数据结构与算法-HashMap与LinkedHashMap
数据结构与算法-HashMap与LinkedHashMap
Map
基本概念
Map 一般在开发中使用非常广泛,常用的有HashMap, LinkedHashMap,TreeMap等等,由于使用的时候一般是有key和value一一对应,所以称之为Map。
百度百科 — Map 接口定义的集合又称为查找表,用于存储所谓“key-value”映射对。Key可以看成是Value 的索引,作为key的对象在集合中不可重复。
这里的数据结构可能跟具体的实现方式不一样,暂时只分析HashMap和LinkedHashMap两个类。
常见操作
put 操作 添加
get 操作 读取
remove 操作 移除
Java中常见数据结构类分析
HashMap
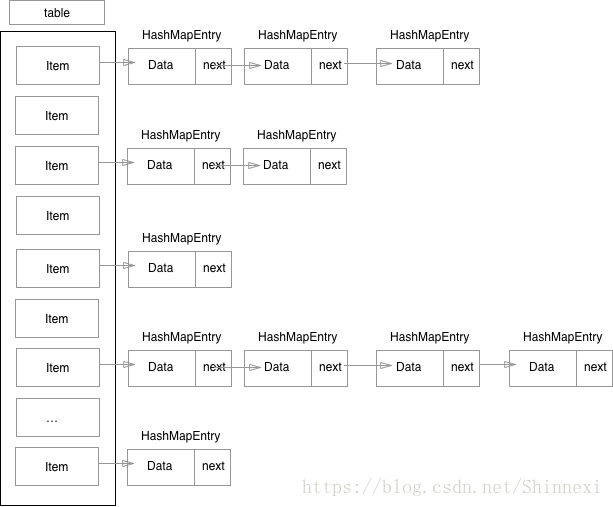
基本结构
/**
* 默认初始化大小 - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 4;
/**
* 最大容量设置,默认最大是2^30-1, 可以通过构造函数设置。
*
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 默认的负载因子。当容量占到当前容量的75% 时,将会进行扩容操作。
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 一个空的链表
*/
static final HashMapEntry[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient HashMapEntry[] table = (HashMapEntry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
// Android-Note: We always use a load factor of 0.75 and ignore any explicitly
// selected values.
final float loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount;
/** @hide */ // Android added.
/// 基本的HashMap 存储单元 Entry
static class HashMapEntry implements Map.Entry {
final K key;
V value;
HashMapEntry next; /// 当前entry 指向的下一个元素
int hash; // 当前元素key 经过二次hash 算出的hash码
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
HashMapEntry(int h, K k, V v, HashMapEntry n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
} HashMap 包含如下几个构造器:
* HashMap():构建一个初始容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75 的 HashMap。
* HashMap(int initialCapacity):构建一个初始容量为 initialCapacity,负载因子为 0.75 的 HashMap。
* HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor):以指定初始容量、指定的负载因子创建一个 HashMap。
put
/**
* Maps the specified key to the specified value.
*
* @param key
* the key.
* @param value
* the value.
* @return the value of any previous mapping with the specified key or
* {@code null} if there was no such mapping.
*/
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
/// 计算该key的hash 码
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
// 拿到临时的table链表
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
/// 计算index
///利用for循环来,遍历HashMapEntry组成的单向链表
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
/// 找到对应的hash码相同和key 相等的位置
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
// 因为已经存在相同key的entry ,所以这里进行覆盖,并且返回old元素。
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
/// 这里如果size++ 超过hash table的极限,则进行扩容操作
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}
/**
* 由此可见 新加入的entry是放在了 table[index] 的位置,next 指向了 原来table[index]的位置, 也就是entry的链表头是table[index]
*/
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
table[index] = new HashMapEntry(key, value, hash, table[index]);
}
/**
* key 为null ,没有hash 默认0 , 也就只有一个元素 没有next
*/
void addNewEntryForNullKey(V value) {
entryForNullKey = new HashMapEntry(null, value, 0, null);
}
看下Collections中的二次hash方法
/**
* Computes a hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to defend
* against poor quality hash functions. This is critical because HashMap
* uses power-of-two length hash tables, that otherwise encounter collisions
* for hash codes that do not differ in lower or upper bits.
* Routine taken from java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.hash(int).
* @hide
*/
public static int secondaryHash(Object key) {
return secondaryHash(key.hashCode());
}
/**
* Applies a 追加的 hash function to a given hashCode, which defends
* against poor quality hash functions.
* 这是关键的这是因为使用了二的n次方长度的hash Tables, 可以使 hash碰撞在高位或者低位的计算降到最低。
*/
private static int secondaryHash(int h) {
// Doug Lea's supplemental hash function
// 这是Doug Lea 追加的hash 算法, 具体算法已经超出本文内容。
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
看一下扩容方法
/**
* Doubles the capacity of the hash table. Existing entries are placed in
* the correct bucket on the enlarged table. If the current capacity is,
* MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method is a no-op. Returns the table, which
* will be new unless we were already at MAXIMUM_CAPACITY.
*/
private HashMapEntry[] doubleCapacity() {
HashMapEntry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
/// 如果目前容量已经超过了最大容量 直接返回。
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
return oldTable;
}
int newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2;
/// 新容量是原来的一倍,用新容量大小来创建table[]
HashMapEntry[] newTable = makeTable(newCapacity);
/// 如果元素个数0 则直接返回新数组
if (size == 0) {
return newTable;
}
//// 接下来会进行循环遍历oldtable中的所有元素,并且进行重新编码,按照newTable的位置进行重构,重新创建链表数组结构。
for (int j = 0; j < oldCapacity; j++) {
/*
* Rehash the bucket using the minimum number of field writes.
* This is the most subtle and delicate code in the class.
*/
HashMapEntry e = oldTable[j];
// 按照数组索引进行index ,如果为null ,直接进入下个元素
if (e == null) {
continue;
}
int highBit = e.hash & oldCapacity;
/// 该方法和indexFor 不同的是, e.hash & oldCapacity进行计算, 则取到的是高位
也就是 ,要么是oldCaPacity的值,要么是0
HashMapEntry broken = null;
newTable[j | highBit] = e;
///// j|highBit 运算则表示 在原来的高位基础上, 要么是原来大小基础之上加上小于原大小的值,要么还是在原大小之内
/// 看一个栗子;
假如 oldCapacity = 16 , 则 e.hash & oldCapacity 之后 ,结果要么是0 ,要么是16
10000000 00000000 00000000 00010000 16
10010100 11100100 00100100 00000101 n ...
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0
10000000 00000000 00000000 00010000 16
如果是0 则 结果是0<= newIndex <16 因为j 15
如果是16 则 结果是16<= newIndex <32
10000000 00000000 00000000 00010000 16
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000101 5
10000000 00000000 00000000 00010101 21
/// 计算出需要原来每个节点的链表中超出原大小,需要构建到16<=n<32中的元素,然后build新的数组链表结构
for (HashMapEntry n = e.next; n != null; e = n, n = n.next) {
int nextHighBit = n.hash & oldCapacity;
if (nextHighBit != highBit) {
if (broken == null)
newTable[j | nextHighBit] = n;
else
broken.next = n;
broken = e;
highBit = nextHighBit;
}
}
if (broken != null)
broken.next = null;
}
return newTable;
}
/**
* Allocate a table of the given capacity and set the threshold accordingly.
* @param newCapacity must be a power of two
*/
private HashMapEntry[] makeTable(int newCapacity) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
/// 创建newTable 数组 以新容量
HashMapEntry[] newTable = (HashMapEntry[]) new HashMapEntry[newCapacity];
table = newTable;
// 极限容量设定为 n/2 + n/2^2 = 3/4 容量
threshold = (newCapacity >> 1) + (newCapacity >> 2); // 3/4 capacity
return newTable;
} get
/**
* 查找到对应key, Mapping的对象并返回
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
/**
* 遍历查询key==null并返回
*/
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (HashMapEntry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : Collections.secondaryHash(key);
/// 使用key的二次hash 计算出的index ,然后遍历链表达到快速查询的目的, 这里如果key ==null 的hash是0 ,对应了 putNullKey的hash值
for (HashMapEntry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
对于任意给定的对象,只要它的 hashCode() 返回值相同,那么程序调用 hash(int h) 方法所计算得到的 Hash 码值总是相同的。接下来程序会调用 indexFor(int h, int length) 方法来计算该对象应该保存在 table 数组的哪个索引处。indexFor(int h, int length) –>>> * h & (length-1)*
因为 length 总是 2 N次方
h & (length-1) 将是一个非常巧妙的设计(旧版本src里边写的是 h%length-1. 两种其实一样) :
length-1 (16-1) 10000000 00000000 00000000 00001111
h & 10010100 11100100 00100100 00010000
h & (length-1) -> 10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
所以我们假设 h=5,length=16, 那么 h & length - 1 将得到 5;如果 h=6,length=16, 那么 h & length - 1 将得到 6 ……如果 h=15,length=16, 那么 h & length - 1 将得到 15;这样保证计算得到的索引值总是位于 table 数组的索引之内。
看完之后是不是有种高屋建瓴的感觉。注意这里插入操作,不是放在了链表尾部,而是头部. 看addNewEntry方法。
LinkedHashMap
基本结构
public class LinkedHashMap<K, V> extends HashMap<K, V> {
/**
* 这是虚拟的循环链表
* A dummy entry in the circular linked list of entries in the map.
* 真正的第一个 元素是header.next , 最后一个元素则是previous
* The first real entry is header.nxt, and the last is header.prv.
* 如果map是空的 则自己抱自己。
* If the map is empty, header.nxt == header && header.prv == header.
*/
transient LinkedEntry header;
/**
* True if access ordered, false if insertion ordered.
* 是否是按照读取的顺序来排序,这里使用
*/
private final boolean accessOrder;
/**
* Constructs a new empty {@code LinkedHashMap} instance.
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
init();
accessOrder = false;
}
@Override
void init() {
header = new LinkedEntry();
}
再看一下基本结构:
/**
* LinkedEntry adds nxt/prv double-links to plain HashMapEntry.
* 相比HashMapEntry 多了previous和nxt 两个字段 , 看注释可以了解到是双向循环链表
*/
static class LinkedEntry<K, V> extends HashMapEntry<K, V> {
/// nxt
LinkedEntry nxt;
LinkedEntry prv;
/** Create the header entry */
LinkedEntry() {
super(null, null, 0, null);
/// 自己指向自己。
nxt = prv = this;
}
/** Create a normal entry */
LinkedEntry(K key, V value, int hash, HashMapEntry next,
LinkedEntry nxt, LinkedEntry prv) {
super(key, value, hash, next);
this.nxt = nxt;
this.prv = prv;
}
} put
从上边继承结构可以看到LinkedHashMap 继承自HashMap ,当然同时也继承了父类的结构
LinkedHashMap类中没有实现put方法,而是重写了父类的addNewEntry方法,
/**
* Evicts eldest entry if instructed, creates a new entry and links it in
* as head of linked list. This method should call constructorNewEntry
* (instead of duplicating code) if the performance of your VM permits.
*
* It may seem strange that this method is tasked with adding the entry
* to the hash table (which is properly the province of our superclass).
* The alternative of passing the "next" link in to this method and
* returning the newly created element does not work! If we remove an
* (eldest) entry that happens to be the first entry in the same bucket
* as the newly created entry, the "next" link would become invalid, and
* the resulting hash table corrupt.
* 接着上边hashMap put的逻辑, 继续,找到hash & key相等重写,否则扩容或者进行添加新元素, 将需要传的key, value , hash , index 传过来之后
*/
@Override void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
LinkedEntry header = this.header;
// Remove eldest entry if instructed to do so.
LinkedEntry eldest = header.nxt;
if (eldest != header && removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
remove(eldest.key);
}
// Create new entry, link it on to list, and put it into table
LinkedEntry oldTail = header.prv;
LinkedEntry newTail = new LinkedEntry(
key, value, hash, table[index], header, oldTail);
table[index] = oldTail.nxt = header.prv = newTail;
/// 将新的节点new出来,添加到原来header.prv之后和现在header.prv之前, 同时将newTail赋值给table[index] ,并将table[index].prv设置给newTail
}
/**
重写父类方法, 插入null key 节点
*/
@Override void addNewEntryForNullKey(V value) {
LinkedEntry header = this.header;
// Remove eldest entry if instructed to do so.
LinkedEntry eldest = header.nxt;
if (eldest != header && removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
remove(eldest.key);
}
// Create new entry, link it on to list, and put it into table
LinkedEntry oldTail = header.prv;
//把newTail 插入到header 之前 ,header.prv之后
// key 为null , hash = 0
LinkedEntry newTail = new LinkedEntry( null, value, 0, null, header, oldTail);
entryForNullKey = oldTail.nxt = header.prv = newTail;
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return false;
}
get
/**
* Returns the value of the mapping with the specified key.
*
* @param key
* the key.
* @return the value of the mapping with the specified key, or {@code null}
* if no mapping for the specified key is found.
*/
@Override public V get(Object key) {
/*
* This method is overridden to eliminate the need for a polymorphic
* invocation in superclass at the expense of code duplication.
*/
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry e = entryForNullKey;
if (e == null)
return null;
/// 即使key为null 同样插入到队尾
if (accessOrder)
makeTail((LinkedEntry) e);
return e.value;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
/// 根据二次哈希算法 得到index, 并循环遍历链表 找到对应的value
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
/// 这一点至关重要, 如果是按照LRU排序,则进入执行,将刚刚访问的元素e断开前后链接,插入到对位,也就是Header.previous之前
if (accessOrder)
makeTail((LinkedEntry) e);
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Relinks the given entry to the tail of the list. Under access ordering,
* this method is invoked whenever the value of a pre-existing entry is
* read by Map.get or modified by Map.put.
* 做个尾巴
*
*/
private void makeTail(LinkedEntry e) {
// Unlink e 断开与e节点关联的前后
e.prv.nxt = e.nxt;
e.nxt.prv = e.prv;
// Relink e as tail
/// 将e插入header的prv 和header.prv之间。 相当于添加了tail
LinkedEntry header = this.header;
LinkedEntry oldTail = header.prv;
e.nxt = header;
e.prv = oldTail;
oldTail.nxt = header.prv = e;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 这个方法当然也是重写HashMap的, 位于put方法内,当key重复时调用。
*/
@Override
void preModify(HashMapEntry e) {
/// 当按照访问排序时
if (accessOrder) {
makeTail((LinkedEntry) e);
}
}
/**
移除node e
*/
@Override
void postRemove(HashMapEntry e) {
LinkedEntry le = (LinkedEntry) e;
le.prv.nxt = le.nxt;
le.nxt.prv = le.prv;
le.nxt = le.prv = null; // Help the GC (for performance)
}
LRUCache与LinkedHashMap
在Android开发中,有一个叫做LruCache类专门用来做图片缓存处理的。LRU 是 Least Recently Used 最近最少使用算法。
它有一个特点,当缓存的图片达到了预先设定的值的时候,那么近期使用次数最少的图片就会被回收掉。
下边我们简单说一下LRUCache的核心工作原理。
本来想简单说一下,看了一下 前后没多少行 ,干脆直接粘出来 一点一点注释。
public class LruCache<K, V> {
// LRUCache 内部持有了LinkedHashMap 引用,泛型类型和LRUCache一一对应 。
private final LinkedHashMap map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size;
private int maxSize;
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;
/**
* @param maxSize for caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, **this is
* the maximum number of entries in the cache**. For all other caches,
* this is the maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
/// 这里使用了LinkedHashMap 自定三个参数构造函数,初始化大小为0, 负载因子0.75f, 并且AccessOrder设置为true
this.map = new LinkedHashMap(0, 0.75f, true);
}
/**
* Returns the value for {@code key} if it exists in the cache or can be
* created by {@code #create}. If a value was returned, it is moved to the
* head of the queue. This returns null if a value is not cached and cannot
* be created.
*/
public final V get(K key) {
/// 这里的key 不允许为null 和HashMap和LinkedHashMap不一样
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
/// 这里做了同步处理 ,也就是说是线程安全的。
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
/// 命中个数++ , 返回value
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
// 没命中个数++
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
*/
/// 正常情况下 如果不重写create方法 则不会走到这里。
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
/// 如果未命中 则创建一个value , 进行put操作。。
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
/// 大小加上value的大小
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
/**
* Caches {@code value} for {@code key}. The value is moved to the head of
* the queue.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
/// 检查内存状况,看是否超标,如果超标则按照LRU算法移除,最近最久未使用的元素,以恢复内存空间。
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
/**
* @param maxSize the maximum size of the cache before returning. May be -1
* to evict even 0-sized elements.
*/
private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
/// 这里也是线程安全的
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
/// 获取队首元素 也就是最旧没有访问的元素,
Map.Entry toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
/// 移除
map.remove(key);
/// 减掉对应的size
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
/// 移除个数++
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
/**
* Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
/// 同步移除node
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
/// size 减去占用的大小
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
/**
* Called for entries that have been evicted or removed. This method is
* invoked when a value is evicted to make space, removed by a call to
* {@link #remove}, or replaced by a call to {@link #put}. The default
* implementation does nothing.
*
* The method is called without synchronization: other threads may
* access the cache while this method is executing.
*
* @param evicted true if the entry is being removed to make space, false
* if the removal was caused by a {@link #put} or {@link #remove}.
* @param newValue the new value for {@code key}, if it exists. If non-null,
* this removal was caused by a {@link #put}. Otherwise it was caused by
* an eviction or a {@link #remove}.
*/
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
/**
* Called after a cache miss to compute a value for the corresponding key.
* Returns the computed value or null if no value can be computed. The
* default implementation returns null.
*
* The method is called without synchronization: other threads may
* access the cache while this method is executing.
*
*
If a value for {@code key} exists in the cache when this method
* returns, the created value will be released with {@link #entryRemoved}
* and discarded. This can occur when multiple threads request the same key
* at the same time (causing multiple values to be created), or when one
* thread calls {@link #put} while another is creating a value for the same
* key.
*/
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Returns the size of the entry for {@code key} and {@code value} in
* user-defined units. The default implementation returns 1 so that size
* is the number of entries and max size is the maximum number of entries.
*
* An entry's size must not change while it is in the cache.
这里一般会重写, 根据实际缓存的内容来计算大小
如果是Image则
** return bitmap.getRowBytes() * bitmap.getHeight() / 1024;**
如果不重写则默认计算个数。
*/
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
/**
* Clear the cache, calling {@link #entryRemoved} on each removed entry.
/// 清空cache
*/
public final void evictAll() {
trimToSize(-1); // -1 will evict 0-sized elements
}
/**
* 如果没有重写sizeOf方法 则是缓存的数量
* 如果重写过就是占用的内存大小。
*/
public synchronized final int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* For caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this returns the maximum
* number of entries in the cache. For all other caches, this returns the
* maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public synchronized final int maxSize() {
return maxSize;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #get} returned a value that was
* already present in the cache.
*/
public synchronized final int hitCount() {
return hitCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #get} returned null or required a new
* value to be created.
*/
public synchronized final int missCount() {
return missCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #create(Object)} returned a value.
*/
public synchronized final int createCount() {
return createCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of times {@link #put} was called.
*/
public synchronized final int putCount() {
return putCount;
}
/**
* Returns the number of values that have been evicted.
*/
public synchronized final int evictionCount() {
return evictionCount;
}
/**
* Returns a copy of the current contents of the cache, ordered from least
* recently accessed to most recently accessed.
*/
public synchronized final Map snapshot() {
return new LinkedHashMap(map);
}
/**
* 重写toString方法, 表述当前cache的状态, 包含最大值,命中个数,命中率,非命中个数。
*/
@Override
public synchronized final String toString() {
int accesses = hitCount + missCount;
int hitPercent = accesses != 0 ? (100 * hitCount / accesses) : 0;
return String.format("LruCache[maxSize=%d,hits=%d,misses=%d,hitRate=%d%%]",
maxSize, hitCount, missCount, hitPercent);
}
}
其中在trimToSize方法中
/** 返回最旧的那个元素,也就是最不经常使用的那个元素, 位于队首。 header.next
*
* Returns the eldest entry in the map, or {@code null} if the map is empty.
* @hide
*/
public Entry eldest() {
LinkedEntry eldest = header.nxt;
return eldest != header ? eldest : null;
}
总结
这次一共分析了三个类, 一个HashMap , LinkedHashMap , LRUCache . 用到的数据结构是顺序型存储结构和链式存储结构相结合的方式。 其中双联回环式结构的LinkedHashMap 对于线性表的使用要求很高。 至于HashMap的链表结构改为平衡树的新code 会择时间进行分析更新。同时由于个人能力不足,文章肯定有很多不足之处,欢迎批评指正。 如果有不理解的地方可以在留言区回复我们共同学习进步。