1、实验目的与要求
(1) 综合掌握java基本程序结构;
(2) 综合掌握java面向对象程序设计特点;
(3) 综合掌握java GUI 程序设计结构;
(4) 综合掌握java多线程编程模型;
(5) 综合编程练习。
2、实验内容和步骤
任务1:填写课程课后调查问卷,网址:https://www.wjx.cn/jq/33108969.aspx。
任务2:综合编程练习
练习1:设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
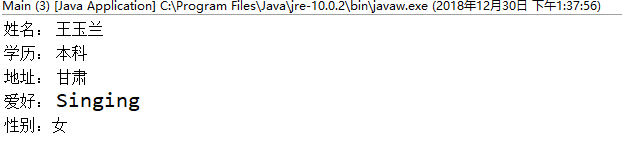
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
(1)用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(2)用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(3)点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class DemoJFrame extends JFrame {
private JPanel jPanel1;
private JPanel jPanel2;
private JPanel jPanel3;
private JPanel jPanel4;
private JTextField fieldname;
private JComboBox comboBox;
private JTextField fieldadress;
private ButtonGroup bg;
private JRadioButton nan;
private JRadioButton nv;
private JCheckBox sing;
private JCheckBox dance;
private JCheckBox read;
public DemoJFrame() {
// 设置窗口大小
this.setSize(800, 400);
// 设置可见性
this.setVisible(true);
// 设置标题
this.setTitle("Students Detail");
// 设置关闭操作
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 设置窗口居中
WinCenter.center(this);
this.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
// 创建四个面板对象
jPanel1 = new JPanel();
setJPanel1(jPanel1);
jPanel2 = new JPanel();
setJPanel2(jPanel2);
jPanel3 = new JPanel();
setJPanel3(jPanel3);
jPanel4 = new JPanel();
setJPanel4(jPanel4);
// 设置容器的为流布局
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout();
this.setLayout(flowLayout);
// 将四个面板添加到容器中
this.add(jPanel1);
this.add(jPanel2);
this.add(jPanel3);
this.add(jPanel4);
}
/*
* 设置面一
*/
private void setJPanel1(JPanel jPanel) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45));
// 给面板的布局设置为网格布局 一行4列
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4));
JLabel name = new JLabel("Name:");
fieldname = new JTextField("");
JLabel study = new JLabel("Qualification:");
comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.addItem("小学");
comboBox.addItem("初中");
comboBox.addItem("高中");
comboBox.addItem("本科");
jPanel.add(name);
jPanel.add(fieldname);
jPanel.add(study);
jPanel.add(comboBox);
this.add(jPanel);
}
/*
* 设置面板二
*/
private void setJPanel2(JPanel jPanel) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50));
// 给面板的布局设置为网格布局 一行4列
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4));
JLabel name = new JLabel("Adress:");
fieldadress = new JTextField();
fieldadress.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(150, 50));
JLabel study = new JLabel("Hobby:");
JPanel selectBox = new JPanel();
selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1));
read = new JCheckBox("Reading");
sing = new JCheckBox("Singing");
dance = new JCheckBox("Dancing");
selectBox.add(read);
selectBox.add(sing);
selectBox.add(dance);
jPanel.add(name);
jPanel.add(fieldadress);
jPanel.add(study);
jPanel.add(selectBox);
}
/*
* 设置面板三
*/
private void setJPanel3(JPanel jPanel) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150));
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel sex = new JLabel("Sex:");
JPanel selectBox = new JPanel();
selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
bg = new ButtonGroup();
nan = new JRadioButton("男");
nv = new JRadioButton("女");
bg.add(nan);
bg.add(nv);
selectBox.add(nan);
selectBox.add(nv);
jPanel.add(sex);
jPanel.add(selectBox);
}
/*
* 设置面板四
*/
private void setJPanel4(JPanel jPanel) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150));
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 50, 10);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
JButton sublite = new JButton("Validate");
JButton reset = new JButton("Reset");
sublite.addActionListener((e) -> valiData());
reset.addActionListener((e) -> Reset());
jPanel.add(sublite);
jPanel.add(reset);
}
/*
* 提交数据
*/
private void valiData() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
// 拿到数据
String name = fieldname.getText().toString().trim();
String qualification = comboBox.getSelectedItem().toString().trim();
String address = fieldadress.getText().toString().trim();
System.out.println("姓名: " + name);
System.out.println("学历: " + qualification);
System.out.println("地址: " + address);
String hobbystring = "";
if (read.isSelected()) {
hobbystring += "Reading ";
}
if (sing.isSelected()) {
hobbystring += "Singing ";
}
if (dance.isSelected()) {
hobbystring += "Dancing ";
}
System.out.println("爱好: " + hobbystring);
if (nan.isSelected()) {
System.out.println("性别:男");
}
if (nv.isSelected()) {
System.out.println("性别:女");
}
}
/*
* 重置
*/
private void Reset() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
fieldadress.setText(null);
fieldname.setText(null);
comboBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
sing.setSelected(false);
dance.setSelected(false);
read.setSelected(false);
bg.clearSelection();
}
}
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
DemoJFrame page = new DemoJFrame();
});
}
}
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.Window;
public class WinCenter {
public static void center(Window win) {
Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize();
Dimension wSize = win.getSize();
if (wSize.height > sSize.height) {
wSize.height = sSize.height;
}
if (wSize.width > sSize.width) {
wSize.width = sSize.width;
}
win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width) / 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height) / 2);
}
}
实验结果:
练习2:采用GUI界面设计以下程序:
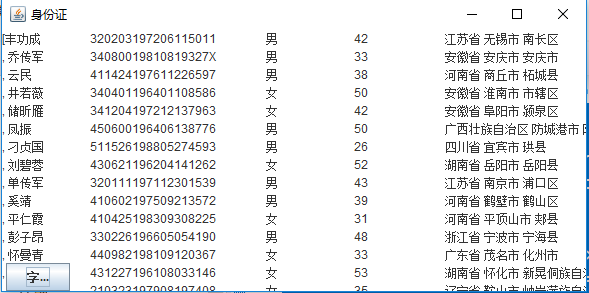
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
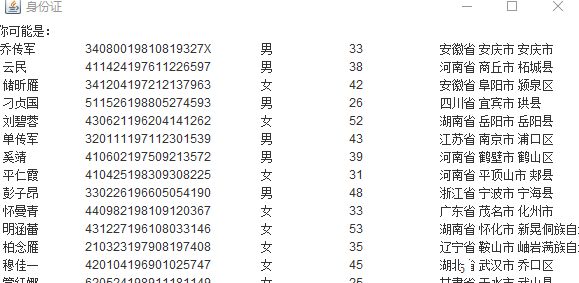
l 输入身份证信息,查询所提供身份证号的人员信息,要求输入一个身份证数字时,查询界面就显示满足查询条件的查询结果,且随着输入的数字的增多,查询匹配的范围逐渐缩小。
package ID;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class button {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Main();
frame.setTitle("身份证");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package ID; public class Person implements Comparable{ private String name; private String ID; private int age; private String sex; private String birthplace; public String getname() { return name; } public void setname(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getID() { return ID; } public void setID(String ID) { this.ID = ID; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getsex() { return sex; } public void setsex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public String getbirthplace() { return birthplace; } public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) { this.birthplace = birthplace; } public int compareTo(Person o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getname()); } public String toString() { return name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + age + "\t" + ID + "\t" + birthplace + "\n"; } }
package ID;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Main extends JFrame {
private static ArrayList personlist;
private static ArrayList list;
private JPanel panel;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 600;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300;
public Main() {
personlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String ID = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String place = linescanner.nextLine();
Person Person = new Person();
Person.setname(name);
Person.setID(ID);
Person.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
Person.setage(a);
Person.setbirthplace(place);
personlist.add(Person);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("查找不到信息");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息读取有误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JTextArea jt = new JTextArea();
panel.add(jt);
add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 7));
JButton jButton = new JButton("字典排序");
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("年龄最大和年龄最小");
JLabel lab = new JLabel("你的老乡");
JTextField jt1 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("查找年龄相近的:");
JTextField jt2 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("输入你的身份证号码:");
JTextField jt3 = new JTextField();
JButton jButton2 = new JButton("退出");
jButton.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jButton1.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jt1.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jt2.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jt3.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jButton2.setBounds(110, 90, 40, 50);
jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Collections.sort(personlist);
jt.setText(personlist.toString());
}
});
jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int max = 0, min = 100;
int j, k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
j = personlist.get(i).getage();
if (j > max) {
max = j;
k1 = i;
}
if (j < min) {
min = j;
k2 = i;
}
}
jt.setText("年龄最大:" + personlist.get(k1) + "年龄最小:" + personlist.get(k2));
}
});
jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
jt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String find = jt1.getText();
String text = "";
String place = find.substring(0, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
if (personlist.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1, 4).equals(place)) {
text += "\n" + personlist.get(i);
jt.setText("老乡:" + text);
}
}
}
});
jt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String yourage = jt2.getText();
int a = Integer.parseInt(yourage);
int near = agenear(a);
int value = a - personlist.get(near).getage();
jt.setText("年龄相近:" + personlist.get(near));
}
});
jt3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.sort(personlist);
String key = jt3.getText();
for (int i = 1; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
if (personlist.get(i).getID().contains(key)) {
list.add(personlist.get(i));
jt.setText("你可能是:\n" + list);
}
}
}
});
buttonPanel.add(jButton);
buttonPanel.add(jButton1);
buttonPanel.add(lab);
buttonPanel.add(jt1);
buttonPanel.add(lab1);
buttonPanel.add(jt2);
buttonPanel.add(lab2);
buttonPanel.add(jt3);
buttonPanel.add(jButton2);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int min = 53, value = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
value = personlist.get(i).getage() - age;
if (value < 0)
value = -value;
if (value < min) {
min = value;
k = i;
}
}
return k;
}
}
实验结果:
练习3:采用GUI界面设计以下程序
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
package math;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class math {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Toolkit t = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension s = t.getScreenSize();
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new main();
frame.setBounds(0, 0, (int) s.getWidth() / 2, (int) s.getHeight() / 2);
frame.setTitle("算术测试");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package math;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.math.*;
public class main extends JFrame {
private String[] c = new String[10];
private String[] c1 = new String[10];
private int[] list = new int[10];
int i = 0, i1 = 0, sum = 0;
private PrintWriter out = null;
private JTextArea text, text1;
private int counter;
public main() {
JPanel Panel = new JPanel();
Panel.setLayout(null);
JLabel JLabel1 = new JLabel("");
JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30);
JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 20));
JButton Button = new JButton("生成题目");
Button.setBounds(50, 150, 150, 50);
Button.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 20));
Button.addActionListener(new Action());
JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定答案");
Button2.setBounds(300, 150, 150, 50);
Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 20));
Button2.addActionListener(new Action1());
JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件");
Button3.setBounds(500, 150, 150, 50);
Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 20));
Button3.addActionListener(new Action2());
text = new JTextArea(30, 80);
text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50);
text.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 30));
text1 = new JTextArea(30, 80);
text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50);
text1.setFont(new Font("Courier", Font.PLAIN, 30));
Panel.add(text);
Panel.add(text1);
Panel.add(Button);
Panel.add(Button2);
Panel.add(Button3);
Panel.add(JLabel1);
add(Panel);
}
private class Action implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
text1.setText("");
if (i <= 10) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
switch (m) {
case 0:
while (a % b != 0) {
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
while (b == 0) {
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
c[i] = (i + ":" + a + "/" + b + "=");
list[i] = Math.floorDiv(a, b);
text.setText(i + ":" + a + "/" + b + "=");
i++;
break;
case 1:
c[i] = (i + ":" + a + "*" + b + "=");
list[i] = Math.multiplyExact(a, b);
text.setText(i + ":" + a + "*" + b + "=");
i++;
break;
case 2:
c[i] = (i + ":" + a + "+" + b + "=");
list[i] = Math.addExact(a, b);
text.setText(i + ":" + a + "+" + b + "=");
i++;
break;
case 3:
while (a < b) {
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
c[i] = (i + ":" + a + "-" + b + "=");
text.setText(i + ":" + a + "-" + b + "=");
list[i] = Math.subtractExact(a, b);
i++;
break;
}
}
}
}
private class Action1 implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
if (i < 10) {
text.setText(null);
String z = text1.getText().toString().trim();
int a = Integer.parseInt(z);
if (text1.getText() != "") {
if (list[i1] == a)
sum += 10;
}
c1[i1] = z;
i1++;
}
}
}
private class Action2 implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
try {
out = new PrintWriter("text.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int counter = 0; counter < 10; counter++) {
out.println(c[counter] + c1[counter]);
}
out.println("成绩" + sum);
out.close();
}
}
}
实验结果:
任务3:本学期课程已结束,请汇总《面向对象程序设计课程学习进度条》的数据,统计个人专业能力提升的数据。并从学习内容、学习方法、学习心得几个方面进行课程学习总结,也希望你对课程的不足提出建议和意见。
学习内容:
学习内容:我们学习的内容就是十四章,老师采用我们自主学习,带领学习,实验演示以及周末完成博客作业的方式。即内容分为主次关系,如前三章,基于学习了C语言,自主学习,从4章开始正式讲授,继承,接口和异常处理,是我们学习的重要内容,这三章概念很多,要会使用具体的API,还有lambda表达式可以简化代码,掌握这一方法是作为一个程序员必掌握。图形用户界面以及线程的模块的学习,老师花了大量精力。在学习Java的过程中,我们不断完善:身份证查询,四则运算和图形用户界面的三个大实验,在学长周五晚上的带领下,最后基本完成了用户使用的要求。
学习方法:我的学习方法就是课上听老师讲解理论的概念,实验课上老师和助教的演示,在周末完成博客作业。暂时还没有遇到一个问题自行处理的能力,力不从心,老师推荐了慕课平台的课程,但是由于时间和自己懒惰的原因,没有坚持下来,我会选择在假期去完成,以便提升自己。
学习心得:领到又厚又重的Java书,就像是昨天一样。转眼间,这本《面向对象程序设计书》在老师的分配任务下,总算是完成了。我们的助教非常负责,在他身上看到了许多优点,比如:坚持,问心无愧,默默无闻,非常认可老师的这种方案,同时也很感谢学长。