1. SKNet
SKNet是SENet的加强版,结合了SE opetator, Merge-and-Run Mappings以及attention on inception block的产物。其最终提出的也是与SE类似的一个模块,名为SK, 可以自适应调节自身的感受野。据作者说,该模块在超分辨率任务上有很大提升,并且论文中的实验也证实了在分类任务上有很好的表现。
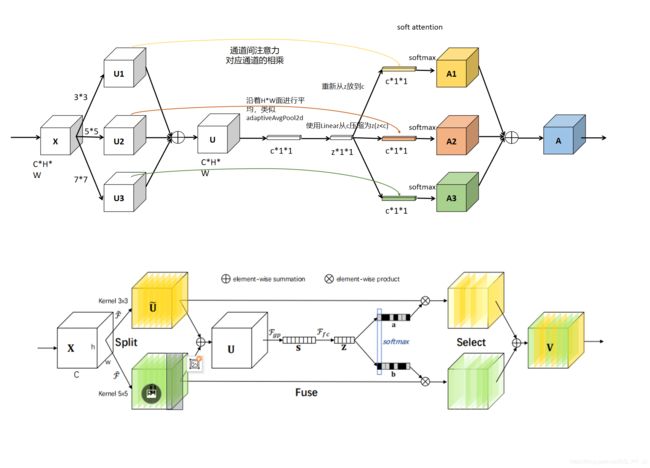
这篇博客重画了SK模块示意图,详见下图,下图中上边的部分是重画的,下边的是论文中的图,虽然比较简洁,但是比较难理解。上边重画的部分分为了三个部分,而原来的模块分成了两个模块。
接下来对照着图先理一遍思路,然后再直接上pytorch版本的代码。
论文中说这个模块可以更好地实现多个分辨率,调节感受野,个人理解就是从不同的分支造成的。下边讲解对照上图进行:
原始feature map X 经过kernel size分别为3×3,5×5....以此类推的卷积进行卷积后得到U1,U2,U3三个,然后相加得到了U,相当于融合了多个感受野的信息。然后得到的U是C×H×W的(C代表channel,H代表height, W代表width)feature map,然后将H和W维度求平均值,具体做法是使用torch.mean完成,最终得到了关于channel的信息是一个C×1×1的一维向量,代表的是各个通道的信息的重要程度。
之后再用了一个线性变换,将原来的C维映射成z维度的信息,进行信息抽取,然后分别使用了三个线性变换,从z维度变为原来的c维度,这样完成了针对channel维度的信息提取,然后使用Softmax进行归一化,这时候每个channel对应一个分数,代表其channel的重要程度,这相当于一个打分mask。将这三个分别得到的mask分别乘以对应的U1,U2,U3,得到A1,A2,A3, 然后相加三个模块,进行信息融合,得到最终模块A, 模块A相比于最初的X经过了信息的提纯,具有了多尺度的信息。
经过以上分析,就能理解了作者的SK模块的构成了:
- 从C线性变换为Z维,再到C维度,这个部分与SE operator比较像
- 多分支的操作借鉴自:inception
- 整个流程类似merge-and-run mapping
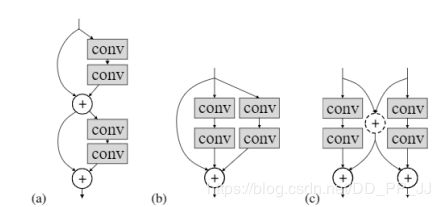
这就是merge-and-run mapping中提出的三个基础模块,与本文sk虽然没有直接联系,但是都是属于先进行分支,然后在合并,也类似于inception中的图。
2. pytorch代码
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class SKConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, WH, M, G, r, stride=1, L=32):
""" Constructor
Args:
features: input channel dimensionality.
WH: input spatial dimensionality, used for GAP kernel size.
M: the number of branchs.
G: num of convolution groups.
r: the radio for compute d, the length of z.
stride: stride, default 1.
L: the minimum dim of the vector z in paper, default 32.
"""
super(SKConv, self).__init__()
d = max(int(features / r), L)
self.M = M
self.features = features
self.convs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
self.convs.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(features,
features,
kernel_size=3 + i * 2,
stride=stride,
padding=1 + i,
groups=G), nn.BatchNorm2d(features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)))
# self.gap = nn.AvgPool2d(int(WH/stride))
print("D:", d)
self.fc = nn.Linear(features, d)
self.fcs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(d, features))
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
for i, conv in enumerate(self.convs):
fea = conv(x).unsqueeze_(dim=1)
if i == 0:
feas = fea
else:
feas = torch.cat([feas, fea], dim=1)
fea_U = torch.sum(feas, dim=1)
# fea_s = self.gap(fea_U).squeeze_()
fea_s = fea_U.mean(-1).mean(-1)
fea_z = self.fc(fea_s)
for i, fc in enumerate(self.fcs):
print(i, fea_z.shape)
vector = fc(fea_z).unsqueeze_(dim=1)
print(i, vector.shape)
if i == 0:
attention_vectors = vector
else:
attention_vectors = torch.cat([attention_vectors, vector],
dim=1)
attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors)
attention_vectors = attention_vectors.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
fea_v = (feas * attention_vectors).sum(dim=1)
return fea_v
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = torch.ones((32, 256, 24,24))
sk = SKConv(256,WH=1,M=2,G=1,r=2)
out = sk(t)
print(out.shape)
3. 资源
sknet论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
作者知乎讲解:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/59690223
代码源自:https://github.com/implus/SKNet
画图、码字不易,求个关注