python+opencv车道线检测(简易实现)
python+opencv车道线检测(简易实现)
技术栈:python+opencv
实现思路:
- canny边缘检测获取图中的边缘信息;
- 霍夫变换寻找图中直线;
- 绘制梯形感兴趣区域获得车前范围;
- 得到并绘制车道线;
效果展示:
代码实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def canny():
gray = cv2.cvtColor(lane_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
#高斯滤波
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
#边缘检测
canny_img = cv2.Canny(blur, 50, 150)
return canny_img
def region_of_interest(r_image):
h = r_image.shape[0]
w = r_image.shape[1]
# 这个区域不稳定,需要根据图片更换
poly = np.array([
[(100, h), (500, h), (290, 180), (250, 180)]
])
mask = np.zeros_like(r_image)
# 绘制掩膜图像
cv2.fillPoly(mask, poly, 255)
# 获得ROI区域
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(r_image, mask)
return masked_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
image = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
lane_image = np.copy(image)
canny = canny()
cropped_image = region_of_interest(canny)
cv2.imshow("result", cropped_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
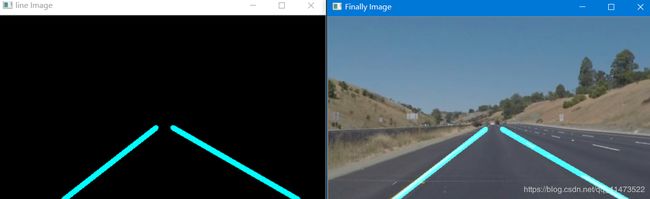
霍夫变换加线性拟合改良:
效果图:
代码实现:
主要增加了根据斜率作线性拟合过滤无用点后连线的操作;
import cv2
import numpy as np
def canny():
gray = cv2.cvtColor(lane_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
canny_img = cv2.Canny(blur, 50, 150)
return canny_img
def region_of_interest(r_image):
h = r_image.shape[0]
w = r_image.shape[1]
poly = np.array([
[(100, h), (500, h), (280, 180), (250, 180)]
])
mask = np.zeros_like(r_image)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, poly, 255)
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(r_image, mask)
return masked_image
def get_lines(img_lines):
if img_lines is not None:
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
# 分左右车道
k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if k < 0:
lefts.append(line)
else:
rights.append(line)
def choose_lines(after_lines, slo_th): # 过滤斜率差别较大的点
slope = [(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) for line in after_lines for x1, x2, y1, y2 in line] # 获得斜率数组
while len(after_lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slope) # 计算平均斜率
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slope] # 每条线斜率与平均斜率的差距
idx = np.argmax(diff) # 找到最大斜率的索引
if diff[idx] > slo_th: # 大于预设的阈值选取
slope.pop(idx)
after_lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
return after_lines
def clac_edgepoints(points, y_min, y_max):
x = [p[0] for p in points]
y = [p[1] for p in points]
k = np.polyfit(y, x, 1) # 曲线拟合的函数,找到xy的拟合关系斜率
func = np.poly1d(k) # 斜率代入可以得到一个y=kx的函数
x_min = int(func(y_min)) # y_min = 325其实是近似找了一个
x_max = int(func(y_max))
return [(x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max)]
if __name__ == '__main__':
image = cv2.imread('F:\\A_javaPro\\test.jpg')
lane_image = np.copy(image)
canny_img = canny()
cropped_image = region_of_interest(canny_img)
lefts = []
rights = []
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(cropped_image, 1, np.pi / 180, 15, np.array([]), minLineLength=40, maxLineGap=20)
get_lines(lines) # 分别得到左右车道线的图片
good_leftlines = choose_lines(lefts, 0.1) # 处理后的点
good_rightlines = choose_lines(rights, 0.1)
leftpoints = [(x1, y1) for left in good_leftlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in left]
leftpoints = leftpoints + [(x2, y2) for left in good_leftlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in left]
rightpoints = [(x1, y1) for right in good_rightlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in right]
rightpoints = rightpoints + [(x2, y2) for right in good_rightlines for x1, y1, x2, y2 in right]
lefttop = clac_edgepoints(leftpoints, 180, image.shape[0]) # 要画左右车道线的端点
righttop = clac_edgepoints(rightpoints, 180, image.shape[0])
src = np.zeros_like(image)
cv2.line(src, lefttop[0], lefttop[1], (255, 255, 0), 7)
cv2.line(src, righttop[0], righttop[1], (255, 255, 0), 7)
cv2.imshow('line Image', src)
src_2 = cv2.addWeighted(image, 0.8, src, 1, 0)
cv2.imshow('Finally Image', src_2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
待改进:
代码实用性差,几乎不能用于实际,但是可以作为初学者的练手项目;
斑马线检测思路:获取车前感兴趣区域,判断白色像素点比例即可实现;
行人检测思路:opencv有内置行人检测函数,基于内置的训练好的数据集;