本文主要针对
首先导入上面的头文件
消息发送
在OC中,调用一个方法的格式如下:
[davin playWith: friend];
在方法调用的时候,runtime会将上面的方法调用转换成一个C语言的函数调用,表示朝着davin发送了一个playWith:消息,并传入了friend这个参数:
objc_msgSend(davin, @selector(playWith:), friend);
那么在这个C语言函数中发生了什么事情?编译器是如何找到这个类的方法的呢?苹果开源了 runtime的实现代码,其中为了高度优化性能,苹果使用汇编实现了这个函数(源码处于Source/objc-msg-arm.s
文件下):
/*****************************************************************
*
* id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL _cmd,...);
*
*****************************************************************/
ENTRY objc_msgSend
MESSENGER_START
cbz r0, LNilReceiver_f // 判断消息接收者是否为nil
ldr r9, [r0] // r9 = self->isa
CacheLookup NORMAL // 到缓存中查找方法
LCacheMiss: // 方法未缓存
MESSENGER_END_SLOW
ldr r9, [r0, #ISA]
b __objc_msgSend_uncached
LNilReceiver: // 消息接收者为nil处理
mov r1, #0
mov r2, #0
mov r3, #0
FP_RETURN_ZERO
MESSENGER_END_NIL
bx lr
LMsgSendExit:
END_ENTRY objc_msgSend
即使不懂汇编,上面的代码通过注释后也足以让各位一窥究竟。从上述代码中我们可以看到一个方法调用过程中发生的事情,包括:
判断接收者是否为nil,如果为nil,清空寄存器,消息发送返回nil
到类缓存中查找方法,如果存在直接返回方法
没有找到缓存,到类的方法列表中依次寻找
查找方法实现是通过
_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
这个奇怪的函数完成的:
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
Class curClass;
IMP methodPC = nil;
Method meth;
bool triedResolver = NO;
methodListLock.assertUnlocked();
// 如果传入的cache为YES,到类缓存中查找方法缓存
if (cache) {
methodPC = _cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (methodPC) return methodPC;
}
// 判断类是否已经被释放
if (cls == _class_getFreedObjectClass())
return (IMP) _freedHandler;
// 如果类未初始化,对其进行初始化。如果这个消息是initialize,那么直接进行类的初始化
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
}
retry:
methodListLock.lock();
// 忽略在GC环境下的部分消息,比如retain、release等
if (ignoreSelector(sel)) {
methodPC = _cache_addIgnoredEntry(cls, sel);
goto done;
}
// 遍历缓存方法,如果找到,直接返回
methodPC = _cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (methodPC) goto done;
// 遍历类自身的方法列表查找方法实现
meth = _class_getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, cls, meth, sel);
methodPC = method_getImplementation(meth);
goto done;
}
// 尝试向上遍历父类的方法列表查找实现
curClass = cls;
while ((curClass = curClass->superclass)) {
// Superclass cache.
meth = _cache_getMethod(curClass, sel, _objc_msgForward_impcache);
if (meth) {
if (meth != (Method)1) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, curClass, meth, sel);
methodPC = method_getImplementation(meth);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// 查找父类的方法列表
meth = _class_getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, curClass, meth, sel);
methodPC = method_getImplementation(meth);
goto done;
}
}
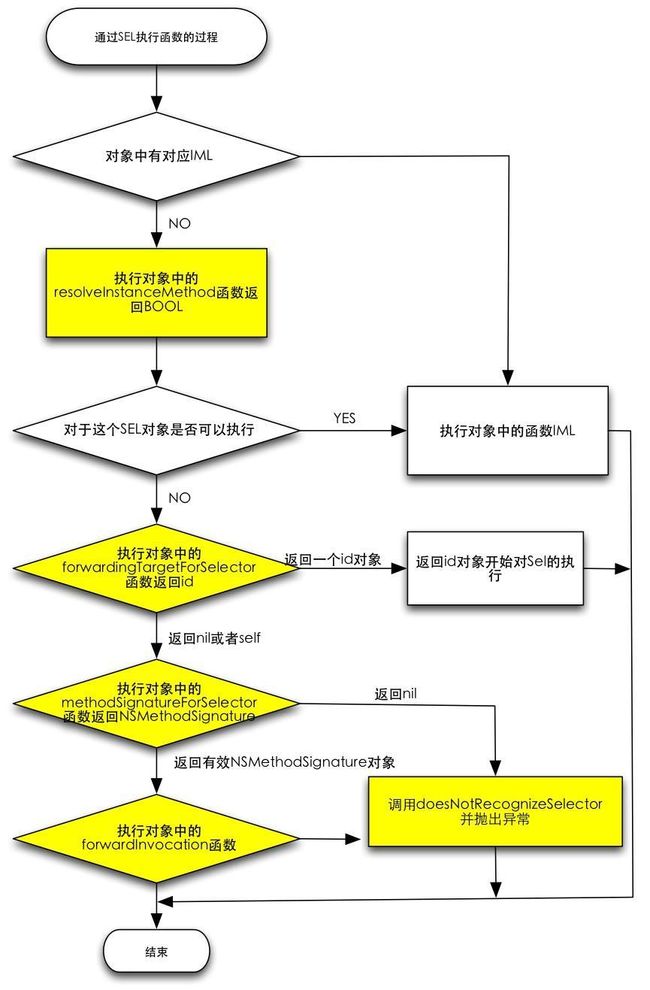
// 没有找到任何的方法实现,进入消息转发第一阶段“动态方法解析”
// 调用+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod: (SEL)selector
// 征询接收者所属的类是否能够动态的添加这个未实现的方法来解决问题
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
methodListLock.unlock();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// 仍然没有找到方法实现进入消息转发第二阶段“备援接收者”
// 先后会调用 -(id)forwardingTargetForSelector: (SEL)selector
// 以及 - (void)forwardInvocation: (NSInvocation*)invocation 进行最后的补救
// 如果补救未成功抛出消息发送错误异常
_cache_addForwardEntry(cls, sel);
methodPC = _objc_msgForward_impcache;
done:
methodListLock.unlock();
assert(!(ignoreSelector(sel) && methodPC != (IMP)&_objc_ignored_method));
return methodPC;
}
上面就是一个方法调用的全部过程。主要分为三个部分:
查找是否存在对应的方法缓存,如果存在直接返回调用为了优化性能,方法的缓存使用了散列表的方式,在下一部分会进行比较详细的讲述
未找到缓存,到类本身或顺着类结构向上查找方法实现,返回的method_t *类型也被命名为Method
//非加锁状态下查找方法实现 static method_t * getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel) { runtimeLock.assertLocked(); assert(cls->isRealized()); // fixme nil cls? // fixme nil sel? for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(), end = cls->data()->methods.endLists(); mlists != end; ++mlists) { method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel); if (m) return m; } return nil; } // 搜索方法列表 static method_t * search_method_list(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel) { int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp(); int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->entsize() == sizeof(method_t); if (__builtin_expect(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize, 1)) { // 对有序数组进行线性探测 return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist); } else { // Linear search of unsorted method list for (auto& meth : *mlist) { if (meth.name == sel) return &meth; } } #if DEBUG // sanity-check negative results if (mlist->isFixedUp()) { for (auto& meth : *mlist) { if (meth.name == sel) { _objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not"); } } } #endif return nil; }
如果在这个步骤中找到了方法的实现,那么将它加入到方法缓存中以便下次调用能快速找到:
// 记录并且缓存方法
static void log_and_fill_cache(Class cls, IMP imp, SEL sel, id receiver, Class implementer)
{
#if SUPPORT_MESSAGE_LOGGING
if (objcMsgLogEnabled) {
bool cacheIt = logMessageSend(implementer->isMetaClass(),
cls->nameForLogging(),
implementer->nameForLogging(),
sel);
if (!cacheIt) return;
}
#endif
cache_fill (cls, sel, imp, receiver);
}
//在无加锁状态下缓存方法
static void cache_fill_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;
if (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return;
cache_t *cache = getCache(cls);
cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);
// 如果缓存占用不到3/4,进行缓存。
mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1;
mask_t capacity = cache->capacity();
if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache()) {
cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE);
}
else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3) {
}
else {
// 扩充缓存。为了性能,扩充后原有缓存方法全部移除
cache->expand();
}
bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver);
if (bucket->key() == 0) cache->incrementOccupied();
bucket->set(key, imp);
}
如果在类自身中没有找到方法实现,那么循环获取父类,重复上面的查找动作,找到后再将方法缓存到本类而非父类的缓存中
未找到任何方法实现,触发消息转发机制进行最后补救
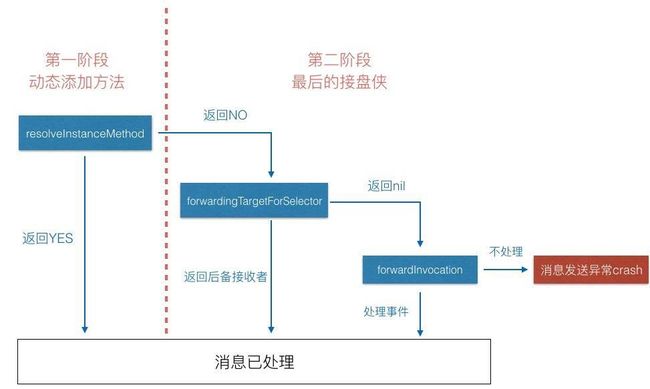
其中消息转发分为两个阶段,第一个阶段我们可以通过动态添加方法之后让编译器再次执行查找方法实现的过程;第二个阶段称作备援的接收者,就是找到一个接盘侠来处理这个事件
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst) { // 非beta类的情况下直接调用 resolveInstanceMethod 方法 if (! cls->isMetaClass()) { _class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst); } else { // 先调用 resolveClassMethod 请求动态添加方法 // 然后进行一次查找判断是否处理完成 // 如果没有添加,再调用 resolveInstanceMethod 方法 _class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst); if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst, NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/)) { _class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst); } } }
方法缓存在上一篇runtime文章中笔者已经说过对于OC的每一个对象来说,本质上都是一个objc_class的结构体封装,在最新的runtime源码的objc-runtime-new.h
中,objc_class的结构如下(笔者已经略去了大部分的函数):
struct objc_class : objc_object {
Class superclass; // Class ISA;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
void setData(class_rw_t *newData) {
bits.setData(newData);
}
// .........
}
结构一目了然,很明显cache存储着我们在方法调用中需要查找的方法缓存。作为缓存方法的cache采用了散列表,以此来大幅度提高检索的速度:
#define CACHE_HASH(sel, mask) (((uintptr_t)(sel)>>2) & (mask))
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets;
mask_t _mask;
mask_t _occupied;
// functions
}
// cache method
buckets = (cache_entry **)cache->buckets;
for (index = CACHE_HASH(sel, cache->mask);
buckets[index] != NULL;
index = (index+1) & cache->mask)
{ }
buckets[index] = entry;
在每次调用完未被缓存的方法时,下面的那段缓存方法的代码就会调用。苹果利用了sel的指针地址和mask做了一个简单的位运算,然后找到一个空槽存储起来。 以此我们可以推出从缓存中查找sel实现的代码CacheLookup,但是为了高度优化性能,苹果同样丧心病狂的使用汇编完成了查找的步骤,官方给出的注释足够我们大致看明白这段代码:
.macro CacheLookup
ldrh r12, [r9, #CACHE_MASK] // r12 = mask
ldr r9, [r9, #CACHE] // r9 = buckets
.if $0 == STRET || $0 == SUPER_STRET
and r12, r12, r2 // r12 = index = SEL & mask
.else
and r12, r12, r1 // r12 = index = SEL & mask
.endif
add r9, r9, r12, LSL #3 // r9 = bucket = buckets+index*8
ldr r12, [r9] // r12 = bucket->sel
2:
.if $0 == STRET || $0 == SUPER_STRET
teq r12, r2
.else
teq r12, r1
.endif
bne 1f
CacheHit $0
1:
cmp r12, #1
blo LCacheMiss_f // if (bucket->sel == 0) cache miss
it eq // if (bucket->sel == 1) cache wrap
ldreq r9, [r9, #4] // bucket->imp is before first bucket
ldr r12, [r9, #8]! // r12 = (++bucket)->sel
b 2b
.endmacro
具体的源码可以从苹果开源这里下载,这个方法苹果已经注释的足够清晰了。
上面所有的操作都是对方法的缓存、查找操作,那么方法究竟是什么?在OC中方法被抽象成的数据类Method
,如果了解并且使用过runtime的读者们可能了解这个类型,其结构如下:
struct old_method {
SEL method_name;
char *method_types;
IMP method_imp;
};
typedef struct method_t *Method;
方法的实现代码,你可以把它看做一个block。事实上,后者确实可以转换成一个IMP类型来实现某些黑魔法。method_types方法的参数编码,什么意思?在属性与变量中我说过每一种数据类型有着自己对应的字符编码,这个表示方法返回值、参数的字符编码,比如-(void)playWith:(id)
的字符编码为v@:@
method_name
顾名思义,方法的名字。通常我们使用@selector()
的方式获取一个方法的sel地址,这个被用来进行散列计算存储方法的imp实现。由于SEL类型采用了散列的算法,因此如果同一个类中存在同样名字的方法,那么就会导致方法的imp地址无法唯一化。这也是苹果不允许同名不同参数类型的方法存在的原因
消息转发
通常情况下,在我们调用不属于某个对象的方法的时候,我们的应用就会崩溃crash,比如笔者经历过好几次因为后台返回的NSNull类型导致了测试反馈应用闪退。通过上面的方法调用源码我们可以看到并不是没有找到方法实现就直接发生了崩溃,在崩溃之前编译器会进行消息转发机制,总共给了我们三次机会来避免这样的崩溃并尽可能的找到方法的响应者。
首先先看第一阶段。我们都知道,在iOS开发当中我们需要非常的注意用户体验。单纯的是因为数据类型错误而导致应用出现闪退,这样的处理会极大的影响使用app的用户。因此,我们可以通过
class_addMethod这个函数来动态的添加这种错误的处理(类可以在
objc_registerClassPair完成类的注册之后动态的添加方法,但不允许动态添加属性,参考
category
机制)
id wrongTypeGetter(id object, SEL sel) {
return nil;
}
void wrongTypeSetter(id object, SEL sel, id value) {
// do nothing
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod: (SEL)selector
{
NSString * selName = NSStringFromSelector(selector);
if ([sel hasPrefix: @"set"]) {
class_addMethod(self, selector, (IMP)wrongTypeSetter, "v@:@");
} else {
class_addMethod(self, selector, (IMP)wrongTypeGetter, "@@:")
}
}
在第二阶段最开始的时候,这时候已经默许了你并不想使用消息接收者来响应这个方法,所以我们需要找到消息接盘侠
—— 这并不是一件坏事。在iOS中不支持多继承,尽管我们可以通过协议和组合模式实现伪多继承。伪多继承和多继承的区别在于:多继承是将多个类的功能组合到一个对象当中,而伪多继承多个类的功能依旧分布在不同对象当中,但是对象彼此对消息发送者透明
。那么,如果我们消息转发给另一个对象可以用来实现这种伪多继承。
@interface Person: NSObject@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber * age;@end@implementation Person- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector: (SEL)aSelector{ // 甚至可以通过runtime遍历自己属性找到可以响应方法的接盘侠 NSString * selName = NSStringFromSelector(aSelector); if ([selName hasSuffix: @"Value"]) { return self.age; } return nil;}@end// View controllerid p = [[Person alloc] init];[p setAge: @(18)];NSLog(@"%lu, %.2f", [p integerValue], [p doubleValue]); //18, 18.00
如果你依旧没有为这个方法找到另外一个调用者,那么阻止你app闪退的最后时刻到来了。runtime需要生成一个methodSignature变量来组装,这将通过调用消息接收者的-(NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:
获取,这个变量包含了方法的参数类型、参数个数以及消息接收者等信息。接着把这个变量组装成一个NSInvocation对象进行最后一次的消息转发,调用接收者的-forwardInvocation:来进行最后的挽救机会。这意味着我们可以尽情的对invocation
做任何事情,包括随意修改参数值、消息接收者等。我最常拿来干的事情就是减少数组的遍历工作:
@implementation NSArray(LXDRuntime)- (void)forwardInvocation: (NSInvocation *)anInvocation{ for (id item in self) { if ([item respondsToSelector: anInvocation.selector]) { [anInvocation invokeWithTarget: item]; } }}@end
总的来说整个消息发送的过程可以归纳成下面这张图:
虽然消息转发可以帮助我们显著的减少app的闪退率,但是在开发阶段千万不要加入这些特性。最好是在app申请上架的那个阶段再加,这样不至于app其他消息发送异常被我们忽略了。
消息机制黑魔法
上面笔者讲解了关于一个调用方法之中发生的事情,确实非常的复杂。同样的这些特性也非常值得我们去学习使用,runtime提供了一系列关于Method的方法给我们实现面向切面编程的工作。这些工作包括了替换原有方法实现,交换方法实现等等工作。
假设现在我需要一个圆角按钮,并且保证点击触发事件的范围必须要这个圆之内,那么通过一个UIButton+LXDRuntime的扩展来替换旧有-pointInside:withEvent:
方法
@interface UIButton(LXDRuntime)@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL roundTouchEnable;@endconst void * LXDRoundTouchEnableKey = & LXDRoundTouchEnableKey;@implementation UIButton(LXDRuntime)- (BOOL)roundTouchEnable{ return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, LXDRoundTouchEnableKey) boolValue];}- (void)setRoundTouchEnable: (BOOL)roundTouchEnable{ objc_setAssociatedObject(self, LXDRoundTouchEnableKey, @(roundTouchEnable), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);}- (BOOL)replacePointInside: (CGPoint)point withEvent: (UIEvent *)event{ if (CGRectGetWidth(self.frame) != CGRectGetHeight(self.frame) || !self. roundTouchEnable) {� return [super pointInside: point withEvent: event]; } CGFloat radius = CGRectGetWidth(self.frame) / 2; CGPoint offset = CGPointMake(point.x - radius, point.y - radius); return sqrt(offset.x * offset.x + offset.y * offset.y) <= radius;}// 替换方法实现+ (void)initialize{ [super initialize]; Method replaceMethod = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(replacePointInside:withEvent:)); Method originMethod = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(pointInside:withEvent:)); method_setImplementation(originMethod, method_getImplementation(replaceMethod));}@end
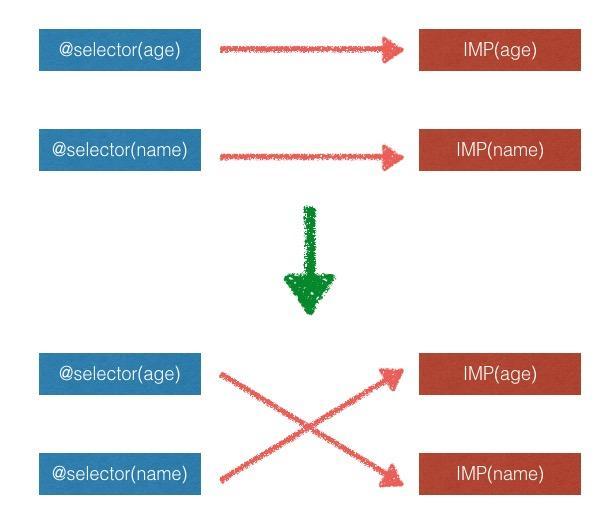
那么当我需要我的按钮只响应圆形点击区域的时候,只需要设置button.roundTouchEnable = YES,就会自动实现了圆形点击的判断。除了上面的上面的方法替换,还有另一个常用的黑魔法是交换两个方法的实现。归功于Method的特殊结构,将方法名字sel
跟代码实现imp分隔开来。你可以把imp当做是一个block代码块,而交换实现的操作就相当于把这两个block交换了。
@interface Person : NSObject@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString * name;@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber * age;@end@implementation Person+ (void)initialize{ [super initialize]; Method ageGetter = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(age)); Method nameGetter = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(name)); method_exchangeImplementations(ageGetter, nameGetter);}// View controllerPerson * p = [[Person alloc] init];p.age = @(56);p.name = @"Job Steve";NSLog(@"%@ is %@ year old", p.name, p.age); // LXDRuntimeDemo[7316:244912] 56 is Job Steve year old@end
上面的代码交换了name和age
的实现,用图示来表示:
应该不难看出,
method_exchangeImplementations
之所以被推崇的原因在于这种方式交换实现的时候不会导致原有的方法实现发生改变(从头到尾,
age的
IMP跟
name的
IMP都没有进行任何的修改),当然了,它的缺点也是非常明显的:
多人开发对同一个方法都进行方法
替换/交换时,会使得业务逻辑复杂,非常的不利于调试
被交换的方法实现会直接的影响到所有该类的实例对象以及子类,不适用于单个对象的实现
可以说runtime提供的这些黑魔法都是双刃剑,合理的运用能让我们更加的强大。另外,除了Method的黑魔法,还要提到一个IMP相关的使用陷阱。上文说过,IMP跟block是非常相似的东西,前者可以跟函数指针强制转换,因此可以看做是一个特殊的block,同样的系统提供了两者相互转换的方法:imp_implementationWithBlock和imp_getBlock。按照上面说的,当调用方法转换成消息转发的时候,objc_msgSend自身已经存在了两个参数id object以及SEL aSelector,那么按照这种思路IMP和block
的切换应该是这样的:
+ (void)initialize
void (^requestBlock)(id object, SEL aSelector, id URL, id parameters) =
^(id object, SEL aSelector, id URL, id parameters) {
// do some networking request
};
IMP requestIMP = imp_implementationWithBlock(requestBlock);
class_addMethod([self class], @selector(networkReuqest:parameters:), requestIMP, "v@:@@");
}
// View controller
[self performSelector: @selector(networkReuqest:parameters:) withObject: URL withObject: parameters];
上面这段代码会crash的非常无厘头,提示你EXC_BAD_ACCESS
错误。重要的事情说三遍:
block参数不存在SEL!!
block参数不存在SEL!!
block参数不存在SEL!!
上面的代码只要去掉了SEL aSelector
这个参数,这段代码就能正常执行。
本文参考自Bison的技术博客