Python协议攻击脚本(一): Scapy的使用
Python协议攻击脚本(一): Scapy基本的使用
文章目录
- Python协议攻击脚本(一): Scapy基本的使用
- 简介
- 安装
- Linux
- Mac
- Windows
- 基本使用
- 交互式
- 模块使用
简介
Scapy官网
Scapy是一个Python程序,使用户能够发送,嗅探和剖析并伪造网络数据包。此功能允许构建可以探测,扫描或攻击网络的工具。Scapy可以轻松处理大多数经典任务,如扫描,跟踪路由,探测,单元测试,攻击或网络发现。它可以取代hping,arpspoof,arp-sk,arping,p0f甚至是Nmap,tcpdump和tshark的某些部分。
安装
详见Scapy官方文档
| 捆绑 | 包含 | Pip命令 |
|---|---|---|
| 默认 | 只有Scapy | pip install scapy |
| 基本 | Scapy和IPython。强烈推荐 | pip install --pre scapy[basic] |
| 完成 | Scapy及其所有主要依赖项 | pip install --pre scapy[complete] |
Linux
- 安装Python 2.7或3.4+。
- 安装tcpdump并确保它在$ PATH中。(它仅用于编译BPF过滤器())
-ddd option - 确保你的内核选择了Packet套接字(
CONFIG_PACKET) - 如果您的内核<2.6,请确保选择了Socket过滤
CONFIG_FILTER
Debian / Ubuntu /
python3
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip tcpdump
pip3 install --pre scapy[basic]
python
sudo apt-get install python python-pip tcpdump
pip install --pre scapy[basic]
kali
默认已安装,但是安装在Python2.7下
如果需要在Python3中使用:
apt-get install python3 python3-pip
pip3 install scapy
Mac
使用Homebrew安装
-
更新Homebrew:
brew update -
安装Python绑定:
brew install --with-python libdnet brew install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/secdev/scapy/master/.travis/pylibpcap.rb sudo brew install --with-python libdnet sudo brew install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/secdev/scapy/master/.travis/pylibpcap.rb
使用MacPorts安装
-
更新MacPorts:
$ sudo port -d selfupdate -
安装Python绑定:
$ sudo port install py-libdnet py-pylibpcap
Windows
Scapy主要是针对类Unix系统开发的,在这些平台上运行得最好。但最新版本的Scapy支持Windows开箱即用。因此,您也可以在Windows机器上使用几乎所有Scapy的功能。
- Python:Python 2.7.X或3.4+。安装后,将Python安装目录及其Scripts子目录添加到PATH。根据您的Python版本,默认值分别为
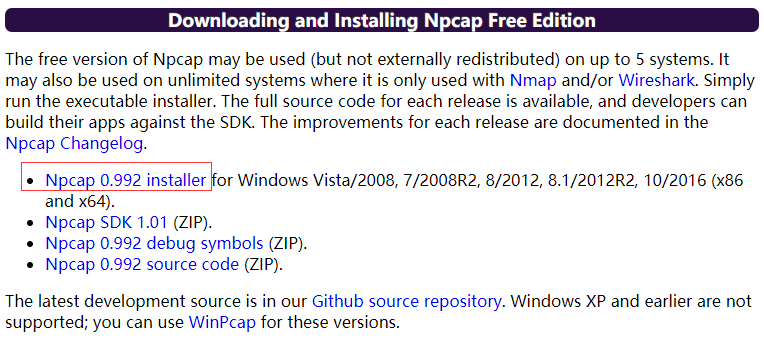
C:\Python27和C:\Python27\Scripts。 - Npcap:建议使用默认值。Scapy也可以使用Winpcap
Dos中输入:
pip install --pre scapy[basic] #需要配置Python的环境变量,如上
基本使用
交互式
主要用来做测试,或者进行简单操作
Linux从终端启动
Windows cmd中启动
列出用户命令lsc()
>>> lsc()
sr : Send and receive packets at layer 3
sr1 : Send packets at layer 3 and return only the first answer
srp : Send and receive packets at layer 2
srp1 : Send and receive packets at layer 2 and return only the first answer
srloop : Send a packet at layer 3 in loop and print the answer each time
srploop : Send a packet at layer 2 in loop and print the answer each time
sniff : Sniff packets
p0f : Passive OS fingerprinting: which OS emitted this TCP SYN ?
arpcachepoison : Poison target's cache with (your MAC,victim's IP) couple
send : Send packets at layer 3
sendp : Send packets at layer 2
traceroute : Instant TCP traceroute
arping : Send ARP who-has requests to determine which hosts are up
ls : List available layers, or infos on a given layer
lsc : List user commands
queso : Queso OS fingerprinting
nmap_fp : nmap fingerprinting
report_ports : portscan a target and output a LaTeX table
dyndns_add : Send a DNS add message to a nameserver for "name" to have a new "rdata"
dyndns_del : Send a DNS delete message to a nameserver for "name"
[...]
常用的方法
sr : 发送和接受三层的包 #三层:网络层
sr1 : 发送和接受返回的第一个三层的包
srp1 : 发送和接受二层的包
srp1 : 发送和接受返回的第一个二层的包
sniff : 嗅探数据包
send : 发送三层的包
sendp : 发送二层的包
rdcap : 打开pcap文件 #eg:wirshark保存的文件
wrpcap : 写入到pcap文件
列出支持的协议ls(),
>>> ls()
AH : AH
AKMSuite : AKM suite
ARP : ARP
ASN1P_INTEGER : None
ASN1P_OID : None
ASN1P_PRIVSEQ : None
ASN1_Packet : None
ATT_Error_Response : Error Response
ATT_Exchange_MTU_Request : Exchange MTU Request
ATT_Exchange_MTU_Response : Exchange MTU Response
ATT_ExecWriteReq : None
ATT_ExecWriteResp : None
[...]
常用的就主要是
Ether 以太网协议
ARP ARP协议
IP IP协议
UDP UDP协议
TCP TCP协议
ICMP ICMP协议
[...]
列出协议的字段
>>> ls(ARP)
hwtype : XShortField = (1)
ptype : XShortEnumField = (2048)
hwlen : FieldLenField = (None)
plen : FieldLenField = (None)
op : ShortEnumField = (1)
hwsrc : MultipleTypeField = (None)
psrc : MultipleTypeField = (None)
hwdst : MultipleTypeField = (None)
pdst : MultipleTypeField = (None)
获得帮助help(send)
>>> help(send)
Help on function send in module scapy.sendrecv:
send(x, inter=0, loop=0, count=None, verbose=None, realtime=None, return_packets=False, socket=None, *args, **kargs)
Send packets at layer 3
send(packets, [inter=0], [loop=0], [count=None], [verbose=conf.verb], [realtime=None], [return_packets=False], # noqa: E501
[socket=None]) -> None
构造一个icmp包
>>> packet =IP(src='192.168.1.115',dst='192.168.1.1')/ICMP()
>>> packet
<IP frag=0 proto=icmp src=192.168.1.1 dst=192.168.1.2 |<ICMP |>>
pkt.show() 数据包详细
>>> packet.show()
###[ IP ]###
version= 4
ihl= None
tos= 0x0
len= None
id= 1
flags=
frag= 0
ttl= 64
proto= icmp
chksum= None
src= 192.168.1.115
dst= 192.168.1.1
\options\
###[ ICMP ]###
type= echo-request
code= 0
chksum= None
id= 0x0
seq= 0x0
send() 发送包
>>> send(packet,count=1)
WARNING: Mac address to reach destination not found. Using broadcast.
.
Sent 1 packets.
sr1() 发送并接受答复包
>>> icmp = sr1(packet)
Begin emission:
.....Finished sending 1 packets..
.*
Received 8 packets, got 1 answers, remaining 0 packets
>>>icmp.show()
###[ IP ]###
version= 4
ihl= 5
tos= 0x0
len= 28
id= 12962
flags=
frag= 0
ttl= 64
proto= icmp
chksum= 0xc47a
src= 192.168.1.1
dst= 192.168.1.115
\options\
###[ ICMP ]###
type= echo-reply
code= 0
chksum= 0xffff
id= 0x0
seq= 0x0
pkt.getlayer() 获取数据包某层
>>> icmp[ICMP]
<ICMP type=echo-reply code=0 chksum=0xffff id=0x0 seq=0x0 |>
>>> icmp.getlayer(ICMP)
<ICMP type=echo-reply code=0 chksum=0xffff id=0x0 seq=0x0 |>
.fields 获取数据包字段
>>> icmp.fields
{'options': [],
'version': 4,
'ihl': 5,
'tos': 0,
'len': 28,
'id': 12962,
'flags': <Flag 0 ()>,
'frag': 0,
'ttl': 64,
'proto': 1,
'chksum': 50298,
'src': '192.168.1.1',
'dst': '192.168.1.115'}
>>> icmp.fields['src']
'192.168.1.1'
>>> icmp.src
'192.168.1.1'
sniff() 嗅探
>>> sniff(filter='tcp',count=5) #捕获5个包
<Sniffed: TCP:5 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0>
>>> sniff(stop_filter=lambda x: x.haslayer(TCP)) #检测到TCP则停止
<Sniffed: TCP:1 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0>
wirshark() 在Wirshark中打开
>>> packet = sniff(count=5)
>>> wireshark(packet)
模块使用
from scapy.all import *
packet =IP(src='192.168.1.1',dst='192.168.1.2')/ICMP()
send(packet,count=1)