ECNUOJ 2150 完美的拯救
完美的拯救
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB
Total Submit:147 Accepted:50
Description
一只可怜的蚂蚁被万恶的魔术师困在了一个魔方上, 蚁后决定委派你去拯救这只可怜的蚂蚁, 你被空投在魔方上的某个位置,你需要在最短的时间内找到那只蚂蚁, 之后使用逃离卷轴返回蚁巢,你只能在格子线上行走,并且知道被困蚂蚁的位置,你需要出色的计算来完成这项艰巨的任务.
假设魔方是3x3x3个正方体小块组成,如下图所示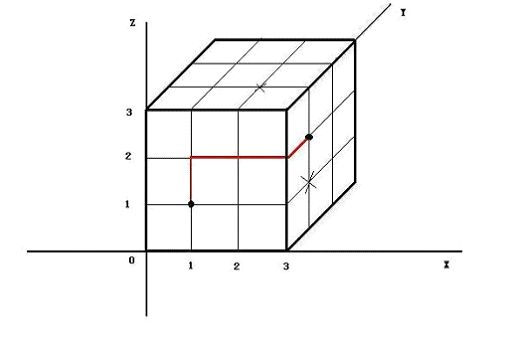
每面皆有4x4个格子道路可以行走.偶尔有些岔路点上有魔术师的魔兵把守,你不可以经过该岔路.现在以某个顶点为坐标原点建立空间坐标系,各个顶点坐标如上图所示. eg. 你被空投至(1,0,1),你要去(3,1,2), 并且(2,1,3)和(3,1,1)不可经过: 那么你可选择如下的四步路线:
(1,0,1) -> (1,0,2) -> (2,0,2) -> (3,0,2) -> (3,1,2),(也有别的选择)
Input
第一行有一个正整数N(1<=N<=500),表示测试数据的组数。
对于每组测试数据:
第一行有7个整数: D, x1 y1 z1 x2 y2 z2,分别是魔方的大小,你的当前坐标以及蚂蚁的坐标(也为出口坐标);(两点均在魔方表面上).
第二行有1个整数t,表示不可经过的岔路个数.接下来t行,每行有一个坐标,是不可经过的岔路的坐标.
( 3 <= D <= 10, 0<=t<=10)
Output
对于每组测试数据输出一个数,即最小步数,若不可到达则输出-1
Sample Input
2
3 1 0 1 3 1 2
2
2 1 3
3 1 1
4 0 1 1 1 4 1
0
Sample Output
4
4
Hint:
因为魔方是实体的,所以你只能在魔方的表面上行走.
Source
解题:无聊宽搜。。

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 struct Point { 4 int x,y,z; 5 int step; 6 } start,des; 7 int n; 8 bool vis[20][20][20]; 9 const int dir[6][3] = { 10 0,-1,0, 11 0,1,0, 12 -1,0,0, 13 1,0,0, 14 0,0,-1, 15 0,0,1 16 }; 17 queue<Point>q; 18 bool check(const Point &t) { 19 if(t.x < 0 || t.x > n || t.y < 0 || t.y > n || t.z < 0 || t.z > n) return false; 20 if(t.x > 0 && t.x < n && t.z > 0 && t.z < n && t.y > 0 && t.y < n) return false; 21 if(vis[t.x][t.y][t.z]) return false; 22 vis[t.x][t.y][t.z] = true; 23 return true; 24 } 25 int bfs() { 26 while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); 27 start.step = 0; 28 q.push(start); 29 Point np; 30 vis[start.x][start.y][start.z] = true; 31 while(!q.empty()) { 32 Point now = q.front(); 33 q.pop(); 34 if(now.x == des.x && now.y == des.y && now.z == des.z) 35 return now.step; 36 for(int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { 37 np.x = now.x + dir[i][0]; 38 np.y = now.y + dir[i][1]; 39 np.z = now.z + dir[i][2]; 40 np.step = now.step + 1; 41 if(check(np)) q.push(np); 42 } 43 } 44 return -1; 45 } 46 int main() { 47 int kase,m,x,y,z; 48 scanf("%d",&kase); 49 while(kase--) { 50 scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&start.x,&start.y,&start.z); 51 scanf("%d%d%d",&des.x,&des.y,&des.z); 52 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 53 scanf("%d",&m); 54 while(m--) { 55 scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); 56 vis[x][y][z] = true; 57 } 58 printf("%d\n",bfs()); 59 } 60 return 0; 61 }
