问题背景
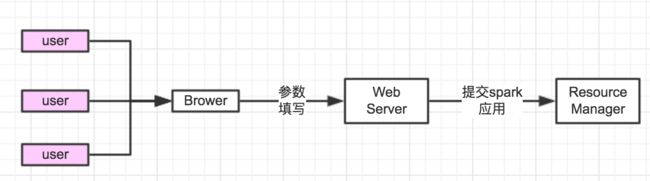
笔者所在的部门属于公司的大数据架构部,现主要参与公司流式计算平台的推广,个人负责spark的平台维护、特性定制、线上问题修改等。为了方便业务用户提交spark应用。我们开发了一套实时计算管理平台,用户在页面上填写应用的相关参数,点击提交按钮后触发后台服务向yarn集群提交应用。具体流程如下图:
从图中我们可以看出,无论前台是什么用户在进行操作,均是由WebServer来进行应用的提交。Hadoop在默认情况下,spark应用提交的用户名均是进程WebServer启动的用户名。而在ResourceManager服务端,为了进行安全的隔离和成本统计,会为不同的用户分配不同的队列,因此我们需要WebServer支持多用户提交。
问题分析
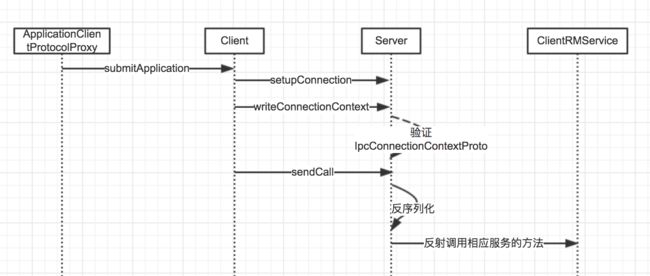
无论是Yarn还是Hdfs的相关接口,底层的通信均是采用统一的RPC模型;下面一ClientRMService为例来进行下整个的调用交互过程:
在rpc接口调用之前,客户端必须和服务端建立socket连接,同时在socket连接建立的过程对客户端的进行认证。读者在这个过程中,肯定有个疑问,就是客户端的用户名是什么时候发送到服务端的,下面我们来看下org.apache.hadoop.ipc.protocolPB.Client类。
/** Connect to the server and set up the I/O streams. It then sends
* a header to the server and starts
* the connection thread that waits for responses.
*/
private synchronized void setupIOstreams(
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) {
if (socket != null || shouldCloseConnection.get()) {
return;
}
try {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Connecting to "+server);
}
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
Trace.addTimelineAnnotation("IPC client connecting to " + server);
}
short numRetries = 0;
Random rand = null;
while (true) {
//和远程的Server端建立socket连接
setupConnection();
InputStream inStream = NetUtils.getInputStream(socket);
OutputStream outStream = NetUtils.getOutputStream(socket);
writeConnectionHeader(outStream);
if (authProtocol == AuthProtocol.SASL) {
final InputStream in2 = inStream;
final OutputStream out2 = outStream;
UserGroupInformation ticket = remoteId.getTicket();
if (ticket.getRealUser() != null) {
ticket = ticket.getRealUser();
}
try {
authMethod = ticket
.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
@Override
public AuthMethod run()
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return setupSaslConnection(in2, out2);
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
authMethod = saslRpcClient.getAuthMethod();
if (rand == null) {
rand = new Random();
}
handleSaslConnectionFailure(numRetries++, maxRetriesOnSasl, ex,
rand, ticket);
continue;
}
if (authMethod != AuthMethod.SIMPLE) {
// Sasl connect is successful. Let's set up Sasl i/o streams.
inStream = saslRpcClient.getInputStream(inStream);
outStream = saslRpcClient.getOutputStream(outStream);
// for testing
remoteId.saslQop =
(String)saslRpcClient.getNegotiatedProperty(Sasl.QOP);
LOG.debug("Negotiated QOP is :" + remoteId.saslQop);
if (fallbackToSimpleAuth != null) {
fallbackToSimpleAuth.set(false);
}
} else if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {
if (!fallbackAllowed) {
throw new IOException("Server asks us to fall back to SIMPLE " +
"auth, but this client is configured to only allow secure " +
"connections.");
}
if (fallbackToSimpleAuth != null) {
fallbackToSimpleAuth.set(true);
}
}
}
if (doPing) {
inStream = new PingInputStream(inStream);
}
this.in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(inStream));
// SASL may have already buffered the stream
if (!(outStream instanceof BufferedOutputStream)) {
outStream = new BufferedOutputStream(outStream);
}
this.out = new DataOutputStream(outStream);
//写入连接的上下文,包括用户名等ugi信息
writeConnectionContext(remoteId, authMethod);
// update last activity time
touch();
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
Trace.addTimelineAnnotation("IPC client connected to " + server);
}
// start the receiver thread after the socket connection has been set
// up
//启动线程接受服务端的response消息
start();
return;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (t instanceof IOException) {
markClosed((IOException)t);
} else {
markClosed(new IOException("Couldn't set up IO streams", t));
}
close();
}
}
连接的上下文的详细信息
/* Write the connection context header for each connection
* Out is not synchronized because only the first thread does this.
*/
private void writeConnectionContext(ConnectionId remoteId,
AuthMethod authMethod)
throws IOException {
// Write out the ConnectionHeader
IpcConnectionContextProto message = ProtoUtil.makeIpcConnectionContext(
RPC.getProtocolName(remoteId.getProtocol()),
//ticket为当前线程的ugi信息
remoteId.getTicket(),
authMethod);
RpcRequestHeaderProto connectionContextHeader = ProtoUtil
.makeRpcRequestHeader(RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
OperationProto.RPC_FINAL_PACKET, CONNECTION_CONTEXT_CALL_ID,
RpcConstants.INVALID_RETRY_COUNT, clientId);
RpcRequestMessageWrapper request =
new RpcRequestMessageWrapper(connectionContextHeader, message);
// Write out the packet length
out.writeInt(request.getLength());
request.write(out);
}
其中ticket获取的方式为UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser,具体的内容如下:
public synchronized
static UserGroupInformation getCurrentUser() throws IOException {
//如果线程的访问上下文中设置了Subject,则直接获取Subject的用户信息
AccessControlContext context = AccessController.getContext();
Subject subject = Subject.getSubject(context);
if (subject == null || subject.getPrincipals(User.class).isEmpty()) {
return getLoginUser();
} else {
return new UserGroupInformation(subject);
}
}
public synchronized
static UserGroupInformation getLoginUser() throws IOException {
if (loginUser == null) {
loginUserFromSubject(null);
}
return loginUser;
}
public synchronized
static void loginUserFromSubject(Subject subject) throws IOException {
ensureInitialized();
try {
if (subject == null) {
subject = new Subject();
}
LoginContext login =
newLoginContext(authenticationMethod.getLoginAppName(),
subject, new HadoopConfiguration());
login.login();
UserGroupInformation realUser = new UserGroupInformation(subject);
realUser.setLogin(login);
realUser.setAuthenticationMethod(authenticationMethod);
realUser = new UserGroupInformation(login.getSubject());
// If the HADOOP_PROXY_USER environment variable or property
// is specified, create a proxy user as the logged in user.
String proxyUser = System.getenv(HADOOP_PROXY_USER);
if (proxyUser == null) {
proxyUser = System.getProperty(HADOOP_PROXY_USER);
}
loginUser = proxyUser == null ? realUser : createProxyUser(proxyUser, realUser);
String fileLocation = System.getenv(HADOOP_TOKEN_FILE_LOCATION);
if (fileLocation != null) {
// Load the token storage file and put all of the tokens into the
// user. Don't use the FileSystem API for reading since it has a lock
// cycle (HADOOP-9212).
Credentials cred = Credentials.readTokenStorageFile(
new File(fileLocation), conf);
loginUser.addCredentials(cred);
}
loginUser.spawnAutoRenewalThreadForUserCreds();
} catch (LoginException le) {
LOG.debug("failure to login", le);
throw new IOException("failure to login", le);
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("UGI loginUser:"+loginUser);
}
}
用户名的获取
@InterfaceAudience.Private
public static class HadoopLoginModule implements LoginModule {
private Subject subject;
@Override
public boolean abort() throws LoginException {
return true;
}
private T getCanonicalUser(Class cls) {
for(T user: subject.getPrincipals(cls)) {
return user;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean commit() throws LoginException {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("hadoop login commit");
}
// if we already have a user, we are done.
if (!subject.getPrincipals(User.class).isEmpty()) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("using existing subject:"+subject.getPrincipals());
}
return true;
}
Principal user = null;
// if we are using kerberos, try it out
if (isAuthenticationMethodEnabled(AuthenticationMethod.KERBEROS)) {
user = getCanonicalUser(KerberosPrincipal.class);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("using kerberos user:"+user);
}
}
//If we don't have a kerberos user and security is disabled, check
//if user is specified in the environment or properties
//从环境变量或者System.properties中获取用户名
if (!isSecurityEnabled() && (user == null)) {
String envUser = System.getenv(HADOOP_USER_NAME);
if (envUser == null) {
envUser = System.getProperty(HADOOP_USER_NAME);
}
user = envUser == null ? null : new User(envUser);
}
// use the OS user,获取操作系统的用户名
if (user == null) {
user = getCanonicalUser(OS_PRINCIPAL_CLASS);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("using local user:"+user);
}
}
// if we found the user, add our principal
if (user != null) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Using user: \"" + user + "\" with name " + user.getName());
}
User userEntry = null;
try {
userEntry = new User(user.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw (LoginException)(new LoginException(e.toString()).initCause(e));
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("User entry: \"" + userEntry.toString() + "\"" );
}
subject.getPrincipals().add(userEntry);
return true;
}
LOG.error("Can't find user in " + subject);
throw new LoginException("Can't find user name");
}
从上面的代码可以,如果当前线程的上下文AccessControllerContext中设置了Subject,则直接通过subject构造ugi对象,用户名取Subject中的用户名;否则用户名取环境变量或则System.properties中的HADOOP_USER_NAME对应的值,默认去操作系统的用户名。
由于从环境变量或者system.properties中获取用户名均是进程级别的,无法做到一个进程以不同的用户提交,唯一的可能性就只能是预先设置线程的Subject信息,具体的操作方式就是通过Subject.doAs方法来实现,我们接下来看一个小例子。
public class UgiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//构建一个Subject对象
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.getPrincipals().add(new User("xielijuan"));
//打印出当前的ugi信息
System.out.println("main before: " + UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getShortUserName());
Subject.doAs(subject, new PrivilegedAction从上面的例子可以看出,确实可以通过构建一个Subject来改变UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser的用户名,同时我们知道,subject只影响doAs中的代码段。另外,如果在doAs中新建线程,那么该现场会继承父线程的AccessControllerContext,其subject和执行进程创建时候父线程的subject一致。在doAs的代码段之外,UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser不受影响。
解决方式
在webServer中提交用户的时候,首先根据待提交的用户名构建一个Subject对象,同时在Subject.doAs方法中进行应用的提交。比如
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.getPrincipals().add(new User("xielijuan"));
Subject.doAs(subject, () -> {
Client.submitApplication(xxx);
return null;
});