A chatroom for all! Part 1 - Introduction to Node.js(转发)
项目组用到了 Node.js,发现下面这篇文章不错。转发一下。原文地址:《原文》。
-------------------------------------------
A chatroom for all! Part 1 - Introduction to Node.js
4 Sep 2014 11:00 AM
This node.js tutorial series will help you build a node.js powered real-time chatroom web app fully deployed in the cloud. You are expected to know HTML5 and JavaScript. Throughout the series, you will learn how to setup node.js on your Windows machine, how to develop a web frontend with express, how to deploy a node express apps to Azure, how to use socketio to add a real-time layer and how to deploy it all together.
Level: Beginner to Intermediate.
Part 1 - Introduction to Node.js
Part 2 - Welcome to Express with Node.js and Azure
Part 3 - Building a Backend with Node, Mongo and Socket.IO
Part 4 – Building a Chatroom UI with Bootstrap
Part 5 - Connecting the Chatroom with WebSockets
Part 6 – The Finale and Debugging Remote Node Apps
Part 1 - Introduction to Node.js
Welcome to Part 1 of the Node.js Tutorial Series: A chatroom for all! In this part, I will explain what node.js is, why you should pay attention to node.js and how to setup your machine.
What is node? Why node?
Node.js is a runtime environment and library for running JavaScript applications outside the browser. Node.js is mostly used to run real-time server applications and shines through its performance using non-blocking I/O and asynchronous events. A complete web ecosystem has been built around node.js with several web app frameworks and protocol implementations available for usage. It’s definitely one of the easiest and fastest way to develop real-time applications on the web today.
Why use node? One word answer: JavaScript. JavaScript is an extremely popular language and is credited with being one of the driving forces that turned the web into the dynamic wonderland that it is today. What you can do in a browser nowadays, rivals all others!
JavaScript arose on the frontend but - thanks to the V8 JavaScript engine and the work of Ryan Dahl - you can now run networked JavaScript applications outside of the browser precisely to build web apps. Node.js lets you unify the programming language used by your app - no longer do you need a different language for your backend, you can use JavaScript throughout. If your background is in building and design websites and web app frontends in HTML, CSS and JavaScript, you don’t need to pick up another language to develop complex data-driven back-ends for your apps.
Node.js plays a critical role in the advancement of WebSockets as a method for real-time communication between the front and back ends. The use of WebSockets and the libraries building on that protocol such as Socket.IO have really pushed what is expected of web applications and lets us developers explore new ways to create the web.
Setting up node.js on Windows 8
To get started, you will need a reasonably up to date machine, I will be showing you how to install Node.js on Windows 8.1.
Firstly, you will need to download and install the node.js runtime. You can download the current version 0.10.30 (as of this writing) here: http://nodejs.org/download/. Choosing the Windows Installer is one of the easiest ways to get started.
Alternatively, if you are a fan of Chocolatey, the package manager for Windows, you can install node by running:
choco install nodejs.install
You should double check that the node executable has been added to your PATH system environment variable. Watch this video, if you want to see how to change your environment variables on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1. You will want to make sure the following folder has been added to the PATH variable:
C:\Program Files (x86)\nodejs\
If you go to your Command Prompt and type in node –h, you should see the help documentation for the node executable displayed.
Along with Node.js, NPM, the system used to manage node packages, should be installed and available on the Command Prompt as well. Simply type in npm –h, you should see the help documentation for NPM displayed.
If you encounter an error similar to this one:
Error: ENOENT, stat 'C:\Users\someuser\AppData\Roaming\npm'
The resolution is to create a folder at the path specified above, as shown in this StackOverflow question. This is only an issue in the latest node.js installer and should be resolved by next release. You can create the folder like so:
mkdir -r C:\Users\someuser\AppData\Roaming\npm
Why use Visual Studio 2013? Node Tools for Visual Studio!
With Node.js installed, it’s time to select a development tool. Of course, you are free to use any editing tool you want but why use a glorified notepad when you can experience the full power of enterprise-grade integrated development environments like Visual Studio. You get it for free to boot!
Now what’s cool about Node Tools for Visual Studio is that is adds Node.js support for editing, Intellisense, performance profiling, npm, TypeScript, Debugging locally and remotely (including on Windows/MacOS/Linux), as well Azure Web Sites and Cloud Service.
Throughout these tutorials, I will be using Visual Studio 2013 to develop, debug and deploy the chat engine, you are welcome to use any development tool you wish. If you want to use Visual Studio, You can download any of the following editions of Visual Studio and then install the free Node Tools for Visual Studio.
· [THIS ONE IS FREE] Visual Studio 2013 Express for Web (requires Update 2). Download here.
· Visual Studio 2013 Pro or higher (requires Update 2)
· Visual Studio 2012 Pro or higher (requires Update 4)
Don’t forget to install the free Node Tools for Visual Studio.
Starting a new node.js project in Visual Studio
Note: Screenshots show Visual Studio 2013 Ultimate.
Starting a new node.js project is fairly straight forward.
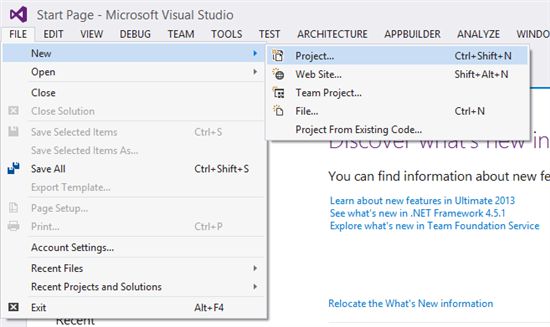
1. You want to boot Visual Studio and go to the File > New > Project menu item.
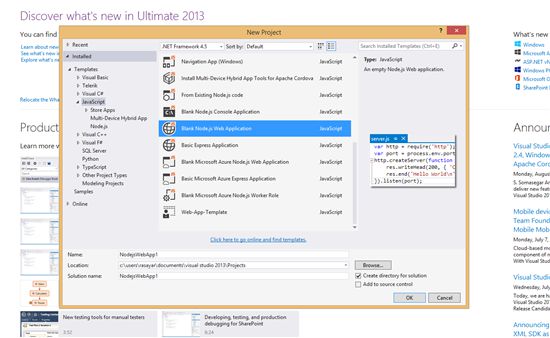
2. You will want to go to Installed > Templates > JavaScript menu item on the left and select Blank Node.js Web Application on the right. Choose a location and name for your project and press OK.
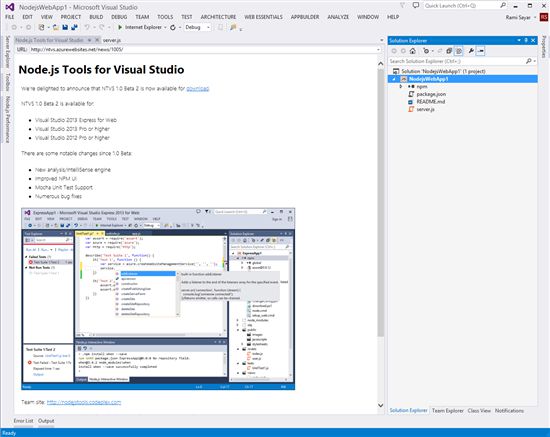
3. You will be presented with the following screen, feel free to explore Visual Studio at this point. You will want to open the generated server.js file in the Solution Explorer (on the right typically but may be located elsewhere on your screen.)
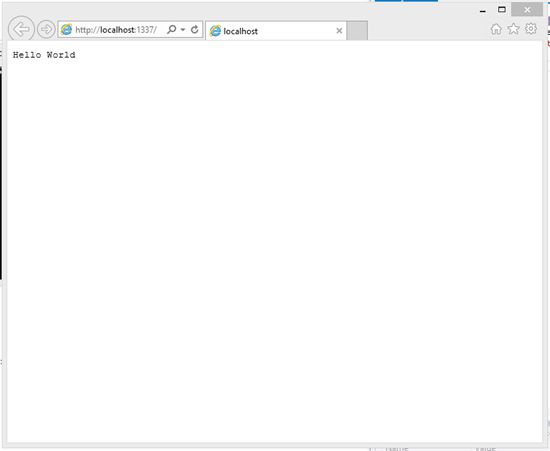
4. You can now debug your node web application in your preferred browser.
Hello World in Node.js
As is typical in other languages, the generated code example shows you how to output “Hello World” in the browser. Let me explain how the generated code in server.js works line by line. *Note: As stated in this tutorial series description, I am assuming you have a knowledge of JavaScript, HTML5 and how HTTP/the Internet work.
Line 1
var http = require('http');
Node.js has a simple module and dependencies loading system. You simply call the function “require” with the path of the file or directory containing the module you would like to load at which point a variable is returned containing all the exported functions of that module.
Line 2
var port = process.env.port || 1337;
On this line, we want to determine on which port the HTTP server serving the HTML should run. If a port number is specified in the environment variables, we will use that one or we will simply use 1337.
Line 3
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
We want to create a server to handle HTTP requests. We will also pass the createServer function a function callback containing two parameters to a handle each individual request and return a response. Take a look at Michael Vollmer’sarticle if you’ve never encountered callback functions in JavaScript. The request received is passed in the req parameter and the response is expected to written to the res parameter.
Line 4
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
Any HTTP response requires a status-line and headers, to learn more about HTTP headers and how they work check out this article. In this case, we want to return 200 OK as the status response and to specify the content-type as plain text. We specify this by calling the writeHead function on the response object.
Line 5
res.end('Hello World\n');
Once we are done writing the response we want to call the end function. We can also pass the final content through the end function, in this case we want to send the string “Hello World” in plain text.
Line 6
}).listen(port);
We close off the callback and call the function listen at the port we defined earlier, this will start the server and start accepting requests sent to the defined port.
To see the result, you can start debugging by pressing on the button shown in the previous screenshot. You can see “Hello World” in the browser.
Voila! You have now successfully run a node.js app on Windows 8.1 using Visual Studio 2013.
Stay Tuned!
Stay tuned for Part 2 – How to Deploy Your Hello World into the Cloud to be released in the next week. You can stay up to date by following my twitter account @ramisayar.