1.SELECT
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
SELECT * FROM table_name;
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column1) FROM table_name;
SELECT DISTINCT只返回不同的值
COUNT关键字返回不同值的数量
2.WHERE
- WHERE clause is used to filter records
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
操作符:
=, <, <=, >, >=: 操作符本意
<>: not equal
BETWEEN: between an inclusive range
LIKE: search for a pattern
“%”:零个,一个或多个
“_”:一个
IN: to specify multiple possible values for a column
SELECT *
FROM table_name
WHERE column2 BETWEEN 1 and 20;
SELECT * FROM table_name
WHERE column LIKE '%n';
SELECT * FROM table_name
WHERE column in (a, b, c);
3. ORDER BY
ascending order by default
use DESC key word for descending order
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name
ORDER BY column1, column2 ASC | DESC;
4. INSERT INTO
insert new records in a table
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3);
\\或者插入全部列
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1, value2, value3);
5. UPDATE and DELETE
update is used to modify the existing records in a table
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE condition;
delete is used to delete existing records in a table
DELETE FORM table_name
WHERE condition
如果没有where,则全部记录都被删除,要很小心
6. MIN and MAX
MIN和MAX都返回一个单一值
SELECT MIN(column1)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
SELECT MAX(column2)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
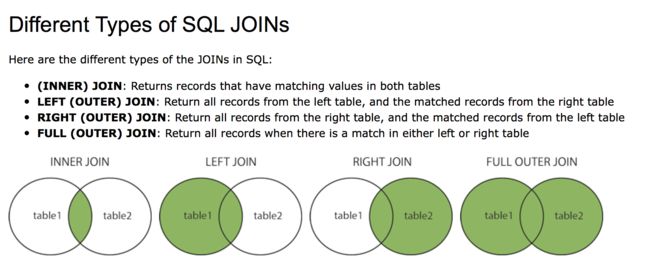
7. JOIN
join is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
8. OTHER CLAUSE
8.1 GROUP BY
used with aggregate functions (COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, AVG) to group the result-set by one or more columns.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
ORDER BY column_name(s);
8.2 HAVING
the HAVING clause was added to SQL because WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
HAVING condition
ORDER BY column_name(s);
8.3 EXISTS
used to test for the existence of any record in a subquery
return true if the subquery returns one or more records
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition);
8.4 ANY and ALL
ANY and ALL operators are used with a WHERE or HAVING clause
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator ANY
(SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition);
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator ALL
(SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition);