流程图如下所示:
读取线程InputReaderThread执行InputReader#loopOnce一次
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector inputDevices;
....
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
....
if (count) {//处理事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
....
} // release lock
...
mQueuedListener->flush();//刷新派发
}
EventHub#getEvents获取事件,线程在此阻塞,直到被唤醒。
InputReader#processEventsLocked方法。如果count数据不空,事件处理。
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
//遍历count个事件RawEvent*
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
//来自input.h中的事件类型
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;
while (batchSize < count) {
if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT
|| rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {
break;
}
batchSize += 1;
}
//处理一批batchSize个事件,从rawEvent指针开始
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);
} else {
...处理其他类型,设备增加删除等
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:
//当受到增加新设备的事件时,addDeviceLocked负
//责创建InputDevice,建立deviceId与InputDevice
//的键值对装入KeyedVector容器mDevices中,根据
//设备class,为InputDevice创建一个InputMapper
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);
break;
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}
在EventHubInterface中定义的枚举中,FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT被设置为DEVICE_ADDED。
在type小于FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT时,说明事件类型不是增加/删除/扫描设备事件。
EventHubInterface类
enum {
DEVICE_ADDED = 0x10000000,//增加设备
DEVICE_REMOVED = 0x20000000,//移除设备
FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN = 0x30000000,
FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT = DEVICE_ADDED,
};
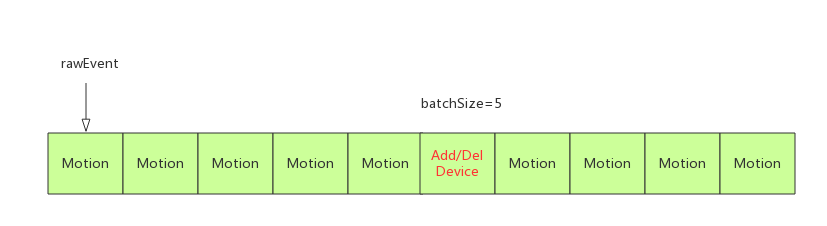
processEventsLocked处理一系列事件的集合如图:
batchSize代表rawEvents中以当前rawEvent为头指针的一批连续待处理事件的数量,deviceId相同且非增加/删除/扫描设备事件。
若rawEvents中存在增加/删除/扫描设备事件(大于FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT)如上图,在偏移batchSize=5处查到rawEvent[batchSize].type满足增加/删除/扫描设备事件,break退出while,之前统计的一批5个Motion事件通过processEventsForDeviceLocked处理,rawEvent设置为头指针。
在最后两行将rawEvent指向batchSize偏移处,即下一次处理的Add/Del事件,count减去已处理的数量batchSize。增加/删除/扫描设备事件处理中,只能处理一个事件,batchSize值保持1。
processEventsForDeviceLocked
负责RawEvent*事件处理,根据设备deviceId,找到InputDevice类,count是此次处理的事件数量,rawEvents代表这些事件的头指针。
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId,const RawEvent* rawEvents,
size_t count){
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (device->isIgnored()) {//设备忽略直接退出
return;
}
device->process(rawEvents, count);
}
InputDevice表示单个输入设备。
InputDevice#process具体设备处理每一个RawEvent*,交给mMappers,InputDevice内部的InputMapper数组。
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count--; rawEvent++) {
if (mDropUntilNextSync) {
.....
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_DROPPED) {
mDropUntilNextSync = true;
reset(rawEvent->when);
} else {
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {//每个InputMapper处理事件
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
mapper->process(rawEvent);
}
}
}
}
每一种类型的设备都有对应的InputMapper,触屏Maper是SingleTouchInputMapper。
InputReader#createDeviceLocked方法
InputDevice* InputReader::createDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, uint32_t classes) {
InputDevice* device = new InputDevice(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),
controllerNumber, identifier, classes);
....其他设备设置与addMapper
//触屏设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
device->addMapper(new MultiTouchInputMapper(device));
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
device->addMapper(new SingleTouchInputMapper(device));
}
....
return device;
}
创建InputDevice,同时创建了InputMapper。根据classes类型,只增加了一个SingleTouchInputMapper,下面所有的RawEvent*交给SingleTouchInputMapper处理。
EventHub.h头文件定义
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH = 0x00000004,//触屏
SingleTouchInputMapper处理流
中间过程繁琐,仅看下流程
从process开始,依次经过方法sync、processRawTouches、cookAndDispatch、dispatchTouches、dispatchMotion,最后包装一个NotifyMotionArgs交给回调监听。
SingleTouchInputMapper#process方法,SingleTouchInputMapper是TouchInputMapper派生类。
void SingleTouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
TouchInputMapper::process(rawEvent);
mSingleTouchMotionAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
}
TouchInputMapper#process方法。
void TouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
mCursorButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
mCursorScrollAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
mTouchButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
sync(rawEvent->when);
}
}
TouchInputMapper#sync方法。
void TouchInputMapper::sync(nsecs_t when) {
const RawState* last = mRawStatesPending.isEmpty() ?
&mCurrentRawState : &mRawStatesPending.top();
mRawStatesPending.push();
RawState* next = &processRawTouchesmRawStatesPending.editTop();
next->clear();
next->when = when;
...
syncTouch(when, next);
//分配手指ids
if (!mHavePointerIds) {
assignPointerIds(last, next);
}
processRawTouches(false /*timeout*/);
}
TouchInputMapper#processRawTouches方法。
void TouchInputMapper::processRawTouches(bool timeout) {
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_DISABLED) {
// Drop all input if the device is disabled.
mCurrentRawState.clear();
mRawStatesPending.clear();
return;
}
const size_t N = mRawStatesPending.size();
size_t count;
for(count = 0; count < N; count++) {
...
cookAndDispatch(mCurrentRawState.when);
}
}
TouchInputMapper#cookAndDispatch方法。
void TouchInputMapper::cookAndDispatch(nsecs_t when) {
....
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_POINTER) {
.....
} else {
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_DIRECT
&& mConfig.showTouches && mPointerController != NULL) {
...
}
if (!mCurrentMotionAborted) {
....
dispatchTouches(when, policyFlags);
...
}
...
}
...
}
TouchInputMapper#dispatchTouches方法。
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchTouches(nsecs_t when, uint32_t policyFlags){
...
dispatchMotion(when, policyFlags, mSource,
AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN, 0, 0, metaState, buttonState, 0,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex,
dispatchedIdBits, downId, mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
...
}
TouchInputMapper#dispatchMotion方法
定义一个通知发送参数NotifyMotionArgs交给回调Listener。
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchMotion(nsecs_t when, uint32_t policyFlags, uint32_t source,
int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState, int32_t edgeFlags,
const PointerProperties* properties, const PointerCoords* coords,
const uint32_t* idToIndex, BitSet32 idBits, int32_t changedId,
float xPrecision, float yPrecision, nsecs_t downTime) {
PointerCoords pointerCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
PointerProperties pointerProperties[MAX_POINTERS];
uint32_t pointerCount = 0;
while (!idBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t id = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
uint32_t index = idToIndex[id];
pointerProperties[pointerCount].copyFrom(properties[index]);
pointerCoords[pointerCount].copyFrom(coords[index]);
...
...
NotifyMotionArgs args(when, getDeviceId(), source, policyFlags,
action, actionButton, flags, metaState, buttonState, edgeFlags,
mViewport.displayId, pointerCount, pointerProperties, pointerCoords,
xPrecision, yPrecision, downTime);
getListener()->notifyMotion(&args);
}
QueuedInputListener
TouchInputMapper#getListener()返回QueuedInputListener
在TouchInputMapper父类InputMapper中,描述了Listener的来源:InputReaderContext#getListener方法。
InputMapper类
inline InputListenerInterface* getListener() { return mContext->getListener(); }
上文mContext是InputReaderContext。ContextImpl是InputReaderContext的派生类(内部封装InputReader),ContextImpl实现InputReaderContext的getListener方法。
InputListenerInterface* InputReader::ContextImpl::getListener() {
return mReader->mQueuedListener.get();
}
大体结构图如下所示:
综上:TouchInputMapper触发内部ContextImpl的getListener方法,获取的Listener是InputReader中的mQueuedListener。
InputReader实例化时创建QueuedInputListener。
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);
上文中listener是InputReader构造方法入参,其实是InputDispatcher。
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
QueuedInputListener#notifyMotion方法
QueuedInputListener是InputListenerInterface接口的派生类
定义了各种类型输入的通知方法notifyXXX()。
class QueuedInputListener : public InputListenerInterface {
public:
QueuedInputListener(const sp& innerListener);
virtual void notifyConfigurationChanged(const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args);
virtual void notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args);
//通知触屏事件
virtual void notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args);
virtual void notifySwitch(const NotifySwitchArgs* args);
virtual void notifyDeviceReset(const NotifyDeviceResetArgs* args);
void flush();
private:
sp mInnerListener;
Vector mArgsQueue;
};
通知参数实体也在此定义,每个事件类型都有自己的通知参数实体
/* Describes a motion event. */
struct NotifyMotionArgs : public NotifyArgs {
nsecs_t eventTime;
int32_t deviceId;
uint32_t source;
...
}
内部封装了一个mInnerListener与mArgsQueue,mInnerListener就是InputDispatcher对象。
mArgsQueue是一个动态的数组容器。
notifyMotion方法
void QueuedInputListener::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyMotionArgs(*args));
}
向数组中增加一个NotifyMotionArgs实体,读取的事件存放在QueuedInputListener的数组mArgsQueue中。
综上,读取线程一次读取的流程结束,可以看出,该线程处于休眠状态,当事件发生时,被唤醒,拿到事件,然后从InputReader对象一步步将事件交给QueuedInputListener对象,事件信息存储在QueuedInputListener内部数组。
接下来读取线程会通过QueuedInputListener的flush方法刷新,将事件消息读出来交给内部InputDispatcher。
Happy
End
^ ^