1. 简介
- 红黑树(Red Black Tree) 是一种自平衡二叉查找树,是二叉查找树的变种之一。它是在1972年由Rudolf Bayer发明的,当时被称为平衡二叉B树(symmetric binary B-trees)。后来,在1978年被 Leo J. Guibas 和 Robert Sedgewick修改为如今的“红黑树”。 2008年 Robert Sedgewick 对其进行了改进,并命名为 LLRBT(Left-leaning Red Black Tree 左倾红黑树)。左倾红黑树相比1978年的红黑树要简单很多,实现的代码量也少很多。Robert Sedgewick也是Algorithms(中文版叫《算法》)这本书的作者,在这本书中就讲了基于2-3树的左倾红黑树。
- 现在的使用的工程代码中的红黑树都是基于78年的算法,比如JDK中的TreeMap。其实红黑树就是2-3-4树的具体实现,所以要想理解红黑树就得先理解2-3-4树。而08年左倾红黑树则是基于2-3树。
2. 定义
红黑树是2-3-4树的实现,所以在讲红黑树之前想讲下2-3-4树有助于理解红黑树。
因为红黑树是一棵自平衡二叉搜索树,通过结点颜色改变和局部旋转来维持平衡,所以除了一些会改变树结构的操作之外,其他的操作都和普通的二叉搜索树相同。因此这里就只讲插入删除操作。
因为我要用红黑树实现一个符号表,所以结点需要存储键值对,而且实现的红黑树是基于2-3-4树。
2-3-4树的定义
- 2-3-4树可以存在三种类型结点。
- 2-结点是一个结点有2条链接和1个键,其中两条链接对应于二叉搜索树中的左右链接。
- 3-结点是一个结点有3条链接和2个键。
- 4-结点是一个结点有4条链接和3个键。
红黑树的定义
- 每个结点都有颜色,不是黑色就是红色。
- 根结点是黑色的。
- 如果一个空结点都是黑色的。
- 如果一个结点是红色的,则与它相连的结点都只能是黑色的,也就是不可以有两个红色结点相连。
- 每个空结点到根结点的简单路径中所含的黑色结点数目相同。
通过观察以上两图基本能看出两者的关系了
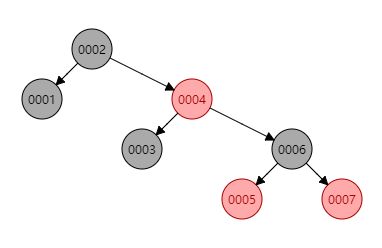
- 第一张图已经存在三种结点了,其中1和3都是2-结点,2和4构成一个3-结点,5和6和7构成一个4-结点。
- 第二张图则是第一张图中2-3-4树在红黑树的表现形式。
现在我总结一下2-3-4树中三种结点在红黑树中的表示: - 2-结点
- 3-结点
- 4-结点
3. 实现
实现部分的代码用Java
结点的定义
每个结点的类型是Node,里面有5个字段。
private class Node {
Key key;
Value value;
Node left;
Node right;
boolean color;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right, boolean color) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.color = color;
}
}
红黑树的插入
当我们想要在树中插入一个新结点时,先在树中搜索与插入结点键相同的结点。
- 如果找到该结点则直接修改对应的
Value字段就完成了。 - 如果找不到该结点则创建一个新的结点并把这个新结点设置为红色(因为插入一个红色结点不会改变红黑树的性质5),随后插到对应树底部对应的结点下。然而插入树底部对应结点下,那这个对应的结点有三种可能,分别是上面说到的2-,3-,4-结点。
如果插到2-结点下,由于2-结点是黑色结点则不会破坏红黑树的任何性质,所以不用做任何操作就完成了。
-
如果插到3-结点下,从上面3-结点的图看,3-结点有三个位置可以插入。
如果插入黑色结点的位置下则变成4-结点也不用做任何操作就完成了。
-
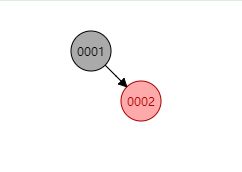
如果插到3-结点的红色结点下,则破坏了红黑树的性质4。如下图新插入的
0003结点,因为插入位置在右边,则需要对0001做一个左旋操作:
-
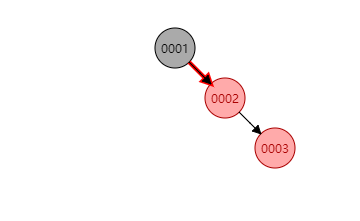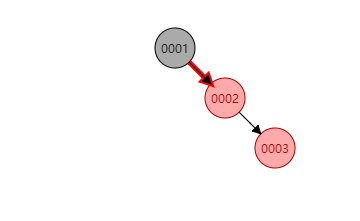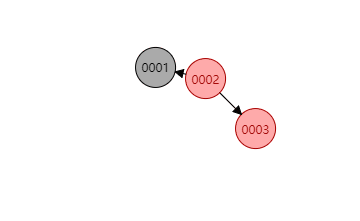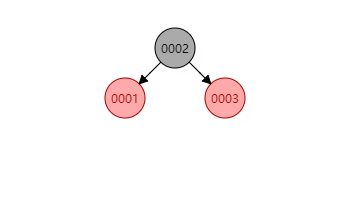
如果插入位置在左边,如下图新插入的
0002结点。则需要对插入结点的父节点做一个右旋操作,再对0001做一个左旋操作:
-
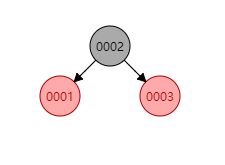
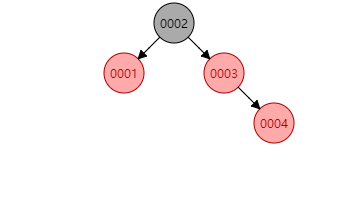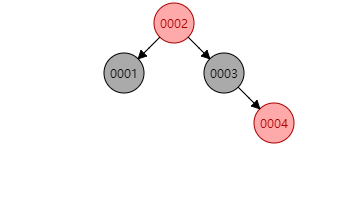
无论插到4-结点的哪个地方都会破坏性质4,这时只要将4-结点分解为两个2-结点并将中间结点往上传给父结点。如下图新插入的
0004结点:
红黑树的删除
首先要删除一个结点的话,这个结点有两种可能的颜色:
删除一个红色结点不会破坏红黑树的任何性质,可以像删除普通二叉树搜索树结点一样删除
-
如果删除的是一个黑色结点则会破坏红黑树的性质5,所以我们只要保证删除的结点是红色的就不会破坏红黑树的性质。具体步骤如下:
在自顶向下搜索要删除结点过程中,保证当前结点是红色的。如果当前结点不是要删除的结点,在接着再往下搜索时判断下一个结点的颜色,定义下一个结点为左结点,(下个结点为右结点的情况与左结点相反):- 如果下个结点是红色或者为空,则不需要做任何操作
- 如果下个结点为黑色且下个结点的兄弟结点也是黑色的话,直接将当前结点和两个子结点合并为一个4-结点。
- 如果下个结点为黑色而下个结点的兄弟结点是红色的话,直接对当前结点做一个左旋操作变成一个4-结点。
当自顶向下删除完结点后,需要向上回溯消除所有破坏红黑树性质4的情况,这一步通过平衡操作来实现。
代码实现
import java.util.*;
public class RBTree , Value>{
private class Node {
Key key;
Value value;
Node left;
Node right;
boolean color;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right, boolean color) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.color = color;
}
}
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
private int size;
private Node root;
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
private boolean isRed(Node node) {
return node != null && node.color;
}
//颜色转换
private void flipColors(Node h) {
h.color = !h.color;
h.left.color = !h.left.color;
h.right.color = !h.right.color;
}
//左旋
private Node rotationLeft(Node node) {
Node x = node.right;
node.right = x.left;
x.left = node;
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
//右旋
private Node rotationRight(Node node) {
Node x = node.left;
node.left = x.right;
x.right = node;
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
//平衡操作
private Node balance(Node node) {
if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node)) {
if ((isRed(node.left.left) || isRed(node.left.right) || isRed(node.right.left) || isRed(node.right.right)))
flipColors(node);
}
else {
if (isRed(node.left)){
if (isRed(node.left.right))
node.left = rotationLeft(node.left);
if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left))
node = rotationRight(node);
}else if (isRed(node.right)){
if (isRed(node.right) && isRed(node.right.left))
node.right = rotationRight(node.right);
if (isRed(node.right) && isRed(node.right.right))
node = rotationLeft(node);
}
if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node)) {
if ((isRed(node.left.left) || isRed(node.left.right) || isRed(node.right.left) || isRed(node.right.right)))
flipColors(node);
}
}
return node;
}
private Node max(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
} else {
while(node.right != null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
}
private Node min(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
} else {
while(node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
}
public Value max() {
return root == null ? null : max(root).value;
}
public Value min() {
return root == null ? null : min(root).value;
}
//插入
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(key, value, root);
root.color = BLACK;
}
private Node put(Key key, Value value, Node node) {
if(node == null) {
++size;
return new Node(key, value, null, null, RED);
} else {
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if(cmp < 0) {
node.left = put(key, value, node.left);
} else if (cmp > 0){
node.right = put(key, value, node.right);
}else{
node.value = value;
}
return balance(node);
}
}
public void deleteMin(){
if (!isEmpty()){
root.color = RED;
root = deleteMin(root);
--size;
if (!isEmpty())
root.color = BLACK;
}
}
private Node deleteMin(Node node){
if (node.left == null){
return node.right;
}
if (!isRed(node.left)) {
if(!isRed(node.left) && !isRed(node.right))
flipColors(node);
else
node = rotationLeft(node);
}
node.left = deleteMin(node.left);
return balance(node);
}
public void deleteMax(){
if (!isEmpty()){
root.color = RED;
root = deleteMax(root);
--size;
if (!isEmpty())
root.color = BLACK;
}
}
private Node deleteMax(Node node){
if (node.right == null){
return node.left;
}
if (!isRed(node.right)) {
if(!isRed(node.left) && !isRed(node.right))
flipColors(node);
else
node = rotationRight(node);
}
node.right = deleteMax(node.right);
return balance(node);
}
//删除
public void delete(Key key){
if (!isEmpty()){
root.color = RED;
root = delete(key, root);
if (!isEmpty())
root.color = BLACK;
}
}
private Node delete(Key key, Node node){
if (node == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0){
if (node.left != null && !isRed(node.left)) {
if(!isRed(node.right))
flipColors(node);
else
node = rotationLeft(node);
}
node.left = delete(key, node.left);
}else if (cmp > 0){
if (node.right != null && !isRed(node.right)) {
if(!isRed(node.left))
flipColors(node);
else
node = rotationRight(node);
}
node.right = delete(key, node.right);
}else {
--size;
if (node.left == null)
return node.right;
if (node.right == null)
return node.left;
Node x = min(node.right);
node.key = x.key;
node.value = x.value;
node.right = deleteMin(node.right);
}
return balance(node);
}
//判断树是否为一棵红黑树
public boolean isRBTree() {
return isRBTree(root);
}
public boolean isRBTree(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return true;
} else if(node.color == RED) {
return false;
} else {
Node x = node;
int count = 0;
for(; x != null; x = x.left) {
if(x.color == BLACK) {
++count;
}
}
return isRBTree(node, count, 0);
}
}
private boolean isRBTree(Node node, int count, int k) {
if(node == null) {
return count == k;
} else if((isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left))
||(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.right))
||(isRed(node.right) && isRed(node.right.right))
||(isRed(node.right) && isRed(node.right.left))) {
return false;
} else {
if(node.color == BLACK) {
++k;
}
return node.left == null && node.right == null ? k == count:isRBTree(node.left, count, k) && isRBTree(node.right, count, k);
}
}
//树的中序遍历
public void inTraverse(){
inTraverse(root);
}
private void inTraverse(Node node){
if (node == null)
return;
inTraverse(node.left);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
inTraverse(node.right);
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 3000, a;
Random random = new Random();
RBTree rbt = new RBTree();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a = random.nextInt(50000);
rbt.put(a, "naoko");
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1500; ++i) {
rbt.delete(i);
}
if (!rbt.isRBTree()) {
System.out.println("不是红黑树");
return;
}
rbt.inTraverse();
System.out.print("是红黑树");
}
}
算法复杂度
红黑树和AVL树类似,都是在进行插入和删除操作时通过特定操作保持树的平衡,从而获得较高的查找性能。不同的是红黑树并不是向AVL树那样追求完美平衡,而是黑色平衡,即从根结点到任意一个空结点的简单路径上黑色结点数都相同。因为一棵红黑树的高度最高不超过2lg(N+1),因此其查找时间复杂度也是O(lgN)级别的。而对于插入和删除操作产生不平衡情况都会在3次旋转之内快速解决,所以复杂度基本为O(lgN)级别,也因为这一点红黑树的效率比AVL树快。
最后
红黑树的插入和删除操作都有自顶向下和自顶向上两种方法,其中自顶向下较为容易,我的删除操作实现属于自顶向下的方法。在JDK中的TreeMap中插入和删除就用了自底向上的方法。