主要内容
- shell编程
- shell基本语法
什么是shell
- Shell是用户与内核进行交互操作的一种接口,目前最流行的Shell称为bash Shell
- Shell也是一门编程语言<解释型的编程语言>,即shell脚本
- 一个系统可以存在多个shell,可以通过cat /etc/shells命令查看系统中安装的shell,不同的shell可能支持的命令语法是不相同的
Shell脚本的执行方式
第一种:输入脚本的绝对路径或相对路径
首先要赋予+x权限
/root/helloWorld.sh
./helloWorld.sh
或者,不用赋予+x权限,而用解释器解释执行
sh helloworld.sh第二种:bash或sh +脚本
sh /root/helloWorld.sh
sh helloWorld.sh第三种:在脚本的路径前再加". "
. /root/helloWorld.sh
. ./helloWorld.sh
区别:第一种和第二种会新开一个bash,不同bash中的变量无法共享
Shell中的变量
- Linux Shell中的变量分为“系统变量”和“用户自定义变量”,可以通过set命令查看那系统变量
- 系统变量:$HOME、$PWD、$SHELL、$USER等等
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $HOME
/root
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $PWD
/root/shell
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $USER
root
[root@hadoop shell]#
- 显示当前shell中所有变量 : set
[root@hadoop shell]# set
BASH=/bin/bash
BASHOPTS=checkwinsize:cmdhist:expand_aliases:extquote:force_fignore:hostcomplete:interactive_comments:login_shell:progcomp:promptvars:sourcepath
BASH_ALIASES=()
BASH_ARGC=()
BASH_ARGV=()
BASH_CMDS=()
BASH_LINENO=()
BASH_SOURCE=()
BASH_VERSINFO=([0]="4" [1]="1" [2]="2" [3]="1" [4]="release" [5]="x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu")
BASH_VERSION='4.1.2(1)-release'
COLORS=/etc/DIR_COLORS
COLUMNS=111
DIRSTACK=()
EUID=0
GROUPS=()
G_BROKEN_FILENAMES=1
HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
HISTFILE=/root/.bash_history
HISTFILESIZE=1000
HISTSIZE=1000
HOME=/root
HOSTNAME=hadoop
HOSTTYPE=x86_64
IFS=$' \t\n'
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/src/jdk1.7.0_45
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LESSOPEN='||/usr/bin/lesspipe.sh %s'
LINES=53
LOGNAME=root
LS_COLORS='rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:mi=01;05;37;41:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.axv=01;35:*.anx=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=01;36:*.au=01;36:*.flac=01;36:*.mid=01;36:*.midi=01;36:*.mka=01;36:*.mp3=01;36:*.mpc=01;36:*.ogg=01;36:*.ra=01;36:*.wav=01;36:*.axa=01;36:*.oga=01;36:*.spx=01;36:*.xspf=01;36:'
MACHTYPE=x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu
MAIL=/var/spool/mail/root
MAILCHECK=60
OLDPWD=/root
OPTERR=1
OPTIND=1
OSTYPE=linux-gnu
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/src/jdk1.7.0_45/bin:/root/bin
PIPESTATUS=([0]="0")
PPID=1481
PS1='[\u@\h \W]\$ '
PS2='> '
PS4='+ '
PWD=/root/shell
SELINUX_LEVEL_REQUESTED=
SELINUX_ROLE_REQUESTED=
SELINUX_USE_CURRENT_RANGE=
SHELL=/bin/bash
SHELLOPTS=braceexpand:emacs:hashall:histexpand:history:interactive-comments:monitor
SHLVL=1
SSH_CLIENT='192.168.25.1 62686 22'
SSH_CONNECTION='192.168.25.1 62686 192.168.25.201 22'
SSH_TTY=/dev/pts/0
TERM=linux
UID=0
USER=root
_=root
colors=/etc/DIR_COLORS
[root@hadoop shell]#
定义变量
- 变量=值 (例如STR=abc)
- 等号两侧不能有空格
- 变量名称一般习惯为大写
- 双引号和单引号有区别,双引号仅将空格脱意,单引号会将所有特殊字符脱意
[root@hadoop shell]# x = 3
-bash: x: command not found
[root@hadoop shell]# x=3
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
3
[root@hadoop shell]# x="hello\world"
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello\world
[root@hadoop shell]# x=hello
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello
[root@hadoop shell]# x="hello world"
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello world
[root@hadoop shell]# x=hello world
-bash: world: command not found
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello world
[root@hadoop shell]# x='hello world'
[root@hadoop shell]# y=bb
[root@hadoop shell]# x="hello $y"
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello bb
[root@hadoop shell]# x='hello $y'
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $x
hello $y
[root@hadoop shell]#
- 撤销变量
STR="hello world"
A=9
unset A 撤销变量 A
- 静态变量
readonly B=2 声明静态的变量 B=2 ,不能 unset
- 全局变量
export 变量名 可把变量提升为全局环境变量,可供其他shell程序使用
将命令的返回值赋给变量
- A=`ls -la` 反引号,运行里面的命令,并把结果返回给变量A
- A=$(ls -la) 等价于反引号
例:统计文件的字符数,并赋值给变量wordcount
[root@hadoop shell]# wc -c shelltest.sh
45 shelltest.sh
[root@hadoop shell]# wc -c shelltest.sh | cut -d ' ' -f1
45
[root@hadoop shell]# wordcount=`wc -c shelltest.sh | cut -d ' ' -f1`
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $wordcount
45
[root@hadoop shell]#
Shell中的特殊变量
-
$?表示上一个命令退出的状态
[root@hadoop shell]# ls -la
total 12
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Aug 7 23:41 .
dr-xr-x---. 4 root root 4096 Aug 7 22:34 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 45 Aug 7 23:41 shelltest.sh
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]# lss -la
-bash: lss: command not found
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
127
[root@hadoop shell]# true
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]# false
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]#
$?本质是上一条命令的返回值
-
$$表示当前进程编号 -
$0表示当前脚本名称 -
$n表示n位置的输入参数(n代表数字,n>=1)
[root@hadoop shell]# vi shelltest.sh
#!/bin/bash
aa="hello"
echo "第一个参数:="$1
echo "第二个参数:="$2
exit
[root@hadoop shell]# ./shelltest.sh hello nihao
第一个参数:=hello
第二个参数:=nihao
[root@hadoop shell]#
-
$#表示参数的个数,常用于循环 -
$*和$@都表示参数列表
例:for循环变量所有参数
[root@hadoop shell]# vi shelltest.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo '$*'
echo $*
for p in $*
do
echo $p
done
echo '$@'
echo $@
for p in $@
do
echo $p
done
exit
[root@hadoop shell]# ./shelltest.sh hello nihao
$*
hello nihao
hello
nihao
$@
hello nihao
hello
nihao
[root@hadoop shell]#
$*与$@区别
-
$* 和 $@都表示传递给函数或脚本的所有参数,不被双引号" "包含时,都以$1 $2 … $n 的形式输出所有参数 - 当它们被双引号" "包含时,
"$*"会将所有的参数作为一个整体,以"$1 $2 … $n"的形式输出所有参数;"$@"会将各个参数分开,以"$1" "$2" … "$n"的形式输出所有参数
#!/bin/bash
for p in "$*"
do
echo $p
done
for p in "$@"
do
echo $p
done
exit
[root@hadoop shell]# ./shelltest.sh hello nihao
hello nihao
hello
nihao
[root@hadoop shell]#
运算符
格式 :expr m + n 或$((m+n)) 注意expr运算符间要有空格
例如计算(2 +3 )×4 的值
- 分步计算
S=`expr 2 + 3`
expr $S \* 4
- 一步完成计算
expr `expr 2 + 3 ` \* 4
echo `expr \`expr 2 + 3\` \* 4`
或
$(((2+3)*4))
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $(((2+3)*4))
20
[root@hadoop shell]# echo expr 2 + 3
expr 2 + 3
[root@hadoop shell]# echo `expr 2 + 3`
5
[root@hadoop shell]# echo `expr \`expr 2 + 3\` \* 4`
20
[root@hadoop shell]#
for循环
- 第一种:
for N in 1 2 3
do
echo $N
done
或
for N in 1 2 3; do echo $N; done
或
for N in {1..3}; do echo $N; done
- 第二种:
for ((i = 0; i <= 5; i++))
do
echo "welcome $i times"
done
或
for ((i = 0; i <= 5; i++)); do echo "welcome $i times"; done
while循环
- 第一种
while expression
do
command
…
done
- 第二种
i=1
while ((i<=3))
do
echo $i
let i++
done
case语句
格式
case $1 in
start)
echo "starting"
;;
stop)
echo "stoping"
;;
*)
echo "Usage: {start|stop} “
esac
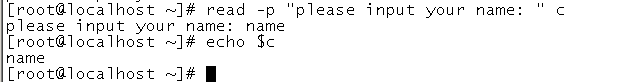
read命令
read -p(提示语句)-n(字符个数) -t(等待时间)
read -p "please input your name: " NAME
使用示例:
if判断
- 语法
if condition
then
statements
[elif condition
then statements. ..]
[else
statements ]
fi
if例子
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please input your name:" NAME
#printf '%s\n' $NAME
if [ $NAME = root ]
then
echo "hello ${NAME}, welcome !"
elif [ $NAME = itcast ]
then
echo "hello ${NAME}, welcome !"
else
echo "SB, get out here !"
fi
判断语句
- [ condition ] (注意condition前后要有空格)
#非空返回true,可使用$?验证(0为true,>1为false)
[ mystring ]
#空返回false
[ ] - [ condition ] && echo OK || echo notok
条件满足,执行后面的语句
常用判断条件
- = 字符串比较
- -lt 小于
- -le 小于等于
- -eq 等于
- -gt 大于
- -ge 大于等于
- -ne 不等于
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 1 -gt 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 3 -gt 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 3 -lt 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 3 -le 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 3 -eq 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]# [ 3 -ne 2 ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
文件常用判断条件
- -r 有读的权限
- -w 有写的权限
- -x 有执行的权限
- -f 文件存在并且是一个常规的文件
- -s 文件存在且不为空
- -d 文件存在并是一个目录
- -b文件存在并且是一个块设备
- -L 文件存在并且是一个链接
[root@hadoop shell]# [ -w myshell.sh ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]# [ -f myshell.sh ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]# [ -e mm.sh ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
1
[root@hadoop shell]# [ -e myshell.sh ]
[root@hadoop shell]# echo $?
0
[root@hadoop shell]#
Shell自定义函数
- 语法
[ function ] funname [()]
{
action;
[return int;]
}
function start() / function start / start()
案例:
#!/bin/bash
fSum 3 2;
function fSum()
{
echo $1,$2;
return $(($1+$2));
}
fSum 5 7;
total=$?;
echo $total,$?;
Shell自定义函数
- 语法
[ function ] funname [()]
{
action;
[return int;]
}
function start() / function start / start()
案例:
- mysehll.sh
#!/bin/bash
fSum 3 2;
function fSum()
{
echo $1,$2;
return $(($1+$2));
}
echo $?;
fSum 5 7;
total=$?;
echo $total,$?;
执行结果
[root@hadoop shell]# ./myshell.sh
./myshell.sh: line 2: fSum: command not found
0
5,7
12,0
[root@hadoop shell]#
- 注意
- 必须在调用函数地方之前,先声明函数,shell脚本是逐行运行。不会像其它语言一样先预编译
- 函数返回值,只能通过$? 系统变量获得,可以显示加:return 返回,如果不加,将以最后一条命令运行结果,作为返回值。 return后跟数值n(0-255)
脚本调试
sh -vx helloWorld.sh- 或者在脚本中增加set -x