增加自定义findbugs规则集
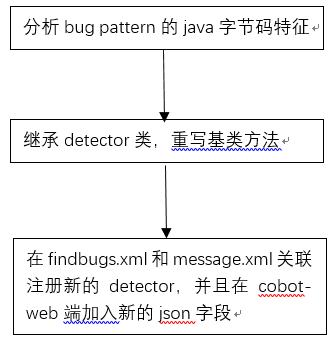
增加自定义检测模式的一般流程
上层接口和父类
Priority接口
public interface Priorities {
public static final int IGNORE_PRIORITY = 5;//忽略bug
public static final int EXP_PRIORITY = 4;
public static final int LOW_PRIORITY = 3;//低优先级
public static final int NORMAL_PRIORITY = 2;//普通优先级
public static final int HIGH_PRIORITY = 1;//高优先级
}
Detector接口
/**
* bug pattern检测必须要实现该接口
*/
public interface Detector extends Priorities {
/**
* Visit the ClassContext for a class which should be analyzed for instances
* of bug patterns.
*/
public void visitClassContext(ClassContext classContext);
/**
* This method is called after all classes to be visited. It should be used
* by any detectors which accumulate information over all visited classes to
* generate results.
*/
public void report();
}
BugInstance类
/**
* @param detector
* the Detector that is reporting the BugInstance
* @param type
* the bug type
*/
public BugInstance(Detector detector, String type, int priority) {
this(type, priority);
if (detector != null) {
// Adjust priority if required
String detectorName = detector.getClass().getName();
adjustForDetector(detectorName);
}
}
Bytecode 框架
- 所有的bug detector都是用bytecode分析
- 大部分的detector用以下技术实现
- inspect class/method/field
- micropattern:simple bytecode pattern
- stack-based pattern
- dataflow analysis
- interprocedural analysis
1. Inspect class/method/field
某些detector不需要code 分析
1. 发现类override equals()方法没重写hashCode()方法
2. 方法命名错误(hashCode()写成了hashcode()方法)
2. Micropatterns: simple bytecode patterns
synchronized (lock) { ALOAD 0
lock.wait(); GETFIELD A.lock
... DUP
} ASTORE 1
MONITORENTER
ALOAD 0
GETFIELD A.lock
INVOKEVIRTUAL
Object.wait()V
3. Stack-based patterns
- Micropatterns where the values on the operand stack are significant
- Example:
- As seen earlier: look for monitorenter on constant String value
- Typical implementation strategy:
- Inquire about values on operand stack
- Warn when suspicious instruction sequence/stack values
seen
一般性检测器
BytecodeScanningDetector
对于扫描字节码的需求,一般是扩展这个类。
Visit
有很多不同参数的方法。表示访问类、或者代码、方法等时候会调用该方法。
一般用该方法进行访问前的初始化**工作**。
public void visit(Code obj) 分析方法内容时调用visit(Code) 方法,往往用于分析方法代码前进行初始化工作
public void visit(JavaClass obj) 分析该类之前,调用该方法。往往用于取得类的信息
public void visitField(Field obj) 分析类的属性前,调用该方法,往往用于取得类的属性信息
分析字节码
>>例1
public void sawOpcode(int seen)
>>在分析方法正文中的每一个操作码时调用sawOpcode(int)方法。
>> seen就是每条的操作码,操作码在反编译后都能看到
指令码都是该类的常量,可以找到
public void show();
Code:
0: getstatic #29; //Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #48; //String ssssssssssssss00s
5: invokevirtual #35; //Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
8: return
>>取得该指令对于的类
getClassConstantOperand()
对于第5行:可以取到java/io/PrintStream
>>取得该指令对应的类执行的方法的名字
getNameConstantOperand()
对于第5行:可以取到println
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
例2
汇编代码:
public void doBadStuff();
Code:
0: invokestatic #2; //Method java/lang/System.gc:()V
3: return
查找调用了System.gc的代码
public void sawOpcode(int seen) {
if (seen == INVOKESTATIC) {
if (getClassConstantOperand().equals("java/lang/System")
&& getNameConstantOperand().equals("gc")) {
bugReporter.reportBug(new BugInstance("SYSTEM_GC", NORMAL_PRIORITY)
.addClassAndMethod(this)
.addSourceLine(this));
}
}
}
}
public void sawMethod()
>>每分析一个方法前,都会调用该方法
>>取得类的名字
String className = super.getClassName().replaceAll("/", ".");
>>取得方法的名字
this.getMethod().getName()
>>取得方法的返回类型
String returnType = this.getMethod().getReturnType().toString();
>>取得方法是否为静态
boolean isStatic = this.getMethod().isStatic();
>>取得方法是否为公开的
boolean isPublic = this.getMethod().isPublic();
>>例如:
public void sawMethod() {
if (isPublicStaticMethord) {
return;
}
//class name: demo/First|| methord name :show|| ReturnType() name : //demo.Second //accce flag= 1
String className = super.getClassName().replaceAll("/", ".");
String returnType = this.getMethod().getReturnType().toString();
boolean isStatic = this.getMethod().isStatic();
boolean isPublic = this.getMethod().isPublic();
//单例判断
if (isPublic && isStatic) {//如果为公有的静态的
if (className != null && className.equals(returnType)) {//如果返回值就是本类
isPublicStaticMethord = true;
}
}
}
生成报表
1、构造函数里面会传递报表参数
public SingletonDector(BugReporter bugReporter) {
this.bugReporter= bugReporter;
}
2.在恰当的地方调用报表
一般是在visitXXX sawXXX地方检查的时候调用
bugReporter.reportBug(newBugInstance("MULTITHREAD_SINGLETON",NORMAL_PRIORITY)
.addClass(this)) ;
>>MULTITHREAD_SINGLETON
就是配置的报表的名字
>>addXXX
就是传递给报表的属性,在报表里面是可以取到的