案例-设备通过X509证书经DPS验证后注册到IoT Hub并开始通信
本案例步骤:
注意,前两个步骤已经在之前的章节中介绍过,本文从第3个步骤开始介绍。
1. 通过openssl和微软示例Powershell脚本生成CA Root证书;
2. 将CA Root证书上传到DPS服务并完成所有权验证;
3. 通过openssl和微软示例Powershll脚本生成 设备证书;
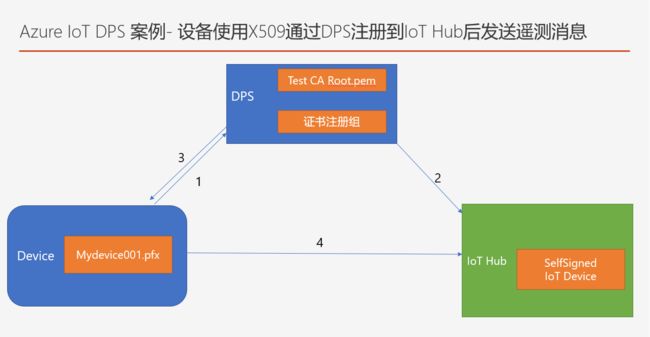
4. 模拟程序(C#)使用设备证书 向DPS进行身份验证并注册到IoT Hub中;
5. 模拟程序使用设备证书直接向IoT Hub 发送遥测消息。
其中第4/5步骤的逻辑图如下:
视频讲解:
您可以在B站观看视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av93099113/
或在本站观看:https://www.51azure.cloud/post/2020/3/4/azure-iot-7-device-with-x509-reg-through-dps-to-iot-hub-send-telemetry
图文讲解:
3. 通过openssl和微软示例Powershll脚本生成 设备证书;
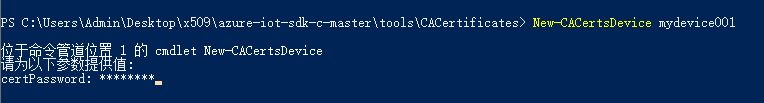
执行如下命令,生成设备证书,其中mydevice001 表示证书名称,也就是最终注册到IoT Hub中的设备ID:
New-CACertsDevice mydevice001
需要输入证书密码,此密码由用户定义,这里我们输入了 12345678
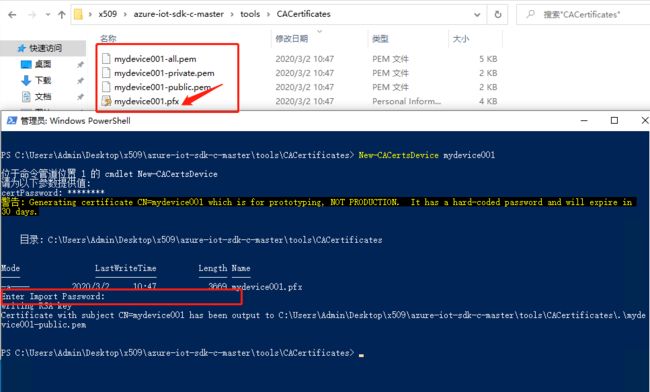
按照提示再次输入密码,即可如下图生成证书,我们在设备中使用的是 mydevice001.pfx 证书文件。
4. 模拟程序(C#)使用设备证书 向DPS进行身份验证并注册到IoT Hub中;
将证书拷贝到示例代码中,该实例代码我们在第三讲《Azure IoT 中级(3)-(案例1)使用DPS通过对称密钥进行单个设备注册》中使用过
下载地址:https://codeload.github.com/Azure-Samples/azure-iot-samples-csharp/zip/master
本节使用的是 azure-iot-samples-csharp-master\provisioning\Samples\device\X509Sample 项目
代码中需要修改的地方:
”GlobalDeviceEndpoint“ 改成"global.azure-devices-provisioning.cn"
"s_certificateFileName"改成证书的名称,此处为”mydevice001.pfx“
”s_idScope“改成实际的DPS的 id scope。
using Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Provisioning.Client;using Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Provisioning.Client.Transport;using Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Shared;using System;using System.IO;using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;using System.Text;namespace Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Provisioning.Client.Samples{ public static class Program { // The Provisioning Hub IDScope. // For this sample either: // - pass this value as a command-prompt argument // - set the DPS_IDSCOPE environment variable
// - create a launchSettings.json (see launchSettings.json.template) containing the variable // private static string s_idScope = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable(""); private static string s_idScope = "0cn0000DC5D"; // In your Device Provisioning Service please go to "Manage enrollments" and select "Individual Enrollments". // Select "Add individual enrollment" then fill in the following: // Mechanism: X.509 // Certificate:
// You can generate a self-signed certificate by running the GenerateTestCertificate.ps1 powershell script. // Select the public key 'certificate.cer' file. ('certificate.pfx' contains the private key and is password protected.) // For production code, it is advised that you install the certificate in the CurrentUser (My) store. // DeviceID: iothubx509device1 // X.509 certificates may also be used for enrollment groups. // In your Device Provisioning Service please go to "Manage enrollments" and select "Enrollment Groups". // Select "Add enrollment group" then fill in the following: // Group name: // Attestation Type: Certificate // Certificate Type:
// choose CA certificate then link primary and secondary certificates
// OR choose Intermediate certificate and upload primary and secondary certificate files // You may also change other enrollemtn group parameters according to your needs private const string GlobalDeviceEndpoint = "global.azure-devices-provisioning.cn"; private static string s_certificateFileName = "mydevice001.pfx"; public static int Main(string[] args) { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(s_idScope) && (args.Length > 0)) { s_idScope = args[0]; } if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(s_idScope)) { Console.WriteLine("ProvisioningDeviceClientX509 "); return 1; } X509Certificate2 certificate = LoadProvisioningCertificate(); using (var security = new SecurityProviderX509Certificate(certificate)) // Select one of the available transports: // To optimize for size, reference only the protocols used by your application. using (var transport = new ProvisioningTransportHandlerAmqp(TransportFallbackType.TcpOnly)) // using (var transport = new ProvisioningTransportHandlerHttp()) // using (var transport = new ProvisioningTransportHandlerMqtt(TransportFallbackType.TcpOnly)) // using (var transport = new ProvisioningTransportHandlerMqtt(TransportFallbackType.WebSocketOnly)) { ProvisioningDeviceClient provClient = ProvisioningDeviceClient.Create(GlobalDeviceEndpoint, s_idScope, security, transport); var sample = new ProvisioningDeviceClientSample(provClient, security); sample.RunSampleAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult(); } return 0; } private static X509Certificate2 LoadProvisioningCertificate() { string certificatePassword = ReadCertificatePassword(); var certificateCollection = new X509Certificate2Collection(); certificateCollection.Import(s_certificateFileName, certificatePassword, X509KeyStorageFlags.UserKeySet); X509Certificate2 certificate = null; foreach (X509Certificate2 element in certificateCollection) { Console.WriteLine($"Found certificate: {element?.Thumbprint} {element?.Subject}; PrivateKey: {element?.HasPrivateKey}"); if (certificate == null && element.HasPrivateKey) { certificate = element; } else { element.Dispose(); } } if (certificate == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException($"{s_certificateFileName} did not contain any certificate with a private key."); } else { Console.WriteLine($"Using certificate {certificate.Thumbprint} {certificate.Subject}"); } return certificate; } private static string ReadCertificatePassword() { var password = new StringBuilder(); Console.WriteLine($"Enter the PFX password for {s_certificateFileName}:"); while(true) { ConsoleKeyInfo key = Console.ReadKey(true); if (key.Key == ConsoleKey.Backspace) { if (password.Length > 0) { password.Remove(password.Length - 1, 1); Console.Write("\b \b"); } } else if (key.Key == ConsoleKey.Enter) { Console.WriteLine(); break; } else { Console.Write('*'); password.Append(key.KeyChar); } } return password.ToString(); } }}
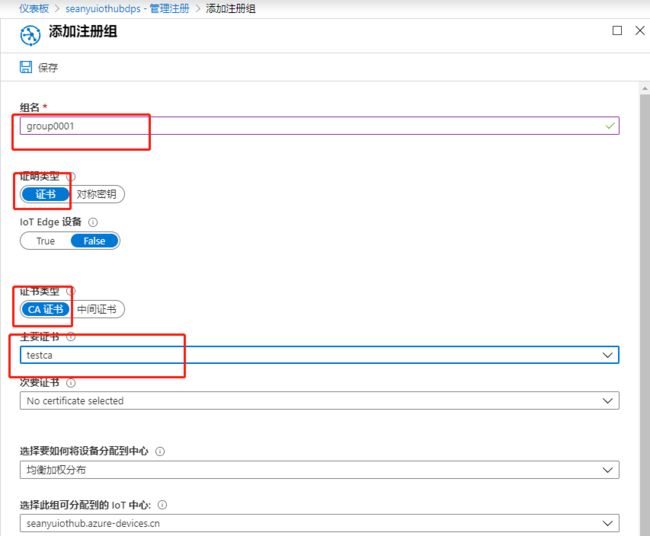
执行代码前,在DPS中添加组注册,选择证书方式,并从下拉列表里选择上一节内容配置到DPS中的证书:
执行代码:
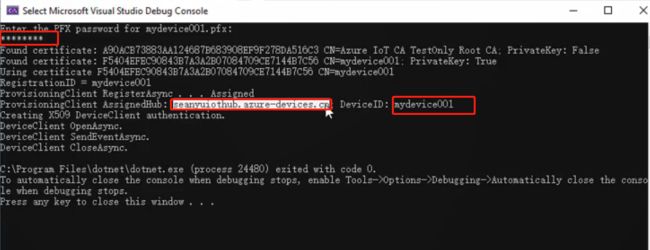
输入证书密码,程序返回DPS将设备注册到的IoT Hub的名称和设备ID
此时,便完成了设备通过X509证书通过DPS注册到IoT Hub的步骤,可以在Portal-DPS中检查到如下结果:
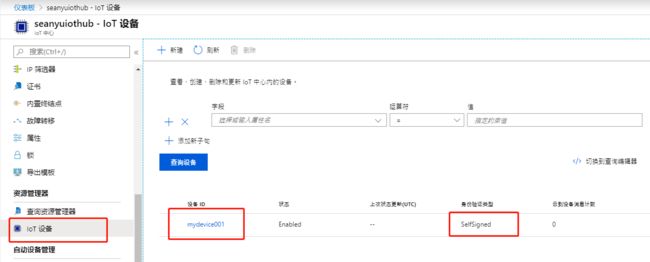
同时,可以在IoT Hub中看到如下设备,验证方式是SelfSigned:
5. 模拟程序使用设备证书直接向IoT Hub 发送遥测消息
本步骤参考如下文档:
https://docs.azure.cn/zh-cn/iot-hub/iot-hub-security-x509-get-started#create-an-x509-device-for-your-iot-hub
示例代码如下:
需要修改的地方有:
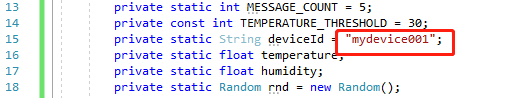
44行mydevice001.pfx, 和 12345678,替换成你的证书路径和 证书密码;
45行mydevice001换成你的deviceid
46行iot hub 换成第四步中,DPS返回的IoT Hub
using System;using Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Client;using Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Shared;using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;using System.Threading.Tasks;using System.Text;namespace x509device{ class Program { private static int MESSAGE_COUNT = 5; private const int TEMPERATURE_THRESHOLD = 30; private static String deviceId = "mydevice001"; private static float temperature; private static float humidity; private static Random rnd = new Random(); static async Task SendEvent(DeviceClient deviceClient) { string dataBuffer; Console.WriteLine("Device sending {0} messages to IoTHub...\n", MESSAGE_COUNT); for (int count = 0; count < MESSAGE_COUNT; count++) { temperature = rnd.Next(20, 35); humidity = rnd.Next(60, 80); dataBuffer = string.Format("{{\"deviceId\":\"{0}\",\"messageId\":{1},\"temperature\":{2},\"humidity\":{3}}}", deviceId, count, temperature, humidity); Message eventMessage = new Message(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(dataBuffer)); eventMessage.Properties.Add("temperatureAlert", (temperature > TEMPERATURE_THRESHOLD) ? "true" : "false"); Console.WriteLine("\t{0}> Sending message: {1}, Data: [{2}]", DateTime.Now.ToLocalTime(), count, dataBuffer); await deviceClient.SendEventAsync(eventMessage); } } static void Main(string[] args) { try { var cert = new X509Certificate2("mydevice001.pfx", "12345678"); var auth = new DeviceAuthenticationWithX509Certificate("mydevice001", cert); var deviceClient = DeviceClient.Create("seanyuiothub.azure-devices.cn", auth, TransportType.Amqp_Tcp_Only); if (deviceClient == null) { Console.WriteLine("Failed to create DeviceClient!"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Successfully created DeviceClient!"); SendEvent(deviceClient).Wait(); } Console.WriteLine("Exiting...\n"); } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine("Error in sample: {0}", ex.Message); } } }}
运行程序,看到如下发送遥测结果成功:
本系列其他文章:
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(1)-Device Provisioning Service(DPS)概览
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(2)-理解DPS组注册和单独注册
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(3)-(案例1)使用DPS通过对称密钥进行单个设备注册
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(4)-(案例2)使用DPS通过对称密钥进行设备组注册
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(5)- 在 DPS/IoT Hub中使用X509证书的准备工作(1)了解证书链
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(6)- 在 DPS/IoT Hub中使用X509证书的准备工作(2)创建自签名证书并验证所有权
(视频)Azure IoT 中级(7)- (案例3)设备通过X509证书经DPS验证后注册到IoT Hub并开始通信