C#设计模式系列:享元模式(Flyweight)
当频繁地从数据源读取数据时,读出的内容存在重复,那么需要使用享元模式(Flyweight)来提高内存效率,Flyweight模式将节省更多空间,共享的Flyweight越多,空间节省越大。
1、享元模式简介
1.1>、定义
享元模式(Flyweight)的存在是为了避免大量拥有相同内容的小类的开销(如内存开销),使大家共享一个类。
1.2>、使用频率
 低
低
2、享元模式结构
2.1>、结构图
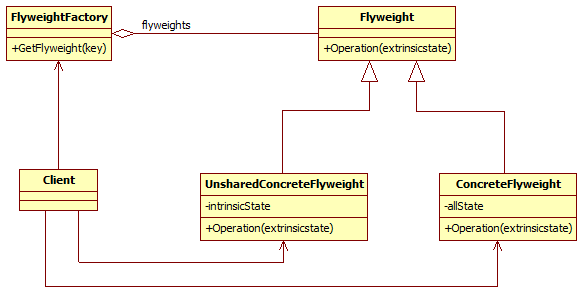
2.2>、参与者
享元模式参与者:
◊ Flyweight:声明一个接口,通过这个接口flyweight可以直接接收并作用于外部状态。
◊ ConcreteFlyweight:实现Flyweight接口,并为内部状态增加存储空间。ConcreteFlyweight对象必须是可以共享的,它所存储的状态必须是内部的,即它必须独立于ConcreteFlyweight对象的场景。
◊ UnsharedConcreteFlyweight:并非所有的Flyweight子类都需要被共享。Flyweight接口使共享成为可能,但它不强制共享。在Flyweight对象结构的某些层次,UnsharedConcreteFlyweight对象通常将ConcreteFlyweight对象作为子节点。
◊ FlyweightFactory
° 创建和管理flyweight对象。
° 确保flyweight对象被合理共享。当Client请求一个flyweight对象时,FlyweightFactory需要可以进行分配,若flyweight对象不存在时,则先创建一个。
◊ Client:维持一个对Flyweight的引用
在享元模式中,Client调用Flyweight下的ConcreteFlyweight,如果ConcreteFlyweight存在则调用成功;否则就调用FlyweightFactory生产所需要的继承Flyweight接口的ConcreteFlyweight,以供调用。
3、享元模式结构实现
Flyweight.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern.Structural { public abstract class Flyweight { public abstract void Operation(int extrinsicstate); } }
ConcreteFlyweight.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern.Structural { public class ConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight { public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteFlyweight: " + extrinsicstate); } } }
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern.Structural { public class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight { public override void Operation(int extrinsicstate) { Console.WriteLine("UnsharedConcreteFlyweight: " + extrinsicstate); } } }
FlyweightFactory.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Collections; namespace DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern.Structural { public class FlyweightFactory { private Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable(); public FlyweightFactory() { flyweights.Add("X", new ConcreteFlyweight()); flyweights.Add("Y", new ConcreteFlyweight()); flyweights.Add("Z", new ConcreteFlyweight()); } public Flyweight GetFlyweight(string key) { return ((Flyweight)flyweights[key]); } } }
Program.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern.Structural; namespace DesignPatterns.FlyweightPattern { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // Arbitrary extrinsic state int extrinsicstate = 22; FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory(); // Work with different flyweight instances Flyweight fx = factory.GetFlyweight("X"); fx.Operation(--extrinsicstate); Flyweight fy = factory.GetFlyweight("Y"); fy.Operation(--extrinsicstate); Flyweight fz = factory.GetFlyweight("Z"); fz.Operation(--extrinsicstate); UnsharedConcreteFlyweight fu = new UnsharedConcreteFlyweight(); fu.Operation(--extrinsicstate); } } }
运行输出:
ConcreteFlyweight: 21 ConcreteFlyweight: 20 ConcreteFlyweight: 19 UnsharedConcreteFlyweight: 18 请按任意键继续. . .
4、享元模式应用分析
享元模式适用情形:
◊ 一个应用程序使用了大量的对象
◊ 完全由于使用大量的对象,造成很大的存储开销
◊ 对象的大多数状态都可变为外部状态
◊ 如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象
◊ 应用程序不依赖对象标识
享元模式特点:
◊ 享元模式的核心是把大量共享的对象收集在一起使用简单工厂模式进行管理,避免由于大量的小对象导致系统内存过度消耗。
◊ 享元当重复对象较多时有很好的空间复杂度,但在查找搜索上消耗了时间复杂度。