iOS Networking - Udacity的笔记
课程笔记目录:
1.http请求和JSON解析
2.Networking的MVC框架(所在文章)
以上文章的简介:iOS Networking
我一直认为,当你开始与世界向这个世界贡献一份力量时,分享时,这个世界就会以一种神奇的方式回报你。比如:有些人旅游将自己的经验分享出来,就会吸引同道之人或者会救人一命让人感激。或者有的人写技术blog就会吸引开发者,如果好的话还会被公司挖去。
不扯了,其实我写笔记的目的就是将自己脑中的思考写下来,让它清晰起来。主要还是为我自己
前言
本笔记是关于udacity的iOS Networking with Swift
Lesson 2:Improving Networking with MVC
Lesson 1中将JSON获取解析实现了,当中是一大段又臃肿的代码。假如每一个API都用到这样的一大段大码,就会使得代码变得臃肿无比,难以管理。
而且上一Lesson中的所有API方法都是写在Controller的,不容易重复使用,也使得Controller很臃肿。
使Controller更‘轻’的技巧有很多种,以下链接提供了比较全的思路[Lighter View Controllers][1]。而本笔记只会关注如何使Model与Controller分离。
Lesson 2这堂课主要教导如何使用MVC(Model View Controller)使数据独立处理。
[1]:https://www.objc.io/issues/1-view-controllers/lighter-view-controllers/
Model与Controller分离的步骤
1.将请求解析JSON复用代码抽象起来
2.将各种API Method封装起来
3.将验证操作需要的一系列API Method步骤封装起来
4.在controller里使用sharedInstance()调回对象,使用authenticateWithViewController完成user登录
将请求解析JSON复用抽象起来
如图是Lesson 1-请求并解析JSON数据的代码。
这些标号的代码是每一次使用一定会 相同的,意味着重用。因此要将其抽象起来,然后将每次请求不同的参数传入,最后通过block将参数回调
于是将请求重用的代码抽象为class
TMDBCline的method
taskForGETMethod
func taskForGETMethod(method: String, parameters: [String : AnyObject], completionHandler: (result: AnyObject!, error: NSError?) -> Void) -> NSURLSessionDataTask {
/* 1. Set the parameters */
var mutableParameters = parameters
mutableParameters[ParameterKeys.ApiKey] = Constants.ApiKey
/* 2/3. Build the URL and configure the request */
let urlString = Constants.BaseURLSecure + method + TMDBClient.escapedParameters(mutableParameters)
let url = NSURL(string: urlString)!
let request = NSURLRequest(URL: url)
/* 4. Make the request */
let task = session.dataTaskWithRequest(request) { (data, response, error) in
/* GUARD: Was there an error? */
guard (error == nil) else {
print("There was an error with your request: \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(error)")
return
}
/* GUARD: Did we get a successful 2XX response? */
guard let statusCode = (response as? NSHTTPURLResponse)?.statusCode where statusCode >= 200 && statusCode <= 299 else {
if let response = response as? NSHTTPURLResponse {
print("Your request returned an invalid response! Status code: \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(response.statusCode)!")
} else if let response = response {
print("Your request returned an invalid response! Response: \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(response)!")
} else {
print("Your request returned an invalid response!")
}
return
}
/* GUARD: Was there any data returned? */
guard let data = data else {
print("No data was returned by the request!")
return
}
/* 5/6. Parse the data and use the data (happens in completion handler) 在下面*/
TMDBClient.parseJSONWithCompletionHandler(data, completionHandler: completionHandler)
}
/* 7. Start the request */
task.resume()
return task
}
taskForGETMethod里面带有block的解析JSON的函数代码
class func parseJSONWithCompletionHandler(data: NSData, completionHandler: (result: AnyObject!, error: NSError?) -> Void) {
var parsedResult: AnyObject!
do {
parsedResult = try NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: .AllowFragments)
} catch {
let userInfo = [NSLocalizedDescriptionKey : "Could not parse the data as JSON: '\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(data)'"]
completionHandler(result: nil, error: NSError(domain: "parseJSONWithCompletionHandler", code: 1, userInfo: userInfo))
}
completionHandler(result: parsedResult, error: nil)
}
将各种API Method封装起来
将各种API Method也抽象为函数,使其更方便,更加能容易重用。
比如:请求Token作为验证登录的函数getRequestToken
func getRequestToken(completionHandler: (success: Bool, requestToken: String?, errorString: String?) -> Void) {
/* 1. Specify parameters, method (if has {key}), and HTTP body (if POST) */
let parameters = [String: AnyObject]()
/* 2. Make the request */
taskForGETMethod(Methods.AuthenticationTokenNew, parameters: parameters) { (JSONResult, error) in
/* 3. Send the desired value(s) to completion handler */
if let error = error {
print(error)
completionHandler(success: false, requestToken: nil, errorString: "Login Failed (Request Token).")
} else {
if let requestToken = JSONResult[TMDBClient.JSONResponseKeys.RequestToken] as? String {
completionHandler(success: true, requestToken: requestToken, errorString: nil)
} else {
print("Could not find \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(TMDBClient.JSONResponseKeys.RequestToken) in \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(JSONResult)")
completionHandler(success: false, requestToken: nil, errorString: "Login Failed (Request Token).")
}
}
}
}
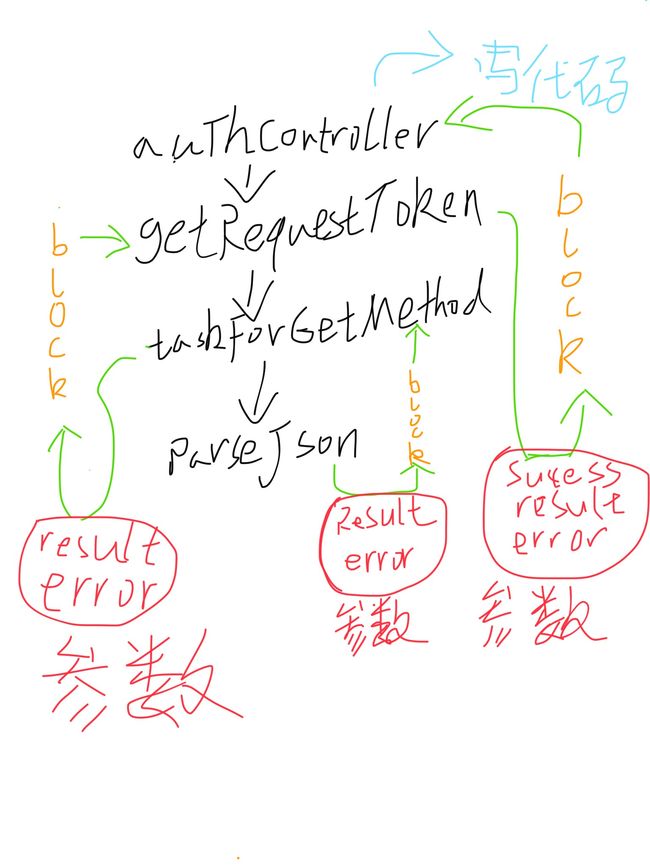
验证操作步骤封装起来
最后为了方便再将,请求token,sessionID,userID等等一系列完整的验证操作也抽象为函数authenticateWithViewController
func authenticateWithViewController(hostViewController: UIViewController, completionHandler: (success: Bool, errorString: String?) -> Void) {
/* Chain completion handlers for each request so that they run one after the other */
self.getRequestToken() { (success, requestToken, errorString) in
if success {
self.loginWithToken(requestToken, hostViewController: hostViewController) { (success, errorString) in
if success {
self.getSessionID(requestToken) { (success, sessionID, errorString) in
if success {
/* Success! We have the sessionID! */
self.sessionID = sessionID
self.getUserID() { (success, userID, errorString) in
if success {
if let userID = userID {
/* And the userID :) */
self.userID = userID
}
}
completionHandler(success: success, errorString: errorString)
}
} else {
completionHandler(success: success, errorString: errorString)
}
}
} else {
completionHandler(success: success, errorString: errorString)
}
}
} else {
completionHandler(success: success, errorString: errorString)
}
}
}
最终在controller类中只需写这么一小段代码就能完成user验证登录。
@IBAction func loginButtonTouch(sender: AnyObject) {
TMDBClient.sharedInstance().authenticateWithViewController(self) { (success, errorString) in
if success {
self.completeLogin()
} else {
self.displayError(errorString)
}
}
}
Tips
文件架构
以上的代码都放在一个TMDBClient类里面,
通过TMDBConstants或者TMDBConvenience对TMDBClient扩展extension。
例如TMDBConstants:
extension TMDBClient {
// MARK: Constants
struct Constants {
// MARK: API Key
static let ApiKey : String = "ab91ed9affc29a894989e8ea3200d963"
// MARK: URLs
static let BaseURL : String = "http://api.themoviedb.org/3/"
static let BaseURLSecure : String = "https://api.themoviedb.org/3/"
static let AuthorizationURL : String = "https://www.themoviedb.org/authenticate/"
}
}
将一些常用的字符串或者常量抽象为常量并用struct分类,
再如TMDBConvenience对TMDBClient method的扩展 如上面提及的authenticateWithViewController和getRequestToken:
通过class methodsharedInstance()回调对象。
essensial的method和变量就写在TMDBClient里,其它的通过扩展调用。
回调函数
里面的函数都通过定义block
然后通过block将值回传给调用函数。
设计model的思路
首先写出名字,再写出返回值的类型。再根据这写入代码。如图:
将每个function里的重复使用的代码抽象一下,就成为
taskForGetMethod。然后再向
taskForGetMethod传入不同参数的步骤封装起来就成为上面的函数。
三个常用method
subtituteKeyInMethod(_:key:value:)函数将参数method(如:account/{id}/favorite/movies),将其中的{key}替换为value值。
class func subtituteKeyInMethod(method: String, key: String, value: String) -> String? {
if method.rangeOfString("{\\\\(key)}") != nil {
return method.stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString("{\\\\(key)}", withString: value)
} else {
return nil
}
}
escapedParameters(_:)传入http参数字典返回http格式的字符串。
class func escapedParameters(parameters: [String : AnyObject]) -> String {
var urlVars = [String]()
for (key, value) in parameters {
/* Make sure that it is a string value */
let stringValue = "\\\\(value)"
/* Escape it */
let escapedValue = stringValue.stringByAddingPercentEncodingWithAllowedCharacters(NSCharacterSet.URLQueryAllowedCharacterSet())
/* Append it */
urlVars += [key + "=" + "\\\\(escapedValue!)"]
}
//通过数组join成字符串
return (!urlVars.isEmpty ? "?" : "") + urlVars.joinWithSeparator("&")
}
sharedInstance()实现单例模式,返回对象
class func sharedInstance() -> TMDBClient {
struct Singleton {
static var sharedInstance = TMDBClient()
}
return Singleton.sharedInstance
}
然后就是
-------END-------
---And Thank U----