本节主要内容
- 如何获取帮助文档
- Linux文件系统简介
- 目录操作
1. 如何获取帮助文档
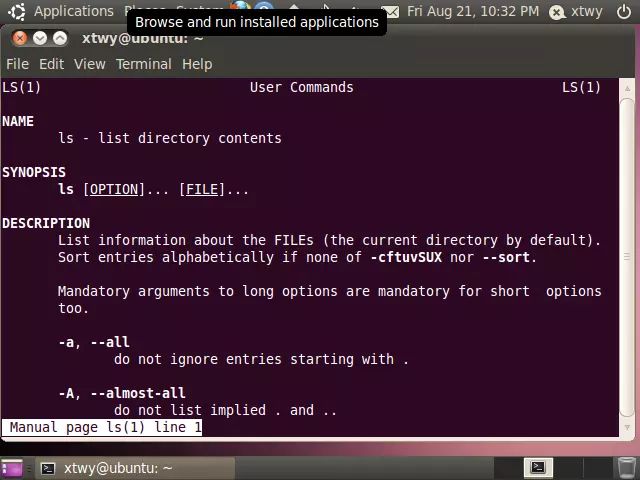
在实际工作过程当中,经常会忘记命令的使用方式,例如ls命令后面可以跟哪些参数,此时可以使用man命令来查看其使用方式,例如
//man命令获取命令帮助手册
xtwy@ubuntu:~$ man ls
可以使用键盘上的
来显示下一行或上一行命令,也可以使用
进行上一页或下一页(屏)命令的查看,另外
空格鍵也可以用来显示下一屏的命令。想退出命令查看,直接按q鍵退出即可,也可以h鍵显示less命令列表(man命令通过less命令输出结果)
2. Linux文件系统简介
(一) 文件和目录
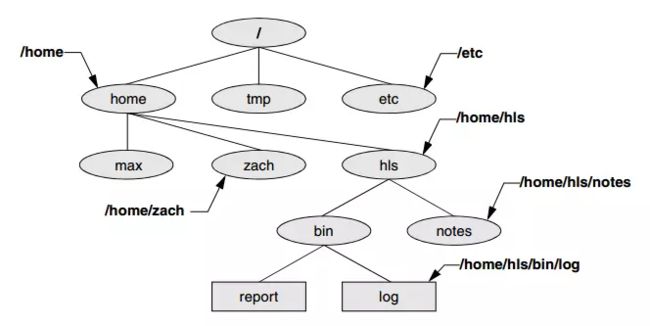
本节从使用者的角度来介绍Linux文件系统,Linux根据文件形式将文件分为目录和普通文件,如下图:
目录或文件的名称长度不超过255个字符,文件或目录名可由下列字符构成:
Uppercase letters (A–Z)
Lowercase letters (a–z)
Numbers (0–9)
Underscore ( _ )
Period(.)
Comma(,)
文件或目录名区分大小写,属于不同的文件或目录
(二) 文件扩展名与不可见文件名
与Window操作系统有很大不同的是,Linux文件对文件扩展名没有强制要求,例如假设编写了一个c语言源文件,你可以将其命名为complier.c,也可以是其它如complier、complier.ccc等文件名,但不推荐这么做,因为如果能将文件扩展名与特定的文件进行关联的话,有利于理解文件内容,目前约定成俗的linux文件扩展名如下表:
带扩展名的文件名 扩展名的含义
max.c C语言源文件
max.o 编码后的目标代码文件
max max.c对应的可执行文件
memo.txt 文本文件
memo.pdf pdf文件,必须在GUI界面上使用xpdf或kpdf才能查看
memo.ps PostScript文件,必须在GUI界面上使用ghostscript或kpdf才能查看
memo.z 经压缩程序压缩后的文件,可使用uncompress或gunzip解压
memo.gz 经gzip压缩程序压缩后的文件,可使用gunzip解压
memo.tar.gz或memo.tgz 经gzip压缩后的tar归档文件,可使用gunzip解压
memo.bz2 经bzip2压缩后的文件,可使用bunzip2解压
memo.html html文件,使用GUI环境的firefox查看
memo.jpg等 图像文件,使用GUI环境的照片查看器打开
在前一讲中我们看到,linux中还存在大量的隐藏文件,采用ls -a 命令可以显示,想定义隐藏文件,只要文件名或目录以.开始即可
(三) 绝对路径与相对路径
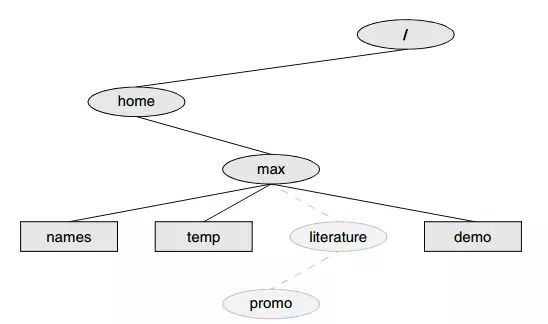
在Linux中绝对路径与相对路径是一个很重要的概念,下图给出了什么是绝对路径
所有以根目录”/”作为开始的都是绝对路径,其它的均为相对路径
//绝对路径访问
xtwy@ubuntu:~/Public$ cd /home/
xtwy@ubuntu:/home$ ls
xtwy
//相对路径访问
xtwy@ubuntu:/home$ cd xtwy/
3. 目录操作
(一) 创建目录 mkdir
为演示方便,使用下列目录结构进行演示:
1 绝对路径创建方式
//使用绝对路径创建
root@ubuntu:/home# mkdir /home/max
root@ubuntu:/home# ls
max xtwy
root@ubuntu:/home#
2 相对路径创建方式
//使用相对路径进行创建
root@ubuntu:/home# mkdir max/names
root@ubuntu:/home# mkdir max/temp
root@ubuntu:/home# mkdir max/literature
root@ubuntu:/home# cd max
root@ubuntu:/home/max# mkdir demo
root@ubuntu:/home/max# ls
demo literature names temp
有时不想层层目录创建,此时可以在mkdir 后面加上参数 -p(parents),将父子目录一起创建
root@ubuntu:/home/max# mkdir -p literature/promo
root@ubuntu:/home/max# ls
demo literature names temp
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cd literature/
root@ubuntu:/home/max/literature# ls
promo
(二) 更改目录 cd
工作目录与主目录的区别
用户每次登录后的默认目录就是主目录,与系统会话期间保持不变,主目录用~表示
xtwy@ubuntu:/root$ cd ~
xtwy@ubuntu:~$ pwd
/home/xtwy
工作目录又称当前目录,cd命令执行完成后的目录就是工作目录,它是可以随意改变的。
//.表示当前目录即工作目录
//..表示当前目录的上一级目录
xtwy@ubuntu:~$ cd .
xtwy@ubuntu:~$ cd ..
xtwy@ubuntu:/home$
(三) 删除目录 rmdir
rmdir是remove directory的简称,用于删除目录,它先删除目录下的所有文件,然后再删除该目录,但当目录下还有子目录时,该命令不能执行,需要使用rm命令,例如
//删除temp目录,先删除目录下的文件
//再删除temp目录自身
root@ubuntu:/home/max# rmdir temp/
root@ubuntu:/home/max# rmdir literature/
rmdir: failed to remove `literature/': Directory not empty
root@ubuntu:/home/max# rm -r literature/
root@ubuntu:/home/max# ls
demo names
其中rm -r中的r指的是递归的删除目录及目录中的文件,因此它具有很强的破坏力,要谨慎使用。
(四) 移动目录 mv
//将目录demo移到/home/xtwy/目录下
root@ubuntu:/home/max# mv demo/ /home/xtwy/
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cd /home/xtwy/
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
demo Documents examples.desktop Pictures Templates
Desktop Downloads Music Public Videos
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# rmdir demo
//原来目录的demo目录已经不存在了
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cd /home/max/
root@ubuntu:/home/max# ls
names
(五) 复制目录 cp
前面用mv命令移动目录,有时候需要对目录进行拷贝,使用方式如下:
//先创建一个演示目录,用-p,父目录如果不存在将会被创建
root@ubuntu:/home/max# mkdir -p literature/demo
//由于literature还包括子目录,此时拷贝不成功
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cp literature/ /home/xtwy/
cp: omitting directory `literature/'
//如果包括子目录的话,则加上-r参数,表示递归地拷贝
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cp -r literature/ /home/xtwy/
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cd /homt
bash: cd: /homt: No such file or directory
root@ubuntu:/home/max# cd /home/xtwy/
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads literature Pictures Templates
Documents examples.desktop Music Public Videos
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cd literature/
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy/literature# ls
demo
4. 文件操作
(一) 创建文件
直接通过命令行的方式创建文件的方式有多种,常用方式如下:
//通过echo命令,将输出的命令重定向到文件
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# echo "hello linux" > hello.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hello.txt Music Public Videos
Documents examples.desktop literature Pictures Templates
//touch命令,如何文件不存在,会创建文件
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# touch hell1.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hell1.txt literature Pictures Templates
Documents examples.desktop hello.txt Music Public Videos
(二) 显示文件内容
cate命令可以显示文件内容,它的全称是catenate,意思是将单词一个接一个地连接起来
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cat hello.txt
hello linux
cat命令会将文件中所有的内容全部一次性显示出现,例如
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cat /etc/profile
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shell (sh(1))
# and Bourne compatible shells (bash(1), ksh(1), ash(1), ...).
if [ -d /etc/profile.d ]; then
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r $i ]; then
. $i
fi
done
unset i
......
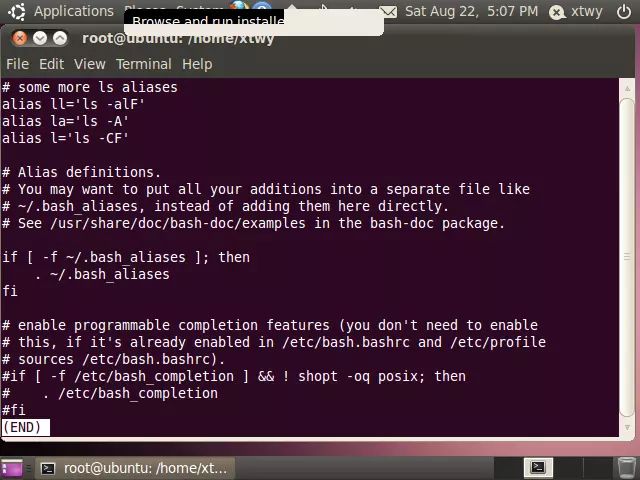
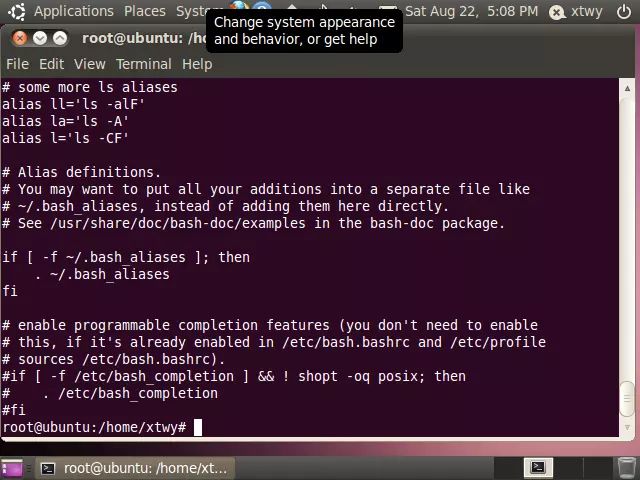
有时候我们希望能够分屏查看文件内容,此时可以使用less或more分页程序,less和more的使用方式相差不大,通过空格键显示下一屏信息,它们之间的差别在于less在文件末尾会显示END消息,而more直接返回shell终端,例如:
less命令
more命令
(三) cp命令复制文件
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hell1.txt literature Pictures Templates
Documents examples.desktop hello.txt Music Public Videos
//复制文件
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cp hell1.txt literature/demo
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cd literature/demo
//cd -返回上一次执行的工作目录
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy/literature/demo# cd -
/home/xtwy
需要注意的是cp命令在复制时,如果目标目录中已存在该文件,系统不会给出警告,而是直接覆盖,因此它可能存在销毁文件的风险,为解决这个问题可以使用-i参数让系统给出警告,例如:
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cp -i hell1.txt literature/demo
cp: overwrite `literature/demo/hell1.txt'?
(三) mv命令移动或重命名文件
//在同一目录时,相当于文件重命名,执行完成后hell1.txt不存在
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# mv hell1.txt hell2.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hell2.txt literature Pictures Templates
Documents examples.desktop hello.txt Music Public Videos
//移动hell2.txt到literature/demo
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# mv hell2.txt literature/demo
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cd literature/demo/
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy/literature/demo# ls
hell1.txt hell2.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy/literature/demo# cd -
/home/xtwy
//源目录hell2.txt已不存在
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hello.txt Music Public Videos
Documents examples.desktop literature Pictures Templates
(四)显示文件头部或尾部
显示文件头部内容用head命令,尾部用tail命令,默认显示行数为10
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# head ~/.bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
[ -z "$PS1" ] && return
# don't put duplicate lines in the history. See bash(1) for more options
# ... or force ignoredups and ignorespace
HISTCONTROL=ignoredups:ignorespace
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# tail ~/.bashrc
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
#if [ -f /etc/bash_completion ] && ! shopt -oq posix; then
# . /etc/bash_completion
#fi
head及tail的默认行数是可以修改的,例如:
//仅显示前两行
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# head -2 ~/.bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
tail命令在查看日志文件内容增长时可能经常会使用,例如在hadoop启动之后,会产生许多日志,但出现问题时,可以采用tail命令动态地监测日志文件内容的增长,查看问题出在哪个地方。
//初始显示情况
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# tail -f hello.txt
hello linux
//向文件中追加内容
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# echo "hello linux linux" >> hello.txt
//追加后的输出情况
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# tail -f hello.txt
hello linux
hello linux linux
(五)其它常见文件操作命令
下面的命令都不会改变文件内容
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# cp hello.txt hello1.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# ls
Desktop Downloads hello1.txt literature Pictures Templates
Documents examples.desktop hello.txt Music Public Videos
//根据文件内容排序
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# sort hello1.txt
hello linux
hello linux linux
//逆序输出
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# sort -r hello1.txt
hello linux linux
hello linux
//diff进行内容比较
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# diff hello1.txt hello.txt
//向文件中追加内容
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# echo "hello linux linux" >> hello.txt
//内容比较
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# diff hello1.txt hello.txt
2a3
> hello linux linux
//格式化输出
//-u参数将文件分成多块
//比较的两个文件分别用-、+表示
//本例中 -表示hello1.txt,+表示hello.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/xtwy# diff -u hello1.txt hello.txt
--- hello1.txt 2015-08-22 17:28:44.071202558 -0700
+++ hello.txt 2015-08-22 17:29:49.131181281 -0700
//@@xxx@@用于标识行起始编号、行数
//-1,2表示 hello1.txt文件起始编号为1,行数为2
//+1,3表示 hello.txt文件起始编号为1,行数为3
@@ -1,2 +1,3 @@
hello linux
hello linux linux
+hello linux linux