vue简介和初始化过程
vue的源码结构如下
src
├── compiler # 编译相关
├── core # 核心代码
├── platforms # 不同平台的支持
├── server # 服务端渲染
├── sfc # .vue 文件解析
├── shared # 共享代码
Vue对象
在使用vue时我们知道都是使用new Vue(),来将vue的实例挂载到dom对象上从而运用数据驱动的方式来扩展我们的代码,我们首先来看一下Vue的定义
从源头上看来自core目录下的instance的index.js文件
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
在js中一切皆函数,其实Vue就是一个函数,在初始化的时候执行原型链上的_init方法,vue没有把所有的方法都写在函数内部,这样从代码上来说,每次实例化的时候不会生成重复的代码
主要还是代码结构更清晰,利用mixin的概念,把每个模块都抽离开,这样代码在结构和扩展性都有很大提高,这里的每个mixin先不说,先看以一下整体结构,这里定义完还要被core里的index.js再次包装调用initGlobalAPI(Vue)来初始化全局的api方法,在web下runtime文件夹下引用再次封装,vue是分为运行时可编译和只运行的版本,所以如果需要编译,在Vue原型上添加了$mount方法,先来看一下initGlobalAPI,在instance中都是在原型链上扩展方法,在这里是直接在Vue上扩展静态方法
function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// exposed util methods.
// NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on
// them unless you are aware of the risk.
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
// 2.6 explicit observable API
Vue.observable = (obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
initUse(Vue)
initMixin(Vue)
initExtend(Vue)
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
数据双向绑定
我们在使用vue时看一个最简单的例子
{{msg}}
var root = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'hello'
}
})
我们可以看到这样简单的几行就可以将数据绑定到dom对象上,那内部做了什么呢,先来看一下前面说的,在实例化会调用原型链上的_init方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
这个方法包括合并配置,初始化生命周期,时间,渲染,data,props等,最后判断有没有传入的el执行$mount方法挂载到dom对象上
看一下compile版本的mount方法,先将之前定义的mount的方法缓存后边使用,判断有没有render方法,vue也可以写类似react的render函数,
如果没有的话,判断有没有模版字符串,获取模版字符串,或者直接获取html字符串使用compileToFunctions编译模版,编译好了之后主要是为了生成
render方法,无论使用单文件组件还是模版方法还是之前demo中的方法都必须经过render方法,最后执行之前缓存的mount方法,这个方法是在runtime的index.js中定义的
这个实际上就是在执行生命周期中的mount周期,mountComponent方法,我删除了一下在dev环境的处理,这不影响逻辑,可以看出mount方法主要就是定义了一个Watcher来相应组件的变化
执行了初始化的一些生命周期,render方法主要就是用来根据模版字符串来生成虚拟dom元素,类似react的jsx编译成ReactElmemnt的,可以看出两个库从设计的基础架构还是很像的
var mount = Vue.prototype.$mount; // 缓存mount方法
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el,
hydrating
) {
el = el && query(el);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
warn(
"Do not mount Vue to or - mount to normal elements instead."
);
return this
}
var options = this.$options;
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) { // 如果没有render方法
var template = options.template;
if (template) { // 如果存在template模版文件
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (!template) {
warn(
("Template element not found or is empty: " + (options.template)),
this
);
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML;
} else {
{
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this);
}
return this
}
} else if (el) { //存在el直接获取当前dom下的html字符串模版
template = getOuterHTML(el);
}
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile');
}
var ref = compileToFunctions(template, {// 编译模版
outputSourceRange: "development" !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines: shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref: shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this);
var render = ref.render;
var staticRenderFns = ref.staticRenderFns;
options.render = render;
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end');
measure(("vue " + (this._name) + " compile"), 'compile', 'compile end');
}
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) // 最后执行原先定义的mount方法
};
function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode // 创建一个空的vnode节点
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') // 执行生命周期方法
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) // 执行原型链上的_update方法,_render()生成虚拟dom,进行虚拟dom的比较
}
}
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}
vue的虚拟dom
vue虚拟dom的实现借鉴了snabbdom,增加了一些vue特有的属性,我们一起来看一下vdom下的vnode.js文件
下边是vnode的数据结构,可以看出相比snabbdom增加了很多,并且提供了一些创建vnode元素的方法
class VNode {
tag: string | void;
data: VNodeData | void;
children: ?Array;
text: string | void;
elm: Node | void;
ns: string | void;
context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope
key: string | number | void;
componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;
componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance
parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
// strictly internal
raw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)
isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static node
isRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition check
isComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?
isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?
isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?
asyncFactory: Function | void; // async component factory function
asyncMeta: Object | void;
isAsyncPlaceholder: boolean;
ssrContext: Object | void;
fnContext: Component | void; // real context vm for functional nodes
fnOptions: ?ComponentOptions; // for SSR caching
devtoolsMeta: ?Object; // used to store functional render context for devtools
fnScopeId: ?string; // functional scope id support
}
来看一看是怎么通过render生成vdom的,实际上是通过_createElement生成的可以看到,先对传入的一些参数进行一些校验,对chilren进行规范化使其是vnode的数组
然后根据tag进行判断,是原生标签直接生成vnode,已注册的组件通过component生成vnode,返回vnode
function _createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class | Function | Object,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode | Array {
if (isDef(data) && isDef((data: any).__ob__)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Avoid using observed data object as vnode data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}\n` +
'Always create fresh vnode data objects in each render!',
context
)
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// object syntax in v-bind
if (isDef(data) && isDef(data.is)) {
tag = data.is
}
if (!tag) {
// in case of component :is set to falsy value
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// warn against non-primitive key
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
isDef(data) && isDef(data.key) && !isPrimitive(data.key)
) {
if (!__WEEX__ || !('@binding' in data.key)) {
warn(
'Avoid using non-primitive value as key, ' +
'use string/number value instead.',
context
)
}
}
// support single function children as default scoped slot
if (Array.isArray(children) &&
typeof children[0] === 'function'
) {
data = data || {}
data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] }
children.length = 0
}
if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) { // 把children格式化成vnode数组
children = normalizeChildren(children)
} else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) {
children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children)
}
let vnode, ns
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) { // 判断是不是一些内置的div,span原生标签
// platform built-in elements
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isDef(data) && isDef(data.nativeOn)) {
warn(
`The .native modifier for v-on is only valid on components but it was used on <${tag}>.`,
context
)
}
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) { // 判断是不是已经注册的组件标签
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements
// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its
// parent normalizes children
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
// direct component options / constructor
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
if (Array.isArray(vnode)) {
return vnode
} else if (isDef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns)
if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data)
return vnode
} else {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
}
看到vnode的生成过程再来看看update这个方法在初次渲染和数据更新会执行,并对dom进行操作,这里比较重要的是patch方法,
我们通过源码最终能找到这个代码是在web下runtime目录index.js下,由于不同平台实现不一样,在浏览器中是在vdom中的patch.js中createPatchFunction,我们在snabbdom中的patch也是根据依赖的hook生成的,在vue中也是基本的思路,在runtime中传入依赖的一些模块传入的两个参数,最终返回一个patch方法,这个放会根据新旧vnode进行diff算法,简单来说就是第一次生成直接创建新的元素,如果新旧的key,tag,isComment相等就执行patchVnode来更新dom和vnode,否则就删除old创建新的到old的位置,这和react的diff算法思想基本一致,只不过实现不一样最后return真实的dom
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el // 真实dom
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm) // 生成还原vm的方法
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) { // 初始化
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else { // 数据更新时
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
restoreActiveInstance()
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) { // 更新真实dom上对虚拟dom的指向
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
function createPatchFunction (backend) {
let i, j
const cbs = {}
const { modules, nodeOps } = backend // 依赖的模块和dom操作api
for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) { // 根据定义好的hooks将依赖中的方法添加到cbs中去方便在不同时期执行不同方法
cbs[hooks[i]] = []
for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) {
if (isDef(modules[j][hooks[i]])) {
cbs[hooks[i]].push(modules[j][hooks[i]])
}
}
}
// ...省略
return function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
', or missing
. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
)
}
}
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// replacing existing element
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// create new node
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// update parent placeholder node element, recursively
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
let ancestor = vnode.parent
const patchable = isPatchable(vnode)
while (ancestor) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor)
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm
if (patchable) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor)
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) {
insert.fns[i]()
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}
}
}
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
}
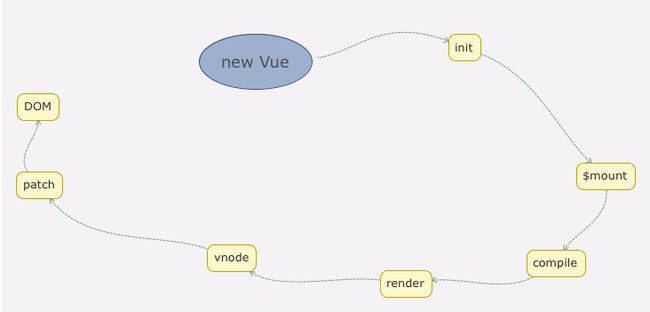
最后盗一张图看一下整个流程
你可能感兴趣的:(Vue源码阅读(一))