大家的关注和点赞关注微信公众号【技术探界】前言Redis的数据都存储在内存中,所以本篇文章将学习Redis的内存机制,以帮助定位Redis的内存相关问题。正文一.查看Redis中的内存Redis提供了infomemory指令来查看Redis的内存情况,但是在查
- OSCP - Proving Grounds - Quackerjack
柴郡猫^O^
OSCP网络安全安全性测试安全
主要知识点端口转发具体步骤执行nmap扫描,开了好多端口,我先试验80和8081,看起来8081比较有趣Nmapscanreportfor192.168.51.57Hostisup(0.0011slatency).Notshown:65527filteredtcpports(no-response)PORTSTATESERVICEVERSION21/tcpopenftpvsftpd3.0.2|ft
- 使用python做出一只懒羊羊
大G哥
python开发语言
今天使用Python的Turtle库做出一只懒羊羊PythonTurtle库功能与用途一、绘图基础功能Turtle库提供了一种简单易用的方式来进行图形绘制。通过控制屏幕上的海龟指针移动来完成线条和形状的创建。可以设置画笔的颜色、大小以及方向等属性,从而实现多样化的视觉效果。importturtlet=turtle.Turtle()t.forward(100)#向前走100像素距离t.right(9
- 【算法】动态规划:从斐波那契数列到背包问题
杰九
优质文章算法动态规划
【算法】动态规划:从斐波那契数列到背包问题文章目录【算法】动态规划:从斐波那契数列到背包问题1.斐波那契数列2.爬楼梯3.零钱转换Python代码4.零钱兑换II5.组合数dp和排列数dp6.为什么动态规划的核心思想计算组合数的正确方法代码实现为什么先遍历硬币再遍历金额可以计算组合数详细解释举例说明最终结果具体组合情况为什么有效7.背包问题01背包问题定义完全背包问题定义示例为什么需要倒序遍历8.
- 【neo4j】neo4j和Cypher 查询语言相关知识点
杰九
neo4j
【neo4j】neo4j和Cypher查询语言相关知识点1.什么是neo4jNeo4j是一个广泛使用的图形数据库管理系统(GraphDatabaseManagementSystem)。它是一种NoSQL数据库,专为存储和查询图形数据而设计。Neo4j支持图形数据模型,允许用户以节点(Nodes)和关系(Relationships)的形式存储数据,并通过属性(Properties)来丰富这些节点和关
- Maven
Array_06
eclipsejdkmaven
Maven
Maven是基于项目对象模型(POM), 信息来管理项目的构建,报告和文档的软件项目管理工具。
Maven 除了以程序构建能力为特色之外,还提供高级项目管理工具。由于 Maven 的缺省构建规则有较高的可重用性,所以常常用两三行 Maven 构建脚本就可以构建简单的项目。由于 Maven 的面向项目的方法,许多 Apache Jakarta 项目发文时使用 Maven,而且公司
- ibatis的queyrForList和queryForMap区别
bijian1013
javaibatis
一.说明
iBatis的返回值参数类型也有种:resultMap与resultClass,这两种类型的选择可以用两句话说明之:
1.当结果集列名和类的属性名完全相对应的时候,则可直接用resultClass直接指定查询结果类
- LeetCode[位运算] - #191 计算汉明权重
Cwind
java位运算LeetCodeAlgorithm题解
原题链接:#191 Number of 1 Bits
要求:
写一个函数,以一个无符号整数为参数,返回其汉明权重。例如,‘11’的二进制表示为'00000000000000000000000000001011', 故函数应当返回3。
汉明权重:指一个字符串中非零字符的个数;对于二进制串,即其中‘1’的个数。
难度:简单
分析:
将十进制参数转换为二进制,然后计算其中1的个数即可。
“
- 浅谈java类与对象
15700786134
java
java是一门面向对象的编程语言,类与对象是其最基本的概念。所谓对象,就是一个个具体的物体,一个人,一台电脑,都是对象。而类,就是对象的一种抽象,是多个对象具有的共性的一种集合,其中包含了属性与方法,就是属于该类的对象所具有的共性。当一个类创建了对象,这个对象就拥有了该类全部的属性,方法。相比于结构化的编程思路,面向对象更适用于人的思维
- linux下双网卡同一个IP
被触发
linux
转自:
http://q2482696735.blog.163.com/blog/static/250606077201569029441/
由于需要一台机器有两个网卡,开始时设置在同一个网段的IP,发现数据总是从一个网卡发出,而另一个网卡上没有数据流动。网上找了下,发现相同的问题不少:
一、
关于双网卡设置同一网段IP然后连接交换机的时候出现的奇怪现象。当时没有怎么思考、以为是生成树
- 安卓按主页键隐藏程序之后无法再次打开
肆无忌惮_
安卓
遇到一个奇怪的问题,当SplashActivity跳转到MainActivity之后,按主页键,再去打开程序,程序没法再打开(闪一下),结束任务再开也是这样,只能卸载了再重装。而且每次在Log里都打印了这句话"进入主程序"。后来发现是必须跳转之后再finish掉SplashActivity
本来代码:
// 销毁这个Activity
fin
- 通过cookie保存并读取用户登录信息实例
知了ing
JavaScripthtml
通过cookie的getCookies()方法可获取所有cookie对象的集合;通过getName()方法可以获取指定的名称的cookie;通过getValue()方法获取到cookie对象的值。另外,将一个cookie对象发送到客户端,使用response对象的addCookie()方法。
下面通过cookie保存并读取用户登录信息的例子加深一下理解。
(1)创建index.jsp文件。在改
- JAVA 对象池
矮蛋蛋
javaObjectPool
原文地址:
http://www.blogjava.net/baoyaer/articles/218460.html
Jakarta对象池
☆为什么使用对象池
恰当地使用对象池化技术,可以有效地减少对象生成和初始化时的消耗,提高系统的运行效率。Jakarta Commons Pool组件提供了一整套用于实现对象池化
- ArrayList根据条件+for循环批量删除的方法
alleni123
java
场景如下:
ArrayList<Obj> list
Obj-> createTime, sid.
现在要根据obj的createTime来进行定期清理。(释放内存)
-------------------------
首先想到的方法就是
for(Obj o:list){
if(o.createTime-currentT>xxx){
- 阿里巴巴“耕地宝”大战各种宝
百合不是茶
平台战略
“耕地保”平台是阿里巴巴和安徽农民共同推出的一个 “首个互联网定制私人农场”,“耕地宝”由阿里巴巴投入一亿 ,主要是用来进行农业方面,将农民手中的散地集中起来 不仅加大农民集体在土地上面的话语权,还增加了土地的流通与 利用率,提高了土地的产量,有利于大规模的产业化的高科技农业的 发展,阿里在农业上的探索将会引起新一轮的产业调整,但是集体化之后农民的个体的话语权 将更少,国家应出台相应的法律法规保护
- Spring注入有继承关系的类(1)
bijian1013
javaspring
一个类一个类的注入
1.AClass类
package com.bijian.spring.test2;
public class AClass {
String a;
String b;
public String getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(Strin
- 30岁转型期你能否成为成功人士
bijian1013
成功
很多人由于年轻时走了弯路,到了30岁一事无成,这样的例子大有人在。但同样也有一些人,整个职业生涯都发展得很优秀,到了30岁已经成为职场的精英阶层。由于做猎头的原因,我们接触很多30岁左右的经理人,发现他们在职业发展道路上往往有很多致命的问题。在30岁之前,他们的职业生涯表现很优秀,但从30岁到40岁这一段,很多人
- [Velocity三]基于Servlet+Velocity的web应用
bit1129
velocity
什么是VelocityViewServlet
使用org.apache.velocity.tools.view.VelocityViewServlet可以将Velocity集成到基于Servlet的web应用中,以Servlet+Velocity的方式实现web应用
Servlet + Velocity的一般步骤
1.自定义Servlet,实现VelocityViewServl
- 【Kafka十二】关于Kafka是一个Commit Log Service
bit1129
service
Kafka is a distributed, partitioned, replicated commit log service.这里的commit log如何理解?
A message is considered "committed" when all in sync replicas for that partition have applied i
- NGINX + LUA实现复杂的控制
ronin47
lua nginx 控制
安装lua_nginx_module 模块
lua_nginx_module 可以一步步的安装,也可以直接用淘宝的OpenResty
Centos和debian的安装就简单了。。
这里说下freebsd的安装:
fetch http://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.1.4.tar.gz
tar zxvf lua-5.1.4.tar.gz
cd lua-5.1.4
ma
- java-14.输入一个已经按升序排序过的数组和一个数字, 在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是输入的那个数字
bylijinnan
java
public class TwoElementEqualSum {
/**
* 第 14 题:
题目:输入一个已经按升序排序过的数组和一个数字,
在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是输入的那个数字。
要求时间复杂度是 O(n) 。如果有多对数字的和等于输入的数字,输出任意一对即可。
例如输入数组 1 、 2 、 4 、 7 、 11 、 15 和数字 15 。由于
- Netty源码学习-HttpChunkAggregator-HttpRequestEncoder-HttpResponseDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
今天看Netty如何实现一个Http Server
org.jboss.netty.example.http.file.HttpStaticFileServerPipelineFactory:
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(&quo
- java敏感词过虑-基于多叉树原理
cngolon
违禁词过虑替换违禁词敏感词过虑多叉树
基于多叉树的敏感词、关键词过滤的工具包,用于java中的敏感词过滤
1、工具包自带敏感词词库,第一次调用时读入词库,故第一次调用时间可能较长,在类加载后普通pc机上html过滤5000字在80毫秒左右,纯文本35毫秒左右。
2、如需自定义词库,将jar包考入WEB-INF工程的lib目录,在WEB-INF/classes目录下建一个
utf-8的words.dict文本文件,
- 多线程知识
cuishikuan
多线程
T1,T2,T3三个线程工作顺序,按照T1,T2,T3依次进行
public class T1 implements Runnable{
@Override
- spring整合activemq
dalan_123
java spring jms
整合spring和activemq需要搞清楚如下的东东1、ConnectionFactory分: a、spring管理连接到activemq服务器的管理ConnectionFactory也即是所谓产生到jms服务器的链接 b、真正产生到JMS服务器链接的ConnectionFactory还得
- MySQL时间字段究竟使用INT还是DateTime?
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
环境:Windows XPPHP Version 5.2.9MySQL Server 5.1
第一步、创建一个表date_test(非定长、int时间)
CREATE TABLE `test`.`date_test` (`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,`start_time` INT NOT NULL ,`some_content`
- Parcel: unable to marshal value
dcj3sjt126com
marshal
在两个activity直接传递List<xxInfo>时,出现Parcel: unable to marshal value异常。 在MainActivity页面(MainActivity页面向NextActivity页面传递一个List<xxInfo>): Intent intent = new Intent(this, Next
- linux进程的查看上(ps)
eksliang
linux pslinux ps -llinux ps aux
ps:将某个时间点的进程运行情况选取下来
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/admin/blogs/2119469
http://eksliang.iteye.com
ps 这个命令的man page 不是很好查阅,因为很多不同的Unix都使用这儿ps来查阅进程的状态,为了要符合不同版本的需求,所以这个
- 为什么第三方应用能早于System的app启动
gqdy365
System
Android应用的启动顺序网上有一大堆资料可以查阅了,这里就不细述了,这里不阐述ROM启动还有bootloader,软件启动的大致流程应该是启动kernel -> 运行servicemanager 把一些native的服务用命令启动起来(包括wifi, power, rild, surfaceflinger, mediaserver等等)-> 启动Dalivk中的第一个进程Zygot
- App Framework发送JSONP请求(3)
hw1287789687
jsonp跨域请求发送jsonpajax请求越狱请求
App Framework 中如何发送JSONP请求呢?
使用jsonp,详情请参考:http://json-p.org/
如何发送Ajax请求呢?
(1)登录
/***
* 会员登录
* @param username
* @param password
*/
var user_login=function(username,password){
// aler
- 发福利,整理了一份关于“资源汇总”的汇总
justjavac
资源
觉得有用的话,可以去github关注:https://github.com/justjavac/awesome-awesomeness-zh_CN 通用
free-programming-books-zh_CN 免费的计算机编程类中文书籍
精彩博客集合 hacke2/hacke2.github.io#2
ResumeSample 程序员简历
- 用 Java 技术创建 RESTful Web 服务
macroli
java编程WebREST
转载:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/web/wa-jaxrs/
JAX-RS (JSR-311) 【 Java API for RESTful Web Services 】是一种 Java™ API,可使 Java Restful 服务的开发变得迅速而轻松。这个 API 提供了一种基于注释的模型来描述分布式资源。注释被用来提供资源的位
- CentOS6.5-x86_64位下oracle11g的安装详细步骤及注意事项
超声波
oraclelinux
前言:
这两天项目要上线了,由我负责往服务器部署整个项目,因此首先要往服务器安装oracle,服务器本身是CentOS6.5的64位系统,安装的数据库版本是11g,在整个的安装过程中碰到很多的坑,不过最后还是通过各种途径解决并成功装上了。转别写篇博客来记录完整的安装过程以及在整个过程中的注意事项。希望对以后那些刚刚接触的菜鸟们能起到一定的帮助作用。
安装过程中可能遇到的问题(注
- HttpClient 4.3 设置keeplive 和 timeout 的方法
supben
httpclient
ConnectionKeepAliveStrategy kaStrategy = new DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy() {
@Override
public long getKeepAliveDuration(HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) {
long keepAlive
- Spring 4.2新特性-@Import注解的升级
wiselyman
spring 4
3.1 @Import
@Import注解在4.2之前只支持导入配置类
在4.2,@Import注解支持导入普通的java类,并将其声明成一个bean
3.2 示例
演示java类
package com.wisely.spring4_2.imp;
public class DemoService {
public void doSomethin