第四章实践
-
sniffex源码分析(www.tcpdump.org/sniffex.c )
sniffex.c是sniffer.c的一个派生工作。因为是个派生品,所以啥都没保障。程序性能和质量没保障,接口,字段啥的也没更新标准,还是用的以前的接口。所以在编译的时候各种bug,各种尝试后,我终于放弃了。
一个问题是最新的libpcap弃用了pacp_lookupdev(),原文是:
理由是不安全。尝试改写使用pacp_findalldevs()后发现其中一个argument未被声明,于是又尝试该arguement的声明,仍然白给。于是尝试注释掉头文件的弃用语句,问题貌似解决。但第二次尝试编译又出现更多问题,于是改回去想别的办法。但突然又编译成功了,却不能执行(binary format)??从头再来时又有别的warning,遂放弃。
虽然问题多(个人向),但是其源码模块的一些设计还是比较完整的,另外源码带文档和比较详细的英文注释,比较好分析。
首先是一些分组长度检测,头部字段的定义(包括以太网,ip,tcp) 等,这没啥好分析的,主要记住几个原始的套接字就行了
如ETH_P_IP = 0x0800, ETH_P_ARP = 0x0806, ETH_P_RARP = 0x8035, ETH_P_IPV6 = 0x086dd等。/* default snap length (maximum bytes per packet to capture) */ #define SNAP_LEN 1518 /* ethernet headers are always exactly 14 bytes [1] */ #define SIZE_ETHERNET 14 /* Ethernet addresses are 6 bytes */ #define ETHER_ADDR_LEN 6 /* Ethernet header */ struct sniff_ethernet { u_char ether_dhost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN]; /* destination host address */ u_char ether_shost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN]; /* source host address */ u_short ether_type; /* IP? ARP? RARP? etc */ }; /* IP header */ struct sniff_ip { u_char ip_vhl; /* version << 4 | header length >> 2 */ u_char ip_tos; /* type of service */ u_short ip_len; /* total length */ u_short ip_id; /* identification */ u_short ip_off; /* fragment offset field */ #define IP_RF 0x8000 /* reserved fragment flag */ #define IP_DF 0x4000 /* dont fragment flag */ #define IP_MF 0x2000 /* more fragments flag */ #define IP_OFFMASK 0x1fff /* mask for fragmenting bits */ u_char ip_ttl; /* time to live */ u_char ip_p; /* protocol */ u_short ip_sum; /* checksum */ struct in_addr ip_src,ip_dst; /* source and dest address */ }; #define IP_HL(ip) (((ip)->ip_vhl) & 0x0f) #define IP_V(ip) (((ip)->ip_vhl) >> 4) /* TCP header */ typedef u_int tcp_seq; struct sniff_tcp { u_short th_sport; /* source port */ u_short th_dport; /* destination port */ tcp_seq th_seq; /* sequence number */ tcp_seq th_ack; /* acknowledgement number */ u_char th_offx2; /* data offset, rsvd */ #define TH_OFF(th) (((th)->th_offx2 & 0xf0) >> 4) u_char th_flags; #define TH_FIN 0x01 #define TH_SYN 0x02 #define TH_RST 0x04 #define TH_PUSH 0x08 #define TH_ACK 0x10 #define TH_URG 0x20 #define TH_ECE 0x40 #define TH_CWR 0x80 #define TH_FLAGS (TH_FIN|TH_SYN|TH_RST|TH_ACK|TH_URG|TH_ECE|TH_CWR) u_short th_win; /* window */ u_short th_sum; /* checksum */ u_short th_urp; /* urgent pointer */ };然后声明所需要的功能模块:
void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet); void print_payload(const u_char *payload, int len); void print_hex_ascii_line(const u_char *payload, int len, int offset); void print_app_banner(void); void print_app_usage(void);其中
print_app_banner()和print_appusage()用来打印一些提示信息,print_hex_ascii_line()和print_payload()主要用来帮助打印信息(格式,编码等)。got_packet()`模块用来处理报文,分析如下://其中,header:收到的数据包指针,类型 pcap_pkthdr* //packet:收到的数据包 void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) { static int count = 1; /* packet counter */ /* declare pointers to packet headers */ const struct sniff_ethernet *ethernet; /* The ethernet header [1] */ //各包头数据 const struct sniff_ip *ip; /* The IP header */ const struct sniff_tcp *tcp; /* The TCP header */ const char *payload; /* Packet payload */ int size_ip; int size_tcp; int size_payload; printf("\nPacket number %d:\n", count); count++; //以太帧字段 /* define ethernet header */ ethernet = (struct sniff_ethernet*)(packet); //ip包头字段 /* define/compute ip header offset */ ip = (struct sniff_ip*)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET); size_ip = IP_HL(ip)*4; if (size_ip < 20) { printf(" * Invalid IP header length: %u bytes\n", size_ip); return; } /* print source and destination IP addresses */ printf(" From: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->ip_src)); printf(" To: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->ip_dst)); // ip,tcp,icmp包分析 /* determine protocol */ switch(ip->ip_p) { case IPPROTO_TCP: printf(" Protocol: TCP\n"); break; case IPPROTO_UDP: printf(" Protocol: UDP\n"); return; case IPPROTO_ICMP: printf(" Protocol: ICMP\n"); return; case IPPROTO_IP: printf(" Protocol: IP\n"); return; default: printf(" Protocol: unknown\n"); return; } /* * OK, this packet is TCP. */ //tcp字段定位及负载数据打印,依赖print_payload() /* define/compute tcp header offset */ tcp = (struct sniff_tcp*)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip); size_tcp = TH_OFF(tcp)*4; if (size_tcp < 20) { printf(" * Invalid TCP header length: %u bytes\n", size_tcp); return; } printf(" Src port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->th_sport)); printf(" Dst port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->th_dport)); /* define/compute tcp payload (segment) offset */ payload = (u_char *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip + size_tcp); /* compute tcp payload (segment) size */ size_payload = ntohs(ip->ip_len) - (size_ip + size_tcp); /* * Print payload data; it might be binary, so don't just * treat it as a string. */ if (size_payload > 0) { printf(" Payload (%d bytes):\n", size_payload); print_payload(payload, size_payload); } return; }main()分析
int main(int argc, char **argv) { char *dev = NULL; /* capture device name */ // pcap_lookupdev()自动获取网络接口,返回一个网络接口的字符串指针 // 但是新版的libpcap把pcap_lookupdev()弃用了,理由是不安全。。 // 推荐是pcap_findalldevs(),并获取第一个有效设备 // 如果出错,放入 errbuf char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; /* error buffer */ pcap_t *handle; /* packet capture handle */ char filter_exp[] = "ip"; /* filter expression [3] */ struct bpf_program fp; /* compiled filter program (expression) */ bpf_u_int32 mask; /* subnet mask */ bpf_u_int32 net; /* ip */ int num_packets = 10; /* number of packets to capture */ print_app_banner(); /* check for capture device name on command-line */ if (argc == 2) { dev = argv[1]; } else if (argc > 2) { fprintf(stderr, "error: unrecognized command-line options\n\n"); print_app_usage(); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } else { /* find a capture device if not specified on command-line */ // 链接最新发布的libpcap,编译会出错 dev = pcap_lookupdev(errbuf); if (dev == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't find default device: %s\n", errbuf); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } } /* get network number and mask associated with capture device */ //pcap_lookupnet()获得设备的IP地址,子网掩码等信息,(上面信息的翻译) //net:网络接口的IP地址 //mask:网络接口的子网掩码 if (pcap_lookupnet(dev, &net, &mask, errbuf) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't get netmask for device %s: %s\n", dev, errbuf); net = 0; mask = 0; } /* print capture info */ printf("Device: %s\n", dev); printf("Number of packets: %d\n", num_packets); printf("Filter expression: %s\n", filter_exp); /* open capture device */ //pcap_open_live()用来打开网络接口 //SNAP_LEN:抓包长度 //第三个参数:0代表非混杂模式,1代表混杂模式 //第四个参数:等待的毫秒数,超过这个值, //获取数据包的函数会立即返回 handle = pcap_open_live(dev, SNAP_LEN, 1, 1000, errbuf); if (handle == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device %s: %s\n", dev, errbuf); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } //pcap_datalink()判断是否是以太网 //DLT_EN10MB,使用tcpdump会经常看到 /* make sure we're capturing on an Ethernet device [2] */ if (pcap_datalink(handle) != DLT_EN10MB) { fprintf(stderr, "%s is not an Ethernet\n", dev); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } //pcap_compile()用来编译过滤表达式 //fp指向编译后的filter_exp //filter_exp过滤表达式 //参数四:是否需要优化过滤表达式 (0应该是默认的??) /* compile the filter expression */ if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle)); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } //pcap_setfilter()表示应用过滤表达式 //完成过滤表达式后,可以使用 //pcap_loop()或pcap_next()登抓包函数抓包了 /* apply the compiled filter */ if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle)); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } /* now we can set our callback function */ //pacp_loop()抓报 //参数分别是 接口,抓包数,got_packet()调用指针 pcap_loop(handle, num_packets, got_packet, NULL); /* cleanup */ pcap_freecode(&fp); pcap_close(handle); //释放网络接口 printf("\nCapture complete.\n"); return 0; }总的来看便是通过调用pacp_*()api进行进行网络抓包,编写信息打印模块和解包模块(根据分组头部字段格式逐层获取数据,包括原宿地址等)用于分析。其实比较麻烦的还是格式和解包的过程,需要考虑的情况多一点。
-
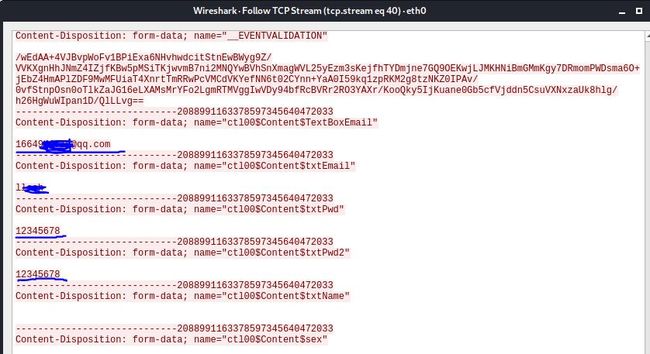
获取网页登录账号和口令:
由于以上源码未能编译成功,于是采用wireshark进行。选择的网页为www.zgwenku.com,嗅探获取数据包后,获取账号密码: