一、下载和测试模型
1. 下载YOLO-v3
git clone https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3.git
这是在Ubuntu里的命令,windows直接去 https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3下载、解压。得到一个 keras-yolo3-master 文件夹
2. 下载权重
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
去 https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights 下载权重。将 yolov3.weights 放入 keras-yolo3-master 文件夹
3. 生成 h5 文件
python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo.h5
执行convert.py文件,这是将darknet的yolo转换为用于keras的h5文件,生成的h5被保存在model_data下。命令中的 convert.py 和 yolo.cfg 已经在keras-yolo3-master 文件夹下,不需要单独下载。
4. 用已经被训练好的yolo.h5进行图片识别测试
python yolo_video.py --image
执行后会让你输入一张图片的路径,由于我准备的图片放在与yolo_video.py同级目录,所以直接输入图片名称,不需要加路径
这就表明测试成功了。
二、制作自己的VOC数据集
参考我原来写的博客:
在Ubuntu内制作自己的VOC数据集
我是在Ubuntu内标注然后移到Windows的,如果在Windows里安装了LabelImg,可以直接在Windows下标注。
最后文件布局为:
三、修改配置文件、执行训练
1. 复制 voc_annotation.py 到voc文件夹下,修改 voc_annotation.py 分类。如下图:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET from os import getcwd sets=[('2018', 'train'), ('2018', 'val'), ('2018', 'test'), ('2018', 'trainval')] classes = [] def convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file): in_file = open('VOCdevkit\VOC%s\Annotations\%s.xml'%(year, image_id), encoding = 'utf-8') tree=ET.parse(in_file) root = tree.getroot() for obj in root.iter('object'): difficult = obj.find('difficult').text cls = obj.find('name').text if cls not in classes or int(difficult)==1: continue cls_id = classes.index(cls) xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox') b = (int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text)) list_file.write(" " + ",".join([str(a) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id)) wd = getcwd() for year, image_set in sets: image_ids = open('VOCdevkit\VOC%s\ImageSets\Main\%s.txt'%(year, image_set)).read().strip().split() list_file = open('%s_%s.txt'%(year, image_set), 'w') for image_id in image_ids: list_file.write('%s\VOCdevkit\VOC%s\JPEGImages\%s.jpg'%(wd, year, image_id)) convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file) list_file.write('\n') list_file.close()
网上都是 train、val、test、三个文件。但我觉得还应该加一个 trainval。还有将所有的 / 改为 \ (Windows下路径表示和linux下不同)。高亮部分是为了防止Windows读取错误(博主就恰好碰到了)
2. 在model_data文件夹下新建一个 my_classes.txt(可以根据你的数据来,比如你检测是花的种类,可以叫 flower.txt。起名最好有意义),将你的类别写入,一行一个。
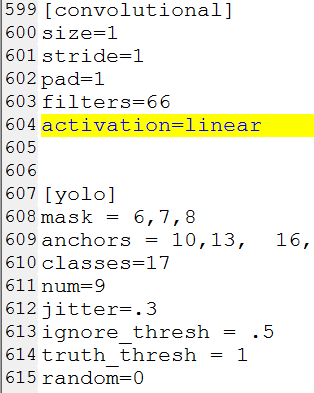
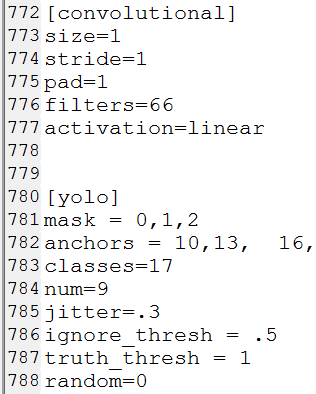
3. 修改yolov3.cfg 文件
使用迁移学习思想,用已经预训练好的权重接着训练。需要下面的修改步骤:
IDE里直接打开cfg文件,ctrl+f搜 yolo, 总共会搜出3个含有yolo的地方。
每个地方都要修改3处,
filter :3*(5+len(classes))
classes:len(classes) 我的类别是17
random:原来是1,显存小改为0
重新生成h5文件
python convert.py -w yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo_weights.h5
4. 训练
执行下面的train.py
python train.py
""" Retrain the YOLO model for your own dataset. """ import numpy as np import keras.backend as K from keras.layers import Input, Lambda from keras.models import Model from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping from yolo3.model import preprocess_true_boxes, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body, yolo_loss from yolo3.utils import get_random_data def _main(): annotation_path = 'voc/2018_trainval.txt' log_dir = 'model_data/logs/' classes_path = 'model_data/my_classes.txt' anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt' class_names = get_classes(classes_path) anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path) input_shape = (416,416) # multiple of 32, hw model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, len(class_names) ) train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, len(class_names), log_dir=log_dir) def train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, num_classes, log_dir='logs/'): model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss={ 'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}) logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir) checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(log_dir + "ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5", monitor='val_loss', save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, period=1) batch_size = 10 val_split = 0.2 with open(annotation_path) as f: lines = f.readlines() np.random.shuffle(lines) num_val = int(len(lines)*val_split) num_train = len(lines) - num_val print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size)) model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrap(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes), steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size), validation_data=data_generator_wrap(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes), validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size), epochs=20, initial_epoch=0) model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights.h5') def get_classes(classes_path): with open(classes_path) as f: class_names = f.readlines() class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names] return class_names def get_anchors(anchors_path): with open(anchors_path) as f: anchors = f.readline() anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')] return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2) def create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=False, freeze_body=False, weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5'): K.clear_session() # get a new session image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3)) h, w = input_shape num_anchors = len(anchors) y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], \ num_anchors//3, num_classes+5)) for l in range(3)] model_body = yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//3, num_classes) print('Create YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes)) if load_pretrained: model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True) print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path)) if freeze_body: # Do not freeze 3 output layers. num = len(model_body.layers)-3 for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers))) model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss', arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})( [*model_body.output, *y_true]) model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss) return model def data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes): n = len(annotation_lines) np.random.shuffle(annotation_lines) i = 0 while True: image_data = [] box_data = [] for b in range(batch_size): i %= n image, box = get_random_data(annotation_lines[i], input_shape, random=True) image_data.append(image) box_data.append(box) i += 1 image_data = np.array(image_data) box_data = np.array(box_data) y_true = preprocess_true_boxes(box_data, input_shape, anchors, num_classes) yield [image_data, *y_true], np.zeros(batch_size) def data_generator_wrap(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes): n = len(annotation_lines) if n==0 or batch_size<=0: return None return data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes) if __name__ == '__main__': _main()
代码标红的地方,需要根据自己实际情况进行修改。
其他可以设置的参数
batch_size = 32:默认值比较大,对电脑性能有要求。可以调小。我设置的是10
val_split = 0.1 : 这个表示,验证集占训练集的比例。建议划分大点。不然验证集的图片会很少。不利于验证集loss的计算
epochs = 100,可以调小一点。我设置的是20
参考地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37857151/article/details/81330699
https://blog.csdn.net/mingqi1996/article/details/83343289