C#集合--ICollection接口和IList接口
虽然列举接口提供了一个协议,用于向前的方式遍历集合,但它们没有提供一种机制来确定集合的大小,通过索引访问集合的成员,搜索集合,或修改集合。为了实现这些功能,.NET Framework定义了ICollection,IList和IDictionary接口。每个接口都有Generic的接口和非Generic的接口,请注意非Generic多数用于支持遗留代码。
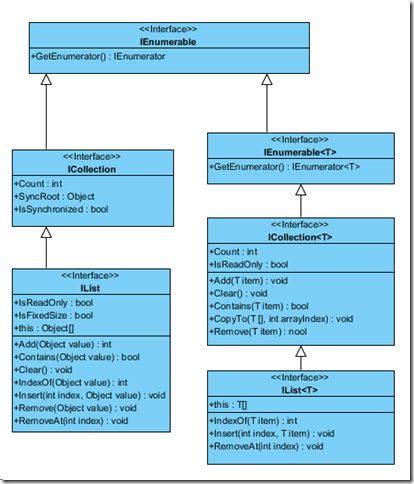
这些接口的继承挂关系如下图所示:
Generic的接口和非Generic的接口之间的差距超出了你的预期,特别是ICollection和ICollection<T>。这是由于历史原因造成的,因为Generic类型是C# 2.0才引入的,所以Generic吸取了非Generic接口的经验和教训,从而设计了与之不同的但更优秀的接口。正式由于这个原因,ICollection<T>并没有派生自ICollection,同样地,IList<T>也没有派生自IList, IDictionary<TKey,TValue>也没有派生自IDinctionary。因此集合类可以同时实现Generic的接口和非Generic的接口。(事实上,集合类一般都实现了两个类型接口,比如class Collection<T>: IList<T>, IList,有比如List<T> : IList<T>, System.Collections.IList)。
ICollection<T>和ICollection
ICollection<T>是可以统计集合中对象的标准接口。该接口可以确定集合的大小(Count),集合是否包含某个元素(Contains),复制集合到另外一个数组(ToArray),集合是否是只读的(IsReadOnly)。如果一个集合是可编辑的,那么可以调用Add,Remove和Clear方法操作集合中的元素。因为该接口继承IEnumerable<T>,所以可以使用foreach语句遍历集合。该接口的定义如下
public interface ICollection<T> : IEnumerable<T> { // Number of items in the collections. int Count { get; } bool IsReadOnly { get; } void Add(T item); void Clear(); bool Contains(T item); // CopyTo copies a collection into an Array, starting at a particular // index into the array. // void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex); //void CopyTo(int sourceIndex, T[] destinationArray, int destinationIndex, int count); bool Remove(T item); }
而非Generic的ICollection定义如下:
public interface ICollection : IEnumerable { void CopyTo(Array array, int index); int Count { get; } Object SyncRoot { get; } bool IsSynchronized { get; } }
与ICollection<T>相比较,ICollection实现了计算集合元素数目的功能,但明没有提供更改集合的功能。此外,ICollection还提供了同步的功能。而ICollection<T>则取消了同步的功能,这是因为对于Generic的集合,它们本身是线程安全的。
这两个接口既简单又容易实现。假如要实现一个只读的ICollection<T>,那么在Add,Remove,和Clear方法中抛出异常即可。
这些接口通常与任何IList或IDictionary接口中的任意一个一起实现。
IList<T>和IList
如果想通过位置获取集合元素,那么IList<T>就是此类集合的标准接口。此外,由于IList<T>继承了ICollection<T>和IEnumerable<T>,所以此接口还提供了根据位置读取或写入元素,或者在指定的位置插入或删除元素。IList<T>定义如下
public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T> { T this[int index] { get; set; } int IndexOf(T item); void Insert(int index, T item); void RemoveAt(int index); }
IndexOf方法在集合上执行线性搜索,如果没有发现指定元素,那么返回-1。
List类的IndexOf方法的实现:(List.IndexOf(T item)调用Array.IndexOf(_items, item, index, _size - index),然后调用EqualityComparer<T>.Default.IndexOf(array, value, startIndex, count))
internal virtual int IndexOf(T[] array, T value, int startIndex, int count) { int endIndex = startIndex + count; for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) { if (Equals(array[i], value)) return i; } return -1; }
而非Generic的IList则包含了更多成员,因为它继承ICollection
public interface IList : ICollection { Object this[int index] { get;set; } int Add(Object value); bool Contains(Object value); void Clear(); bool IsReadOnly { get; } bool IsFixedSize { get; } int IndexOf(Object value); void Insert(int index, Object value); void Remove(Object value); void RemoveAt(int index); }
IList接口的Add方法返回一个整数,这是加到集合中元素的位置。而IList<T>接口的Add方法返回值为空。
C#中,List<T>就是典型的既实现了IList<T>又实现了IList的类。
public class List<T> : IList<T>, System.Collections.IList, IReadOnlyList<T>
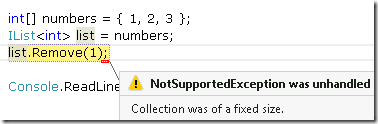
C#数组也实现了generic和非generic的IList接口。C#中Array类的部分代码(实现IList接口的代码)
public abstract class Array : ICloneable, IList, IStructuralComparable, IStructuralEquatable { ...... public bool IsReadOnly { get { return false; } } public bool IsFixedSize { get { return true; } } Object IList.this[int index] { get { return GetValue(index); } set { SetValue(value, index); } } int IList.Add(Object value) { throw new NotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_FixedSizeCollection")); } bool IList.Contains(Object value) { return Array.IndexOf(this, value) >= this.GetLowerBound(0); } void IList.Clear() { Array.Clear(this, this.GetLowerBound(0), this.Length); } int IList.IndexOf(Object value) { return Array.IndexOf(this, value); } void IList.Insert(int index, Object value) { throw new NotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_FixedSizeCollection")); } void IList.Remove(Object value) { throw new NotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_FixedSizeCollection")); } void IList.RemoveAt(int index) { throw new NotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_FixedSizeCollection")); } ...... }
而Generic的IList<T>是在sealed class SZArrayHelper中实现的。SZ(Single dimensional, Zero-based)。请注意,如果你在技术与上调用add或者remove方法,那么会返回NotSupportedException异常
IReadonlyList<T>
为了与Windows运行时的制度集合互操作,Framework4.5引入了一个新的集合接口IReadOnlyList<T>。该接口自身就非常有用,也可以看作IList的缩减版,对外只公开用于只读的操作。其定义如下:
public interface IReadOnlyCollection<out T> : IEnumerable<T> { int Count { get; } } public interface IReadOnlyList<out T> : IReadOnlyCollection<T> { T this[int index] { get; } }
因为类型参数仅仅用于输出位置,所以其标记为协变(covariant)。比如,一个cats列表,可以看作一个animals的只读列表。相反,在IList<T>中,T没有标记为协变,因为T应用于输入和输出位置。
你可能认为IList<T>派生自IReadonlyList<T>,然后,微软并没有这么做,这是因为这么做就要求把IList<T>的成员移动到IReadonlyList<T>,这就给CLR4.5带来重的变化(程序员需要重新编辑程序以避免运行时错误)。实际上,微软在IList<T>的实现类中手动地添加了对IReadonlyList<T>接口的实现。
在Windows运行时中IVectorView<T>与.NET Framework的IReadonlyList<T>相对应。
参考
线性搜索(Linear Search): http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_search; http://blog.teamleadnet.com/2012/02/quicksort-binary-search-and-linear.html
数组实现IList<T>: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11163297/how-do-arrays-in-c-sharp-partially-implement-ilistt/11164210#11164210
数组的奥秘: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19914523/mystery-behind-system-array