Linux设备驱动剖析之IIC(一)
写在前面
由于IIC总线只需要两根线就可以完成读写操作,而且通信协议简单,一条总线上可以挂载多个设备,因此被广泛使用。但是IIC总线有一个缺点,就是传输速率比较低。本文基于Linux-2.6.36版本,说说IIC子系统在Linux中的实现。
借用某书上的IIC子系统的体系结构图:
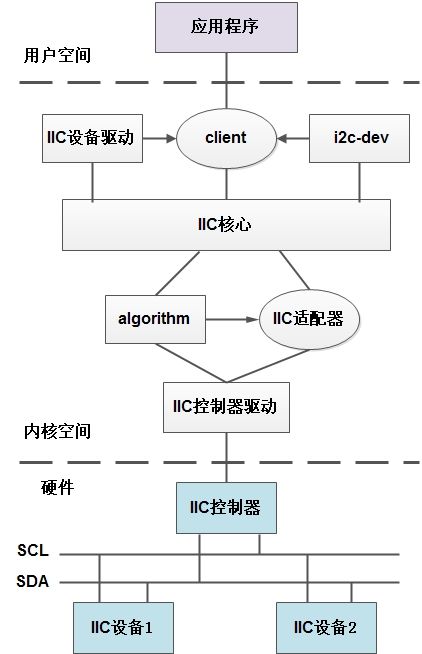
Linux IIC子系统体系结构
下面开始分析IIC子系统。
IIC子系统的初始化在drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c文件中的i2c_init函数中:
00001221 static int __init i2c_init(void) 00001222 { 00001223 int retval; 00001224 00001225 retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type); 00001226 if (retval) 00001227 return retval; 00001228 #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT 00001229 i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register("i2c-adapter"); 00001230 if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) { 00001231 retval = -ENOMEM; 00001232 goto bus_err; 00001233 } 00001234 #endif 00001235 retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver); 00001236 if (retval) 00001237 goto class_err; 00001238 return 0; 00001239 00001240 class_err: 00001241 #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT 00001242 class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class); 00001243 bus_err: 00001244 #endif 00001245 bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type); 00001246 return retval; 00001247 }
1225行,向系统注册IIC总线,其中i2c_bus_type的定义为:
00000343 struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = { 00000344 .name = "i2c", 00000345 .match = i2c_device_match, 00000346 .probe = i2c_device_probe, 00000347 .remove = i2c_device_remove, 00000348 .shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown, 00000349 .pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops, 00000350 };
345行,i2c_device_match函数时用来匹配IIC总线上的设备和设备驱动的,下面看下它的定义:
00000068 static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) 00000069 { 00000070 struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev); 00000071 struct i2c_driver *driver; 00000072 00000073 if (!client) 00000074 return 0; 00000075 00000076 /* Attempt an OF style match */ 00000077 if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv)) 00000078 return 1; 00000079 00000080 driver = to_i2c_driver(drv); 00000081 /* match on an id table if there is one */ 00000082 if (driver->id_table) 00000083 return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL; 00000084 00000085 return 0; 00000086 }
在IIC子系统中,用struct i2c_client来描述一个具体的IIC设备(IIC从机)。73行,如果没有IIC设备的话就直接返回0,表示匹配不成功。
77行,用of的方式进行匹配,应该是设备树方面的,具体没了解过。
82行,如果驱动的id table存在则调用83行的i2c_match_id函数进行匹配:
00000057 static const struct i2c_device_id *i2c_match_id(const struct i2c_device_id *id, 00000058 const struct i2c_client *client) 00000059 { 00000060 while (id->name[0]) { 00000061 if (strcmp(client->name, id->name) == 0) 00000062 return id; 00000063 id++; 00000064 } 00000065 return NULL; 00000066 }
很简单,就是拿驱动的id table中的每一项与i2c_client的name成员进行比较,如果它们的名字相同就表示匹配成功,否则匹配失败,返回NULL。从这里也可以看出IIC的总线匹配方式与platform总线的匹配方式是不一样,一般情况下,IIC总线的匹配方式是根据设备名字和驱动中的id table,而platfrom总线的匹配方式是根据设备名字和驱动名字。下面看i2c_device_probe函数:
00000106 static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev) 00000107 { 00000108 struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev); 00000109 struct i2c_driver *driver; 00000110 int status; 00000111 00000112 if (!client) 00000113 return 0; 00000114 00000115 driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver); 00000116 if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table) 00000117 return -ENODEV; 00000118 client->driver = driver; 00000119 if (!device_can_wakeup(&client->dev)) 00000120 device_init_wakeup(&client->dev, 00000121 client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_WAKE); 00000122 dev_dbg(dev, "probe\n"); 00000123 00000124 status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client)); 00000125 if (status) { 00000126 client->driver = NULL; 00000127 i2c_set_clientdata(client, NULL); 00000128 } 00000129 return status; 00000130 }
112行,检查IIC设备是否存在。
119至121行,电源管理方面的,IIC在电源管理方面做得还是不错的,有兴趣可以看一下。
124行,重要,调用IIC设备驱动中probe函数。
下面以tiny6410为具体平台去说IIC子系统的其他内容。S3c6410的IIC控制器驱动位于drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c文件中,首先看初始化函数:
00001009 static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = { 00001010 .probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe, 00001011 .remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove, 00001012 .id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids, 00001013 .driver = { 00001014 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 00001015 .name = "s3c-i2c", 00001016 .pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS, 00001017 }, 00001018 }; 00001019 00001020 static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void) 00001021 { 00001022 return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver); 00001023 } 00001024 subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_s3c_init);
1022行,注册平台驱动,看下s3c24xx_i2c_driver的定义可以发现.driver.name的值与板文件中定义的platform device的name不一样,所以这里采用的是id table方式进行匹配。我们知道,当此驱动与设备匹配后,驱动中的probe函数将会被调用,那么下面看probe函数的定义:
00000790 static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) 00000791 { 00000792 struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c; 00000793 struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata; 00000794 struct resource *res; 00000795 int ret; 00000796 00000797 pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; 00000798 if (!pdata) { 00000799 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no platform data\n"); 00000800 return -EINVAL; 00000801 } 00000802 00000803 i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c24xx_i2c), GFP_KERNEL); 00000804 if (!i2c) { 00000805 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no memory for state\n"); 00000806 return -ENOMEM; 00000807 } 00000808 00000809 strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name)); 00000810 i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE; 00000811 i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm; 00000812 i2c->adap.retries = 2; 00000813 i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD; 00000814 i2c->tx_setup = 50; 00000815 00000816 spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock); 00000817 init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait); 00000818 00000819 /* find the clock and enable it */ 00000820 00000821 i2c->dev = &pdev->dev; 00000822 i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c"); 00000823 if (IS_ERR(i2c->clk)) { 00000824 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot get clock\n"); 00000825 ret = -ENOENT; 00000826 goto err_noclk; 00000827 } 00000828 00000829 dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "clock source %p\n", i2c->clk); 00000830 00000831 clk_enable(i2c->clk); 00000832 00000833 /* map the registers */ 00000834 00000835 res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); 00000836 if (res == NULL) { 00000837 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IO resource\n"); 00000838 ret = -ENOENT; 00000839 goto err_clk; 00000840 } 00000841 00000842 i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, resource_size(res), 00000843 pdev->name); 00000844 00000845 if (i2c->ioarea == NULL) { 00000846 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot request IO\n"); 00000847 ret = -ENXIO; 00000848 goto err_clk; 00000849 } 00000850 00000851 i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, resource_size(res)); 00000852 00000853 if (i2c->regs == NULL) { 00000854 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot map IO\n"); 00000855 ret = -ENXIO; 00000856 goto err_ioarea; 00000857 } 00000858 00000859 dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "registers %p (%p, %p)\n", 00000860 i2c->regs, i2c->ioarea, res); 00000861 00000862 /* setup info block for the i2c core */ 00000863 00000864 i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c; 00000865 i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev; 00000866 00000867 /* initialise the i2c controller */ 00000868 00000869 ret = s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c); 00000870 if (ret != 0) 00000871 goto err_iomap; 00000872 00000873 /* find the IRQ for this unit (note, this relies on the init call to 00000874 * ensure no current IRQs pending 00000875 */ 00000876 00000877 i2c->irq = ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); 00000878 if (ret <= 0) { 00000879 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IRQ\n"); 00000880 goto err_iomap; 00000881 } 00000882 00000883 ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED, 00000884 dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c); 00000885 00000886 if (ret != 0) { 00000887 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot claim IRQ %d\n", i2c->irq); 00000888 goto err_iomap; 00000889 } 00000890 00000891 ret = s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(i2c); 00000892 if (ret < 0) { 00000893 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register cpufreq notifier\n"); 00000894 goto err_irq; 00000895 } 00000896 00000897 /* Note, previous versions of the driver used i2c_add_adapter() 00000898 * to add the bus at any number. We now pass the bus number via 00000899 * the platform data, so if unset it will now default to always 00000900 * being bus 0. 00000901 */ 00000902 00000903 i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num; 00000904 00000905 ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap); 00000906 if (ret < 0) { 00000907 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add bus to i2c core\n"); 00000908 goto err_cpufreq; 00000909 } 00000910 00000911 platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c); 00000912 00000913 dev_info(&pdev->dev, "%s: S3C I2C adapter\n", dev_name(&i2c->adap.dev)); 00000914 return 0; 00000915 00000916 err_cpufreq: 00000917 s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c); 00000918 00000919 err_irq: 00000920 free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c); 00000921 00000922 err_iomap: 00000923 iounmap(i2c->regs); 00000924 00000925 err_ioarea: 00000926 release_resource(i2c->ioarea); 00000927 kfree(i2c->ioarea); 00000928 00000929 err_clk: 00000930 clk_disable(i2c->clk); 00000931 clk_put(i2c->clk); 00000932 00000933 err_noclk: 00000934 kfree(i2c); 00000935 return ret; 00000936 }
797至801行,没有平台数据是不行的。
803至807行,为具体平台的IIC控制器数据结构申请内存,一般来说,不仅是IIC控制器,每一个控制器都会有一个结构体来描述。struct s3c24xx_i2c的定义也是在drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c中:
00000060 struct s3c24xx_i2c { 00000061 spinlock_t lock; 00000062 wait_queue_head_t wait; 00000063 unsigned int suspended:1; 00000064 00000065 struct i2c_msg *msg; 00000066 unsigned int msg_num; 00000067 unsigned int msg_idx; 00000068 unsigned int msg_ptr; 00000069 00000070 unsigned int tx_setup; 00000071 unsigned int irq; 00000072 00000073 enum s3c24xx_i2c_state state; 00000074 unsigned long clkrate; 00000075 00000076 void __iomem *regs; 00000077 struct clk *clk; 00000078 struct device *dev; 00000079 struct resource *ioarea; 00000080 struct i2c_adapter adap; 00000081 00000082 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ 00000083 struct notifier_block freq_transition; 00000084 #endif 00000085 };
63行,表示IIC控制器是否已经挂起,挂起的话就不能操作IIC控制器了。
65行,struct i2c_msg用来描述一次读写操作包含的信息。定义在include/linux/i2c.h,比较简单:
00000507 struct i2c_msg { 00000508 __u16 addr; /* slave address */ 00000509 __u16 flags; 00000510 #define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */ 00000511 #define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */ 00000512 #define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ 00000513 #define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ 00000514 #define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ 00000515 #define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ 00000516 #define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */ 00000517 __u16 len; /* msg length */ 00000518 __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */ 00000519 };
508行,IIC从机的地址。
509行,flags的取值就是510至516行这些值。
517行,这次读写操作的数据长度。518行,读写数据的地址。
回到struct s3c24xx_i2c,66行,message的数量。67行,当前是第几个message。68行,缓冲区数组成员的索引值,表示当前要读写的是第几个数据。
70行,当数据写入IIC控制器的数据移位寄存器后需要延时多久,在s3c6410里的单位是ns。
71行,IIC控制器使用的中断号。
73行,IIC控制器的状态,具体来说有以下几种状态:
00000047 enum s3c24xx_i2c_state { 00000048 STATE_IDLE, 00000049 STATE_START, 00000050 STATE_READ, 00000051 STATE_WRITE, 00000052 STATE_STOP 00000053 };
74行,IIC总线的速率。76行,IIC控制器寄存器起始地址。
77行,IIC控制器时钟。78行,设备模型相关的。79行,IO口资源。
80行,每一个IIC控制器对应一个adapter。struct i2c_adapter同样是在include/linux/i2c.h中定义:
00000354 struct i2c_adapter { 00000355 struct module *owner; 00000356 unsigned int id; 00000357 unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */ 00000358 const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */ 00000359 void *algo_data; 00000360 00000361 /* data fields that are valid for all devices */ 00000362 struct rt_mutex bus_lock; 00000363 00000364 int timeout; /* in jiffies */ 00000365 int retries; 00000366 struct device dev; /* the adapter device */ 00000367 00000368 int nr; 00000369 char name[48]; 00000370 struct completion dev_released; 00000371 00000372 struct mutex userspace_clients_lock; 00000373 struct list_head userspace_clients; 00000374 };
355行,模块的所有者。
356行,此适配器的编号,第1个适配器的编号为0,以此类推。
358行,算法?第一眼看到的时候差点被吓倒了,其实就是定义了3个函数指针,这些函数来完成具体的读写操作。
364行,超时时间。365行,重试次数,一次读写操作不成功的话就多试几次。368行,适配器编号。369行,适配器的名字。
回到s3c24xx_i2c_probe函数,809行,设置适配器的名字。
811行,s3c6410的IIC控制器进行读写操作时所使用的逻辑,等碰到时再详细说吧。
813行,刚才在说struct i2c_adapter时被忽略的成员class就是在这里被赋值的。
814行,对于s3c6410的IIC控制器而言,数据被写入移位寄存器后需要延时50ns。
822至831行,获取IIC时钟并使能。
835至857行,获取IO口资源并进行映射。
869行,设置相应的IO口为IIC功能,并设置IICADD寄存器和IICCON寄存器。
877至889行,申请IIC中断,中断处理函数为s3c24xx_i2c_irq,后面会遇到,到时再说。
891至895行,CPU频率相关的,略过吧。
905行,“重头戏”啊,注册IIC适配器和注册IIC设备等都发生在里面,i2c_add_numbered_adapter函数在drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c里定义:
00000948 int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap) 00000949 { 00000950 int id; 00000951 int status; 00000952 00000953 if (adap->nr & ~MAX_ID_MASK) 00000954 return -EINVAL; 00000955 00000956 retry: 00000957 if (idr_pre_get(&i2c_adapter_idr, GFP_KERNEL) == 0) 00000958 return -ENOMEM; 00000959 00000960 mutex_lock(&core_lock); 00000961 /* "above" here means "above or equal to", sigh; 00000962 * we need the "equal to" result to force the result 00000963 */ 00000964 status = idr_get_new_above(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap, adap->nr, &id); 00000965 if (status == 0 && id != adap->nr) { 00000966 status = -EBUSY; 00000967 idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, id); 00000968 } 00000969 mutex_unlock(&core_lock); 00000970 if (status == -EAGAIN) 00000971 goto retry; 00000972 00000973 if (status == 0) 00000974 status = i2c_register_adapter(adap); 00000975 return status; 00000976 }