唧唧堂:论文收录无上限!新冠病毒主题社科类论文导读专栏
导读单简介
唧唧堂COVID-19新冠病毒主题社科论文导读专栏,将集中收录发布所有唧唧堂解析导读的新冠病毒主题的经济学、金融学、社会学、心理学及其他社科类论文,同时或也将收录部分医学论文。
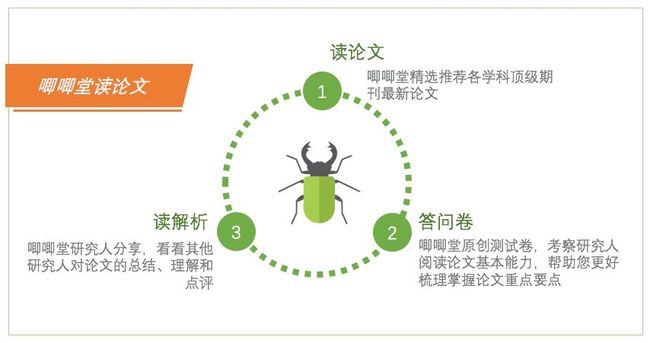
本专栏预测至少将收录50篇论文,现已有45篇NBER工作论文解析中。若导读论文为工作论文,则该条导读将包含论文原文及解析;若导读论文为发表于例如AER、JPE、JFE等顶级期刊的论文,则该条导读将包含原文、解析及测试卷。唧唧堂论文测试卷及解析均由唧唧堂原创,测试卷主要测试研究人阅读论文的基本能力,帮助研究人更快更好梳理掌握论文重点要点,解析为中文,是对该论文的客观总结和解读。读单收费只针对测试卷及解析,原文仅供分享。购买阅读单的小伙伴将可直接加入唧唧堂论文阅读微信群,克服拖延症,克服懒惰病,抱团读论文。
本专栏论文收录无截止时限,也就是说,唧唧堂将源源不断把所有发现的新冠病毒专题论文放入本专栏。随着收入论文增多,专栏订阅价格也将有所抬升,所以,越早订阅越合算哦!
希望研究人们热情关注订阅,支持唧唧堂产出更多好内容!同时我们也招募更多研究人加入写作小组,一起参与内容生产!
订阅专栏
原价50(暂定),预售特惠19.9
如何快速进入专栏/微信群
1、添加“小鹅知识助手” 服务号
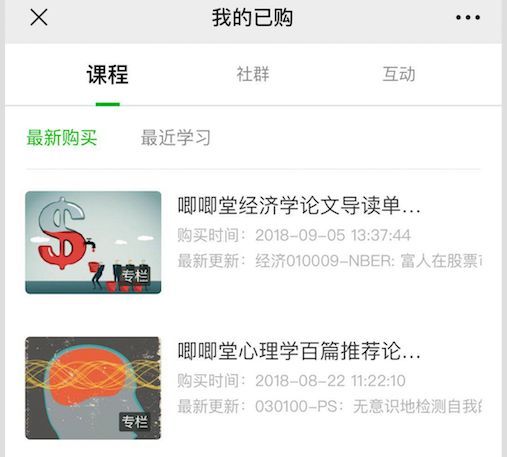
2、进入我的已购
3、导读单就在这里哦
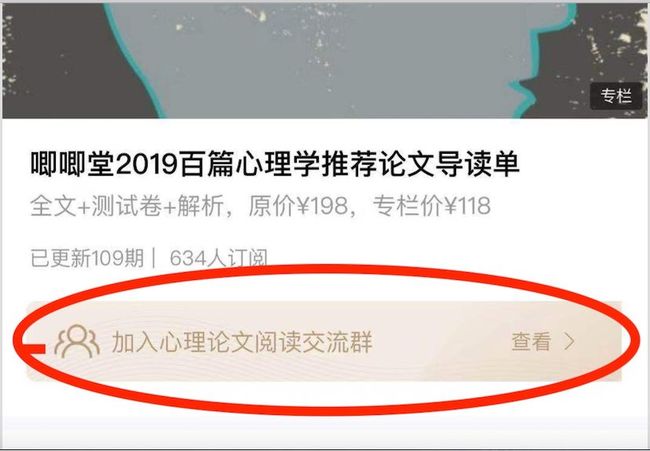
4、订阅后不要忘了加入阅读微信群哦!
专栏包含论文
已有30篇NBER工作论文解析中:
1) Estimating the COVID-19 Infection Rate: Anatomy of an Inference Problem / COVID-19感染率估计
2) The Subways Seeded the Massive Coronavirus Epidemic in New York City / 纽约地铁是大规模新冠病毒爆发的源头
3) Covid-19: Testing Inequality in New York City / 新冠病毒:在纽约市测试不平等
4) Labor Markets During the COVID-19 Crisis: A Preliminary View / COVID-19危机期间的劳动力市场:初步观点
5) Covid-19 Infection Externalities: Trading Off Lives vs. Livelihoods / Covid-19 感染外部性:与生计交易
6) Risk Perception Through the Lens of Politics in the Time of the COVID-19 Pandemic / 在COVID-19大流行时期,从政治视角感知风险
7) Policy Implications of Models of the Spread of Coronavirus: Perspectives and Opportunities for Economists / 冠状病毒传播模型的政策影响:经济学家的视角与机遇
8) Did California’s Shelter-in-Place Order Work? Early Coronavirus-Related Public Health Benefits / 加州的就地避难所秩序奏效了吗?早期冠状病毒相关公共卫生益处
9) The Geographic Spread of COVID-19 Correlates with Structure of Social Networks as Measured by Facebook / COVID-19 的地理分布与 Facebook 衡量的社交网络结构相关
10) How Are Small Businesses Adjusting to COVID-19? Early Evidence from a Survey / 小型企业如何适应 COVID-19?调查的早期证据
11) Covid19 and the Macroeconomic Effects of Costly Disasters / 新冠病毒与代价高昂的灾害的宏观经济影响
12) Optimal Mitigation Policies in a Pandemic: Social Distancing and Working from Home / 大流行中的最佳缓解政策:社交距离和在家工作
13) COVID-Induced Economic Uncertainty / 新冠病毒引起的经济不确定性
14) A Simple Planning Problem for COVID-19 Lockdown / 新冠病毒封城的简单规划问题
15) News that Takes Your Breath Away: Risk Perceptions During an Outbreak of Vaping-related Lung Injuries Firm-level Exposure to Epidemic Diseases: Covid-19, SARS, and H1N1 / 传染病的公司层面暴露:新冠病毒、非典和H1N1
16) How Deadly Is COVID-19? Understanding The Difficulties With Estimation Of Its Fatality Rate / COVID-19有多致命?了解其死亡率估计的困难
17) U.S. Economic Activity During the Early Weeks of the SARS-Cov-2 Outbreak / 在非典和新冠病毒疫情的最初几周美国的经济活动
18) Demographic Determinants of Testing Incidence and COVID-19 Infections in New York City Neighborhoods / 纽约市邻里检测发生率和COVID-19感染的人口决定因素
19) Polarization and Public Health: Partisan Differences in Social Distancing during the Coronavirus Pandemic / 两极分化与公共卫生:冠状病毒大流行期间社会疏远的党派差异
20) Aggregate and Firm-Level Stock Returns During Pandemics, in Real Time / 疫情大流行期间实时汇总和公司级股票回报
21) How Does Household Spending Respond to an Epidemic? Consumption During the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic / COVID-19前所未有的股票市场影响
22) How Many Jobs Can be Done at Home? / 家里能做多少工作?
23) The Impact of COVID-19 on Gender Equality / COVID-19对两性平等的影响
24) The Unprecedented Stock Market Impact of COVID-19 / COVID-19前所未有的股票市场影响
25) The Coronavirus Epidemic Curve is Already Flattening in New York City / 纽约市的冠状病毒流行曲线已经趋于平缓
26) Macroeconomic Implications of COVID-19: Can Negative Supply Shocks Cause Demand Shortages? / COVID-19的宏观经济影响:负供给冲击能否导致需求短缺?
27) Compliance with COVID-19 Social-Distancing Measures in Italy: The Role of Expectations and Duration / 意大利COVID-19社会分离措施的遵守:期望的作用和持续时间
28) Human Mobility Restrictions and the Spread of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China / 人口行动限制与新型冠状病毒在中国的传播
29) What Will Be the Economic Impact of COVID-19 in the US? Rough Estimates of Disease Scenarios / COVID-19在美国的经济影响是什么?疾病情景的粗略估计
30) "The Coronavirus and the Great Influenza Pandemic: Lessons from the “Spanish Flu” for the Coronavirus’s Potential Effects on Mortality and Economic Activity / 冠状病毒与大流行:从"西班牙流感"中吸取的冠状病毒对死亡率和经济活动的潜在影响的教训"
31)Health vs. Wealth? Public Health Policies and the Economy During Covid-19 / 健康与财富?Covid-19 期间的公共卫生政策与经济
32)When Do Shelter-in-Place Orders Fight COVID-19 Best? Policy Heterogeneity Across States and Adoption Time / 何时,就地避难所订单最能对抗 COVID-19?跨州的政策异质性和采用时间
33)Did COVID-19 Improve Air Quality Near Hubei? / COVID-19改善了湖北附近的空气质量吗?
34)Global Behaviors and Perceptions at the Onset of the COVID-19 Pandemic / COVID-19大流行爆发时的全球行为和看法
35)Sequential Lifting of COVID-19 Interventions with Population Heterogeneity / COVID-19 具有种群异质性的连续解除
36)Labor Demand in the Time of COVID-19: Evidence from Vacancy Postings and UI Claims / COVID-19 时代的劳动力需求:空缺职位和 UI 索赔的证据
37)Corporate Immunity to the COVID-19 Pandemic / 企业对COVID-19大流行的免疫力
38)Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions and Mortality in U.S. Cities during the Great Influenza Pandemic, 1918-1919
/ 1918-1919年流感大流行期间美国城市的非药物干预和死亡率
39)Macroeconomic Dynamics and Reallocation in an Epidemic / 流行病中的宏观经济动态与再分配
40)Health versus Wealth: On the Distributional Effects of Controlling a Pandemic / 健康与财富:控制大流行的分布效应
41)A Model of Asset Price Spirals and Aggregate Demand Amplification of a "Covid-19" Shock / 资产价格螺旋模型和总需求放大的"Covid-19" 冲击
42)Demographic Perspectives on Mortality of Covid-19 and Other Epidemics / Covid-19和其他流行病死亡率的人口视角
43)Voluntary and Mandatory Social Distancing: Evidence on COVID-19 Exposure Rates from Chinese Provinces and Selected Countries / 自愿和强制性社会分离:来自中国各省和选定国家的COVID-19暴露率的证据
44)Estimating the Fraction of Unreported Infections in Epidemics with a Known Epicenter: an Application to COVID-19 / 估计已知震中流行中未报告感染的分数:COVID-19 的应用
45) Tracking Public and Private Response to the COVID-19 Epidemic: Evidence from State and Local Government Actions / 追踪公共和私人对COVID-19疫情的反应:州和地方政府行动的证据