时间过得不惊觉,一晃2017年走过了一大半。入了Android的坑,那就把工作生活中有关Android的事分享出来,此为开篇,我们来讲讲悬浮窗的事。
悬浮窗的坑主要是两点,一是对不同厂商悬浮窗的适配,这个很难彻底解决;二是频繁与WindowManager交互产生的TransactionTooLargeException,所以尽量减少窗口的数据量并在与WindowManager交互的时候注意catch这些Exception。
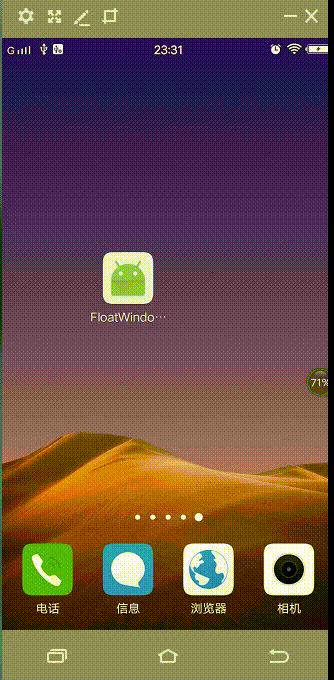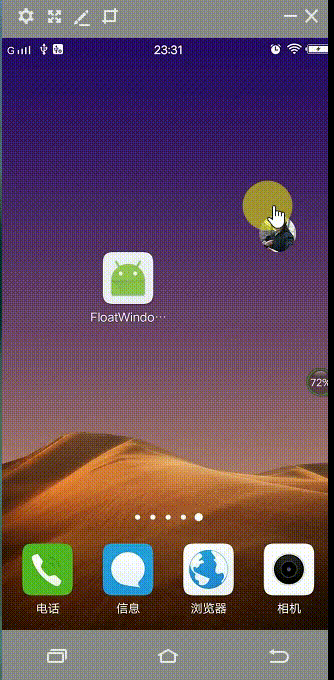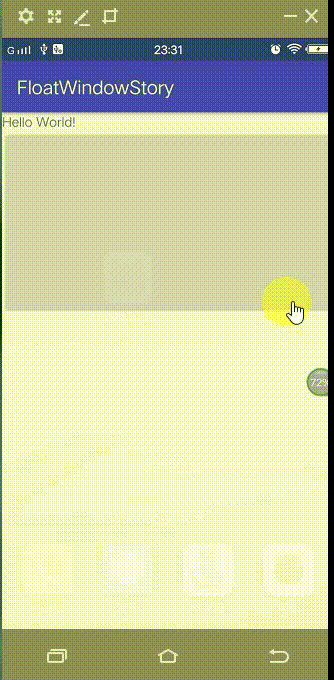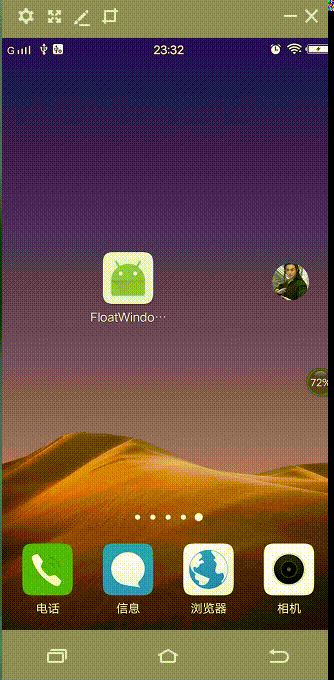
先来看看效果图(进入App,退到home后显示悬浮球,点击之后悬浮球展开,点击小球就会进入app):
总体实现思路:因为悬浮窗主要是当App退到后台之后还可以对App进行操作,所以我们启动一个service来承载悬浮窗。悬浮窗的显示主要是通过WindowManager这个类来实现的,调用这个类的addView方法用于添加一个悬浮窗,updateViewLayout方法用于更新悬浮窗的参数,removeView用于移除悬浮窗。其中主要参数在WindowManager.LayoutParams中,下面对其几个参数具体说下:
type值用于确定悬浮窗的类型,一般设为2002,表示在所有应用程序之上,但在状态栏之下。
flags值用于确定悬浮窗的行为,比如说不限制在屏幕内,不可聚焦,非模态对话框等等,属性非常多,大家可以查看文档。
gravity值用于确定悬浮窗的对齐方式,一般设为左上角对齐,这样当拖动悬浮窗的时候方便计算坐标。
x值用于确定悬浮窗的位置,如果要横向 移动悬浮窗,就需要改变这个值。
y值用于确定悬浮窗的位置,如果要纵向移动悬浮窗,就需要改变这个值。
width值用于指定悬浮窗的宽度。
height值用于指定悬浮窗的高度。
先来看看小悬浮窗的代码:
public class FloatWindowShrink extends LinearLayout {
private static final String TAG = FloatWindowShrink.class.getSimpleName();
/**
* 记录收缩悬浮窗的宽度
*/
public static int viewWidth;
/**
* 记录收缩悬浮窗的高度
*/
public static int viewHeight;
/**
* 记录系统状态栏的高度
*/
private static int statusBarHeight;
/**
* 用于更新收缩悬浮窗的位置
*/
private WindowManager windowManager;
/**
* 收缩悬浮窗的参数
*/
private WindowManager.LayoutParams mParams;
/**
* 记录当前手指位置在屏幕上的横坐标值
*/
private float xTouchScreen;
/**
* 记录当前手指位置在屏幕上的纵坐标值
*/
private float yTouchScreen;
/**
* 记录手指按下时在屏幕上的横坐标的值
*/
private float xDownTouchScreen;
/**
* 记录手指按下时在屏幕上的纵坐标的值
*/
private float yDownTouchScreen;
/**
* 记录手指按下时在收缩悬浮窗的View上的横坐标的值
*/
private float xTouchView;
/**
* 记录手指按下时在收缩悬浮窗的View上的纵坐标的值
*/
private float yTouchView;
public static WindowManager.LayoutParams lastPara;
public FloatWindowShrink(Context context) {
super(context);
windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.float_window_shrink, this);
View view = findViewById(R.id.float_window_shrink);
viewHeight = view.getLayoutParams().height;
viewWidth = view.getLayoutParams().width;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
xTouchView = event.getX();
yTouchView = event.getY();
xDownTouchScreen = event.getRawX();
yDownTouchScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
xTouchScreen = event.getRawX();
yTouchScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
xTouchScreen = event.getRawX();
yTouchScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
updateViewPosition();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
if (xDownTouchScreen == xTouchScreen && yDownTouchScreen == yTouchScreen) {
openExpandWindow();
}
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private void openExpandWindow() {
FloatWindowManager.removeShrinkWindow(getContext());
FloatWindowManager.showExpandWindow(getContext());
}
/**
* 更新收缩悬浮窗在屏幕中的位置。
*/
private void updateViewPosition() {
mParams.x = (int) (xTouchScreen - xTouchView);
mParams.y = (int) (yTouchScreen - yTouchView);
lastPara = mParams;
try {
windowManager.updateViewLayout(this, mParams);
}
if (FloatWindowManager.floatWindowExpand != null) {
windowManager.removeView(FloatWindowManager.floatWindowExpand);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "updateViewPosition exception",e);
}
}
/**
* 用于获取状态栏的高度。
*
* @return 返回状态栏高度的像素值。
*/
private int getStatusBarHeight() {
if (statusBarHeight == 0) {
try {
Class c = Class.forName("com.android.internal.R$dimen");
Object o = c.newInstance();
Field field = c.getField("status_bar_height");
int x = (Integer) field.get(o);
statusBarHeight = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(x);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return statusBarHeight;
}
public void setParams(WindowManager.LayoutParams params) {
mParams = params;
}
}
再来看看大悬浮窗的代码:
public class FloatWindowExpand extends LinearLayout {
private final static String TAG = FloatWindowExpand.class.getSimpleName();
/**
* 记录扩展悬浮窗的宽度
*/
public static int viewWidth;
/**
* 记录扩展悬浮窗的高度
*/
public static int viewHeight;
/**
* 记录系统状态栏的高度
*/
private static int statusBarHeight;
/**
* 用于更新收缩悬浮窗的位置
*/
private WindowManager windowManager;
/**
* 收缩悬浮窗的参数
*/
private WindowManager.LayoutParams mParams;
private CircleImageView fci_room;
public FloatWindowExpand(final Context context) {
super(context);
windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.float_window_expand, this);
View view = findViewById(R.id.float_window_expand);
fci_room = (CircleImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.fci_room);
fci_room.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//这里由桌面悬浮窗进入Activity,显示方式要注意,详见Service代码
FloatWindowService.enterMainListener.enterMain();
}
});
viewHeight = view.getLayoutParams().height;
viewWidth = view.getLayoutParams().width;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
FloatWindowManager.removeExpandWindow(getContext());
FloatWindowManager.showShrinkWindow(getContext());
break;
default:
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
public void setParams(WindowManager.LayoutParams params) {
mParams = params;
}
}
再来看看悬浮窗管理类的代码:
public class FloatWindowManager {
private static final String TAG = FloatWindowManager.class.getSimpleName();
public static FloatWindowShrink floatWindowShrink;
public static FloatWindowExpand floatWindowExpand;
private static WindowManager.LayoutParams shrinkWindowParams;
private static WindowManager.LayoutParams expandWindowParams;
private static WindowManager mWindowManager;
public static void showShrinkWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
int screenWidth = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int screenHeight = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
shrinkWindowParams = FloatWindowShrink.lastPara;
floatWindowShrink = new FloatWindowShrink(context);
if (shrinkWindowParams == null) {
shrinkWindowParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
if (false) {//这里需要判断是否开启悬浮窗权限,因为国内的rom对各自的悬浮窗权限进行了管理
//所以没有通用的方法进行判断,虽然google在6.0以上系统做了统一管理,但是很多厂商已经绕过这个管理
//(如Vivo,Oppo),但是像Vivo如果没有开启悬浮窗会权限有Toast提示,这里暂时没有很好的解决办法。
//详情可见:https://github.com/zhaozepeng/FloatWindowPermission,
shrinkWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
} else {
shrinkWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
}
shrinkWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
shrinkWindowParams.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
shrinkWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
shrinkWindowParams.width = FloatWindowShrink.viewWidth;
shrinkWindowParams.height = FloatWindowShrink.viewHeight;
shrinkWindowParams.x = screenWidth;
shrinkWindowParams.y = screenHeight / 2;
}
floatWindowShrink.setParams(shrinkWindowParams);
windowManager.addView(floatWindowShrink, shrinkWindowParams);
}
public static void removeShrinkWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
try {
if (floatWindowShrink != null) {
windowManager.removeView(floatWindowShrink);
floatWindowShrink = null;
shrinkWindowParams = null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
floatWindowShrink = null;
shrinkWindowParams = null;
Log.e(TAG, "removeSmallWindow exception",e);
}
}
public static void showExpandWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
int screenWidth = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int screenHeight = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
floatWindowExpand = new FloatWindowExpand(context);
if (expandWindowParams == null) {
expandWindowParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
expandWindowParams.x = screenWidth / 2 - FloatWindowExpand.viewWidth / 2;
expandWindowParams.y = screenHeight / 2 - FloatWindowExpand.viewHeight / 2;
if (false) { //PermissionUtil.checkFloatWindowPermission(context)
expandWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
} else {
expandWindowParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
}
expandWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
expandWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
expandWindowParams.width = FloatWindowExpand.viewWidth;
expandWindowParams.height = FloatWindowExpand.viewHeight;
}
floatWindowExpand.setParams(expandWindowParams);
windowManager.addView(floatWindowExpand, expandWindowParams);
}
public static void removeExpandWindow(Context context) {
try {
if (floatWindowExpand != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
windowManager.removeView(floatWindowExpand);
floatWindowExpand = null;
expandWindowParams = null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
floatWindowExpand = null;
expandWindowParams = null;
Log.e(TAG, " removeBigWindow exception : ", e);
}
}
public static boolean isWindowShowing() {
return floatWindowShrink != null || expandWindowParams != null;
}
private static WindowManager getWindowManager(Context context) {
if (mWindowManager == null) {
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
return mWindowManager;
}
}
再来看看Service的代码:
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/7/4.
*/
public class FloatWindowService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = FloatWindowService.class.getSimpleName();
public static EnterMainListener enterMainListener;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
//这里的回调实现从悬浮窗到Activity,如果用普通的Intent进入通过service的Context进入Activity
//会延迟几秒,这个是google的限制,所以这里才PendingInten封装一下。
enterMainListener = new EnterMainListener() {
@Override
public void enterMain() {
Intent intent = new Intent(FloatWindowService.this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(FloatWindowService.this,0,
intent,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
try {
pendingIntent.send();
} catch (PendingIntent.CanceledException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
FloatWindowManager.removeExpandWindow(FloatWindowService.this);
}
};
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new FloatWindowBinder();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
public class FloatWindowBinder extends Binder {
public void updateFloatWindow() {
if (!isInApp() && !FloatWindowManager.isWindowShowing()) {
FloatWindowManager.showShrinkWindow(getApplicationContext());
FloatWindowManager.removeExpandWindow(getApplicationContext());
} else {
FloatWindowManager.removeExpandWindow(getApplicationContext());
FloatWindowManager.removeShrinkWindow(getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
public interface EnterMainListener {
void enterMain();
}
/**
* 判断当前界面是否是Hello
* 这里使用的通过ActivityManager的方法来判断当前app是不是本app,其实这个方法的调用时机很难把握
* 很多时候用户看到的界面已经不是本App了,但是返回的isInApp值任然是true;所以推荐用另一种方法
* 在Activity的周期中添加计数统计,onResume(+1)与onPause(-1),这样当计数值为0时就表示不在本app
*/
private boolean isInApp() {
return getApplicationContext().getPackageName()
.equals(getTopPackageName());
}
private String getTopPackageName() {
ActivityManager manager = ((ActivityManager)getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE));
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
List pis = manager.getRunningAppProcesses();
if (pis != null && !pis.isEmpty()) {
ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo topAppProcess = pis.get(0);
if (topAppProcess != null
&& topAppProcess.importance == ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo.IMPORTANCE_FOREGROUND) {
return topAppProcess.processName;
}
}
} else {
//getRunningTasks() is deprecated since API Level 21 (Android 5.0)
List localList = manager.getRunningTasks(1);
if (localList != null && !localList.isEmpty()) {
ActivityManager.RunningTaskInfo localRunningTaskInfo = (ActivityManager.RunningTaskInfo)localList.get(0);
if (localRunningTaskInfo != null && localRunningTaskInfo.topActivity != null) {
return localRunningTaskInfo.topActivity.getPackageName();
}
}
}
return "";
}
}
最后看看MainActivity的实现
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private Button btn;
private static FloatWindowService.FloatWindowBinder floatWindowBinder;
ServiceConnection floatWindowConn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (service != null && (service instanceof FloatWindowService.FloatWindowBinder)) {
floatWindowBinder = (FloatWindowService.FloatWindowBinder) service;
floatWindowBinder.updateFloatWindow();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
floatWindowBinder = null;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_show_float_window);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
}
});
if (floatWindowConn != null && floatWindowBinder == null) {
Intent floatIntent = new Intent(this, FloatWindowService.class);
bindService(floatIntent, floatWindowConn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
if (floatWindowBinder != null) {
floatWindowBinder.updateFloatWindow();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (floatWindowBinder != null) {
floatWindowBinder.updateFloatWindow();
}
if(floatWindowBinder != null) {
unbindService(floatWindowConn);
floatWindowBinder = null;
floatWindowConn = null;
}
}
}
具体demo见GitHub:https://github.com/truyayong/FloatWindow
参考以下文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/8689140/
https://github.com/zhaozepeng/FloatWindowPermission