语音自适应回声消除(AEC)算法
自适应回声消除算法
欢迎留言交流
AEC算法早期用在Voip,电话这些场景中,自从智能设备诞生后,智能语音设备也要消除自身的音源,这些音源包括音乐或者TTS机器合成声音。
本文基于开源算法阐述AEC的原理和实现,基于WebRTC和speex两种算法,文末会附上两种算法的matlab实现。
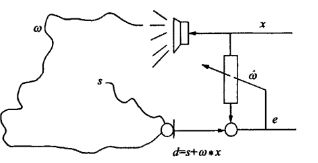
回声消除原理
回声消除的基本原理是使用一个自适应滤波器对未知的回声信道: ω \omega ω 进行参数辨识,根据扬声器信号与产生的多路回声的相关性为基础,建立远端信号模型,模拟回声路径,通过自适应算法调整,使其冲击响应和真实回声路径相逼近。然后将麦克风接收到的信号减去估计值,即可实现回声消除功能。
e c h o = x ∗ ω echo = x *\omega echo=x∗ω 1.1
$d = s + echo $ 1.2
y ^ = x ∗ ω ^ \hat{y}=x*\hat\omega y^=x∗ω^ 1.3
e = d − y ^ e=d - \hat{y} e=d−y^ 1.4
式中 ω \omega ω是回声通道的时域冲击响应函数,x是远端语音;echo是所得回声;s是近端说话人语音,d为麦克风采集到的信号, y ^ \hat{y} y^是对回声信号的估计值,e为误差。
为了消除较长时间的回声,需要FIR滤波器的阶数较高,时域计算法,有两个问题,一个是实时性较差,一个是计算量大。为了在实时性/计算量以及可以消除的回声时长之间找到使这三个最优的算法,采用了频谱分块自适应滤波算法。
这里用到了很多信号处理算法,为了让算法理解起来容易些,简单罗列涉及到的算法:
FFT/IFFT
循环卷积和线性卷积的关系;重叠保留法
功率谱密度
互相关
NLMS自适应算法
##NLMS权重调整

关于NLMS,可以下载http://download.csdn.net/detail/shichaog/9832657
下面直接开始WebRTC的matlab梳理,由于matlab代码和webRTC的c++代码命名几乎一致。所以c++的实现就一笔带过。
首先解释几个名词:
RERL-residual_echo_return_loss
ERL-echo return loss
ERLE echo return loss enhancement
NLP non-linear processing
首先matlab读入远端和近端信号。
%near is micphone captured signal
fid=fopen('near.pcm', 'rb'); % Load far end
ssin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
fclose(fid);
%far is speaker played music
fid=fopen('far.pcm', 'rb'); % Load fnear end
rrin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
fclose(fid);
然后对一些变量赋初值
fs=16000;
NLPon=1; % NLP on
M = 16; % Number of partitions
N = 64; % Partition length
L = M*N; % Filter length
VADtd=48;
alp = 0.15; % Power estimation factor
alc = 0.1; % Coherence estimation factor
step = 0.1875;%0.1875; % Downward step size
上述初始化中,M=16和最新的WebRTC代码并不一致,且最新的WebRTC中支持aec3最新一代算法。
len=length(ssin);
NN=len;
Nb=floor(NN/N)-M;
for kk=1:Nb
pos = N * (kk-1) + start;
可以看出Nb是麦克风采集到的数据块数-16(分区数),这是因为第一次输入了16块,所以这里减掉了16。pos是每一次添加一块时的地址指针。
%far is speaker played music
xk = rrin(pos:pos+N-1);
%near is micphone captured signal
dk = ssin(pos:pos+N-1);
xk和dk是读取到的64个点,这里是时域信号。
##功率计算
%----------------------- far end signal process
xx = [xo;xk];
xo = xk;
tmp = fft(xx);
XX = tmp(1:N+1);
dd = [do;dk]; % Overlap
do = dk;
tmp = fft(dd); % Frequency domain
DD = tmp(1:N+1);
将xk和上一次的数据结合在一起,做FFT变换,由于两次组合在一起,那么得到的应该是N=128点,这里可以知道得到的谱分辨率是 n ∗ f s / N n*fs/N n∗fs/N, f s fs fs前面设置过了,是16k,则得到的每一个bin的频谱分辨率是16000/128=125Hz。这里XX和DD取了前65个点,这是因为N点FFT变换后频谱是关于N/2对称的,对称的原因是奈奎斯特采样定理,如果 f s = 16000 H z fs=16000Hz fs=16000Hz,那么要求采样到的信号的截止频率必然小于等于 f s / 2 = 8000 H z fs/2=8000Hz fs/2=8000Hz,对于实信号,N/2~N,实际上表示的是 − f s / 2 -fs/2 −fs/2 ~ 0 0 0之间的频率。第一个点是直流分量,所以取65个点。和上一帧64个点信号合并在一起的另一个原因是使用重叠保(overlap-save)留法将循环卷积变成线性卷积,这里做的FFT变换,就是为了减少时域里做卷积的计算量的。
计算远端信号功率谱
% ------------------------far end Power estimation
pn0 = (1 - alp) * pn0 + alp * real(XX.* conj(XX));
pn = pn0;
平滑功率谱,上一次的功率谱占85%(alp=0.15),后面的频域共轭相乘等于功率是有帕斯瓦尔定理支撑的。pn0是65*1的矩阵。
##滤波
XFm(:,1) = XX;
首先将远端信号频谱赋给XFm,XFm是65*16的矩阵,16就是前面初始化的M值,这里将XX给第一列,其2~16列对应的是之前的输入频谱。
for mm=0:(M-1)
m=mm+1;
YFb(:,m) = XFm(:,m) .* WFb(:,m);
end
YFb,WFb以及XFm都是65*16的矩阵,WFb是自适应滤波器的频谱表示,XFm是原始的speaker数据,上式的意义对应于插图中的 y ^ \hat{y} y^的频域值,变换到时域后就可以得到 y y y的估计值 y ^ \hat{y} y^.
yfk = sum(YFb,2);
tmp = [yfk ; flipud(conj(yfk(2:N)))];
ykt = real(ifft(tmp));
ykfb = ykt(end-N+1:end);
首先yfk是651的矩阵,sum求和就是将估计的频谱按行求和,也就是yfk包含了最近16个块的远端频谱估计信息,这样,只要近端麦克采集到的信号里有这16个块包含的远端信号,那么就可以消掉,从这里也可以看出来,容许的延迟差 在1664/16=64ms,也就是说,如果麦克风采集到的speaker信号滞后speaker播放超过64ms,那么这种情况是无法消掉的,当然,延迟差越小越好。
flipud(conj(yfk(2:N))是因为前面计算频谱时利用奈奎斯特定理,也即实数的FFT结果按N/2对称,所以这里为了得到正确的ifft变换结果,先把频谱不全到 f s fs fs.
ykfb就是 y ^ \hat{y} y^.后面再看WFb是如何跟新。
##误差估计
ekfb = dk - ykfb;
dk是麦克风采集到的信号,ykfb是 y ^ \hat{y} y^,这样得到的是误差信号,理想情况下,那么得到的误差信号就是需要的人声信号,而完全滤除 掉了speaker信号(远端信号)。
erfb(pos:pos+N-1) = ekfb;
tmp = fft([zm;ekfb]); % FD version for cancelling part (overlap-save)
Ek = tmp(1:N+1);
erfb是近端信号数组长度×1矩阵,存放的是全部样本对应的误差信号,这个保存仅仅是为了plot用的。
然后补了64个零,然后做FFT,Ek是误差信号FFT的结果。
##自适应调节
Ek2 = Ek ./(pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
pn是当前帧远端信号功率谱,Ek是误差信号频谱。Ek2是归一化误差频谱。NLMS公式要求。
absEf = max(abs(Ek2), threshold);
absEf = ones(N+1,1)*threshold./absEf;
Ek2 = Ek2.*absEf;
max的作用是为了防止归一化后误差频谱过小,最终得到的Ek2是一个限幅矩阵,如果该点的值比门限大,则取门限,如果该点的值比门限小,则保持不变。
mEk = mufb.*Ek2;
mufb是步长,对于16000情况,步长取了0.8.NLMS公式。
PP = conj(XFm).*(ones(M,1) * mEk')';
tmp = [PP ; flipud(conj(PP(2:N,:)))];
IFPP = real(ifft(tmp));
PH = IFPP(1:N,:);
tmp = fft([PH;zeros(N,M)]);
FPH = tmp(1:N+1,:);
WFb = WFb + FPH;
PP是将远端信号的共轭乘以误差信号频谱,这一项用于调节步长,NLMS(步长=参考信号×步长×误差)的可变步长就提现在这里。PH是频域到时域的变换值。这和前面频域到时域的变换原理一样。WFb是权中系数的更新。
if mod(kk, 10*mult) == 0
WFbEn = sum(real(WFb.*conj(WFb)));
%WFbEn = sum(abs(WFb));
[tmp, dIdx] = max(WFbEn);
WFbD = sum(abs(WFb(:, dIdx)),2);
%WFbD = WFbD / (mean(WFbD) + 1e-10);
WFbD = min(max(WFbD, 0.5), 4);
end
dIdxV(kk) = dIdx;
上述的作用是更新dIdx和dIdxV。这里的更新并不是每一次都更新,一来是为了稳定,而来也是变相的减少计算量,提高实时性。就算是每一次都更新dIdx,WebRTC计算速度评估的结果也是很满意的。WFb是权重向量的频谱表示,WFbEn是权重向量按列求和,得到的是161的矩阵。这样得到的是16个块对权重的累加和。这样的区分度比直接累加和要大。
[tmp, dIdx] = max(WFbEn);作用就是找到16个块中权重累加和最大值及其对应的索引。
WFbD首先计算了权重最大那个块dIdx的列,然后将其按行求和,得到的就是651矩阵。WFbD不能低于0.5也不能高于4,算法中并未使用到,plot性能分析时用到。
最后把索引值dIdx存放到dIdxV(kk)中,这样每来一帧,就会有一个最大索引值放到dIdxV向量中。
##功率谱密度和相关性计算
###NLP
这里的NLP不是native language processing,而是Non-linear processing的意思。
ee = [eo;ekfb];
eo = ekfb;
window = wins;
上述作用是将上次的误差和ekfb组合,其中eo可以理解为error old。eo也确实保存了上一次的误差。window是简单将窗函数赋值。
tmp = fft(xx.*window);
xf = tmp(1:N+1);
tmp = fft(dd.*window);
df = tmp(1:N+1);
tmp = fft(ee.*window);
ef = tmp(1:N+1);
上述代码是把xx,dd,ee加窗后做FFT变换,并且取了 f s / 2 fs/2 fs/2的频谱部分存放到xf,df以及ef中。加窗的目的是为了减小频谱泄露,提高谱分辨率。
xfwm(:,1) = xf;
xf = xfwm(:,dIdx);
%fprintf(1,'%d: %f\n', kk, xf(4));
dfm(:,1) = df;
将xf存放到xfwm的第一列,xfwm是65*16的矩阵,df做类似处理。
然后把dIdx指向的那一列传给xf,dIdx是之前计算的权重矩阵能量最大的那块的索引,这样从xfwm矩阵里把真正要处理近端信号对应的远端信号(speaker,参考信号)获取到。
Se = gamma*Se + (1-gamma)*real(ef.*conj(ef));
Sd = gamma*Sd + (1-gamma)*real(df.*conj(df));
Sx = gamma*Sx + (1 - gamma)*real(xf.*conj(xf));
计算ef,df和xf的平滑功率谱,gamma这里取值是0.92.相对于8k信号取值略大。它们都是65*1的矩阵,包括了直流分量的能力,剩下的64点是 f s / 2 fs/2 fs/2及以下的频点能量。
Sxd = gamma*Sxd + (1 - gamma)*xf.*conj(df);
Sed = gamma*Sed + (1-gamma)*ef.*conj(df);
计算互功率谱,这里计算了远端信号和近端信号功率谱,如果该值较大,则说明它们的相关性较强,说明近端信号采集到了远端信号的概率很大,这时需要进行噪声抑制,同样的如果误差信号和近端信号功率谱较大,则说明估计的 y ^ \hat{y} y^是比较准的,误差信号里剩余的远端信号较少,需要进行噪声抑制的概率就小。它们也都是65*1矩阵,对应频点的bin。但是上述获得的是绝对值而非相对值,门限设置不容易,需要一个归一化的过程。归一化的过程可以通过求互相关得到。
cohed = real(Sed.*conj(Sed))./(Se.*Sd + 1e-10);
cohedAvg(kk) = mean(cohed(echoBandRange));
cohxd = real(Sxd.*conj(Sxd))./(Sx.*Sd + 1e-10);
如上,计算误差信号和近端信号的互相关,1e-10是为了防止除0报错。cohed越大,表示回声越小,cohxd越大,表示回声越大,这里就可以设置一个统一的门限评判上下限了。
cohedMean = mean(cohed(echoBandRange));
计算设置的echoBandRange里频点的均值,如果echoBandRange设置的过大,则低音部分如鼓点声则不易消掉。
hnled = min(1 - cohxd, cohed);
这里的作用就是把最小值赋值给hnled,该值越大,则说明越不需要消回声。之所以取二者判断,是为了最大可能性的消除掉回声。
[hnlSort, hnlSortIdx] = sort(1-cohxd(echoBandRange));
[xSort, xSortIdx] = sort(Sx);
对1-cohxd(echoBandRange)进行升序排序,同样对Sx也进行升序排序。
hnlSortQ = mean(1 - cohxd(echoBandRange));
对远端和近端信号的带内互相关求均值。hnlSortQ表示远端和近端不相关性的平均值,其值越大约没有回声,与cohed含义一致。
[hnlSort2, hnlSortIdx2] = sort(hnled(echoBandRange));
对hnled进行升序排序。
hnlQuant = 0.75;
hnlQuantLow = 0.5;
qIdx = floor(hnlQuant*length(hnlSort2));
qIdxLow = floor(hnlQuantLow*length(hnlSort2));
hnlPrefAvg = hnlSort2(qIdx);
hnlPrefAvgLow = hnlSort2(qIdxLow);
这里主要取了两个值,一个值取在了排序后的3/4处,一个值取在了排序后的1/2处。
if cohedMean > 0.98 & hnlSortQ > 0.9
suppState = 0;
elseif cohedMean < 0.95 | hnlSortQ < 0.8
suppState = 1;
end
如果误差和近端信号的互相关均值大于0.98,且远端和近端频带内的互不相关大于0.9,则说明不需要进行回声抑制,将suppState标志设置成0,如果误差和近端信号小于0.95或者远端和近端频带内信号不相关性小于0.8则需要进行印制,在这个范围之外的,回声抑制标志保持前一帧的状态。
if hnlSortQ < cohxdLocalMin & hnlSortQ < 0.75
cohxdLocalMin = hnlSortQ;
end
cohxdLocalMin的初始值是1,表示远端和近端完全不相关,这里判断计算得到的远端近端不相关性是否小于前一次的不相关性,如果小于且不相关性小于0.75,则更新cohxdLocalMin。
if cohxdLocalMin == 1
ovrd = 3;
hnled = 1-cohxd;
hnlPrefAvg = hnlSortQ;
hnlPrefAvgLow = hnlSortQ;
end
如果cohxdLocalMin=1,则说明要么是发现远端和近端完全不相关,要么就是cohxdLocalMin一直没有更新,既然不相关性很大,那么也说明有回声的可能性小,那么使用较小的ovrd(over-driven)值,和较大的hnled(65*1)值。
if suppState == 0
hnled = cohed;
hnlPrefAvg = cohedMean;
hnlPrefAvgLow = cohedMean;
end
如果suppState==0,则说明不需要进行回声消除,直接用误差近端相关性修正误差信号,hnl的两个均值读取cohed的均值,在这种情况下hnled的值接近于1.
if hnlPrefAvgLow < hnlLocalMin & hnlPrefAvgLow < 0.6
hnlLocalMin = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlMin = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlNewMin = 1;
hnlMinCtr = 0;
if hnlMinCtr == 0
hnlMinCtr = hnlMinCtr + 1;
else
hnlMinCtr = 0;
hnlMin = hnlLocalMin;
SeLocalMin = SeQ;
SdLocalMin = SdQ;
SeLocalAvg = 0;
minCtr = 0;
ovrd = max(log(0.0001)/log(hnlMin), 2);
divergeFact = hnlLocalMin;
end
end
hnlLocalMin是hnl系数的最小值,在满足这条判断的情况下发现了更小的值,需要对其进行更新,同时表标志设置成1,计数清0,这种情况下回声的概率较大,所以把ovrd设大以增强抑制能力。
if hnlMinCtr == 2
hnlNewMin = 0;
hnlMinCtr = 0;
ovrd = max(log(0.00000001)/(log(hnlMin + 1e-10) + 1e-10), 5);
end
hnlMinCtr==2,说明之前有满足<0.6的块使得hnlMinCtr=2,然后其下一块又没有满足<0.6的条件,进而更新了ovrd值。默认是和3比较取最大值,这里调节成5是为了增加抑制效果,实际情况还需要针对系统调试。
hnlLocalMin = min(hnlLocalMin + 0.0008/mult, 1);
cohxdLocalMin = min(cohxdLocalMin + 0.0004/mult, 1);
跟新上述两个值,mult是 f s / 8000 fs/8000 fs/8000,对于16kHz,就是2.就是0.0004和0.0002的差异。
if ovrd < ovrdSm
ovrdSm = 0.99*ovrdSm + 0.01*ovrd;
else
ovrdSm = 0.9*ovrdSm + 0.1*ovrd;
end
平滑更新ovrdSm,上述结果倾向于保持ovrdSm是一个较大的值,这个较大的值是为了尽量抑制回声。
ekEn = sum(Se);
dkEn = sum(Sd);
按行求和,物理意义分别是误差能量和近端信号能量。
##发散处理
if divergeState == 0
if ekEn > dkEn
ef = df;
divergeState = 1;
end
else
if ekEn*1.05 < dkEn
divergeState = 0;
else
ef = df;
end
end
如果不进行发散处理,误差能量大于近端能力,则用近端频谱更新误差频谱并把发散状态设置成1,如果误差能量的1.05倍小于近端能量,则发散处理标志设置成0.
if ekEn > dkEn*19.95
WFb=zeros(N+1,M); % Block-based FD NLMS
end
如果误差能量大于近端能量×19.95则,将权重系数矩阵设置成0.
ekEnV(kk) = ekEn;
dkEnV(kk) = dkEn;
相应能量存放在相应的向量中。
hnlLocalMinV(kk) = hnlLocalMin;
cohxdLocalMinV(kk) = cohxdLocalMin;
hnlMinV(kk) = hnlMin;
上述三个向量保存对应值。
##平滑滤波器系数和抑制指数
wCurve = [0; aggrFact*sqrt(linspace(0,1,N))' + 0.1];
权重系数曲线生成,线性均匀分布。
hnled = weight.*min(hnlPrefAvg, hnled) + (1 - weight).*hnled;
使用权重平滑hnled,wCurve分布是让65点中频率越高的点本次hnled占的比重越大,反之则以前的平滑结果所占比重大。
od = ovrdSm*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1))' + 1);
产生65*1的曲线,用作更新hnled的幂指数。
hnled = hnled.^(od.*sshift);
od作为幂指数跟新hnled。
##输出回声消除后的信号
hnl = hnled;
ef = ef.*(hnl);
用hnl系数与误差频谱相乘,即频域卷积,就是将误差信号通过了传递函数为hnnl的滤波器。
ovrdV(kk) = ovrdSm;
hnledAvg(kk) = 1-mean(1-cohed(echoBandRange));
hnlxdAvg(kk) = 1-mean(cohxd(echoBandRange));
hnlSortQV(kk) = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlPrefAvgV(kk) = hnlPrefAvg;
相关值的暂存
没有开启舒适噪声产生,则Fmix=ef。
% Overlap and add in time domain for smoothness
tmp = [Fmix ; flipud(conj(Fmix(2:N)))];
mixw = wins.*real(ifft(tmp));
mola = mbuf(end-N+1:end) + mixw(1:N);
mbuf = mixw;
ercn(pos:pos+N-1) = mola;
则使用重叠想加法获得时域平滑信号。
XFm(:,2:end) = XFm(:,1:end-1);
YFm(:,2:end) = YFm(:,1:end-1);
xfwm(:,2:end) = xfwm(:,1:end-1);
dfm(:,2:end) = dfm(:,1:end-1);
全体后移一个块,进入下一块迭代。
执行完了之后,如果想听回声消除后信号的声音,使用如下命令:
sound(10*ercn,16000)
其中16000是输入信号的频率。
整体的Matlab代码如下:
% Partitioned block frequency domain adaptive filtering NLMS and
% standard time-domain sample-based NLMS
%near is micphone captured signal
fid=fopen('near.pcm', 'rb'); % Load far end
ssin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
fclose(fid);
%far is speaker played music
fid=fopen('far.pcm', 'rb'); % Load fnear end
rrin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
fclose(fid);
rand('state',13);
fs=16000;
mult=fs/8000;
if fs == 8000
cohRange = 2:3;
elseif fs==16000
cohRange = 2;
end
% Flags
NLPon=1; % NLP on
CNon=0; % Comfort noise on
PLTon=0; % Plotting on
M = 16; % Number of partitions
N = 64; % Partition length
L = M*N; % Filter length
if fs == 8000
mufb = 0.6;
else
mufb = 0.8;
end
VADtd=48;
alp = 0.15; % Power estimation factor
alc = 0.1; % Coherence estimation factor
beta = 0.9; % Plotting factor
%% Changed a little %%
step = 0.1875;%0.1875; % Downward step size
%%
if fs == 8000
threshold=2e-6; % DTrob threshold
else
%threshold=0.7e-6;
threshold=1.5e-6;
end
if fs == 8000
echoBandRange = ceil(300*2/fs*N):floor(1800*2/fs*N);
else
echoBandRange = ceil(60*2/fs*N):floor(1500*2/fs*N);
end
suppState = 1;
transCtr = 0;
Nt=1;
vt=1;
ramp = 1.0003; % Upward ramp
rampd = 0.999; % Downward ramp
cvt = 20; % Subband VAD threshold;
nnthres = 20; % Noise threshold
shh=logspace(-1.3,-2.2,N+1)';
sh=[shh;flipud(shh(2:end-1))]; % Suppression profile
len=length(ssin);
w=zeros(L,1); % Sample-based TD(time domain) NLMS
WFb=zeros(N+1,M); % Block-based FD(frequency domain) NLMS
WFbOld=zeros(N+1,M); % Block-based FD NLMS
YFb=zeros(N+1,M);
erfb=zeros(len,1);
erfb3=zeros(len,1);
ercn=zeros(len,1);
zm=zeros(N,1);
XFm=zeros(N+1,M);
YFm=zeros(N+1,M);
pn0=10*ones(N+1,1);
pn=zeros(N+1,1);
NN=len;
Nb=floor(NN/N)-M;
erifb=zeros(Nb+1,1)+0.1;
erifb3=zeros(Nb+1,1)+0.1;
ericn=zeros(Nb+1,1)+0.1;
dri=zeros(Nb+1,1)+0.1;
start=1;
xo=zeros(N,1);
do=xo;
eo=xo;
echoBands=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohxdAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohxdSlow=zeros(Nb+1,N+1);
cohedSlow=zeros(Nb+1,N+1);
%overdriveM=zeros(Nb+1,N+1);
cohxdFastAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohxdAvgBad=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohedAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohedFastAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnledAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnlxdAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
ovrdV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
dIdxV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
SLxV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnlSortQV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnlPrefAvgV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
mutInfAvg=zeros(Nb+1,1);
%overdrive=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnled = zeros(N+1, 1);
weight=zeros(N+1,1);
hnlMax = zeros(N+1, 1);
hnl = zeros(N+1, 1);
overdrive = ones(1, N+1);
xfwm=zeros(N+1,M);
dfm=zeros(N+1,M);
WFbD=ones(N+1,1);
fbSupp = 0;
hnlLocalMin = 1;
cohxdLocalMin = 1;
hnlLocalMinV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
cohxdLocalMinV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
hnlMinV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
dkEnV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
ekEnV=zeros(Nb+1,1);
ovrd = 2;
ovrdPos = floor((N+1)/4);
ovrdSm = 2;
hnlMin = 1;
minCtr = 0;
SeMin = 0;
SdMin = 0;
SeLocalAvg = 0;
SeMinSm = 0;
divergeFact = 1;
dIdx = 1;
hnlMinCtr = 0;
hnlNewMin = 0;
divergeState = 0;
Sy=ones(N+1,1);
Sym=1e7*ones(N+1,1);
wins=[0;sqrt(hanning(2*N-1))];
ubufn=zeros(2*N,1);
ebuf=zeros(2*N,1);
ebuf2=zeros(2*N,1);
ebuf4=zeros(2*N,1);
mbuf=zeros(2*N,1);
cohedFast = zeros(N+1,1);
cohxdFast = zeros(N+1,1);
cohxd = zeros(N+1,1);
Se = zeros(N+1,1);
Sd = zeros(N+1,1);
Sx = zeros(N+1,1);
SxBad = zeros(N+1,1);
Sed = zeros(N+1,1);
Sxd = zeros(N+1,1);
SxdBad = zeros(N+1,1);
hnledp=[];
cohxdMax = 0;
hh=waitbar(0,'Please wait...');
%progressbar(0);
%spaces = ' ';
%spaces = repmat(spaces, 50, 1);
%spaces = ['[' ; spaces ; ']'];
%fprintf(1, spaces);
%fprintf(1, '\n');
for kk=1:Nb
pos = N * (kk-1) + start;
% FD block method
% ---------------------- Organize data
%far is speaker played music
xk = rrin(pos:pos+N-1);
%near is micphone captured signal
dk = ssin(pos:pos+N-1);
%----------------------- far end signal process
xx = [xo;xk];
xo = xk;
tmp = fft(xx);
XX = tmp(1:N+1);
dd = [do;dk]; % Overlap
do = dk;
tmp = fft(dd); % Frequency domain
DD = tmp(1:N+1);
% ------------------------far end Power estimation
pn0 = (1 - alp) * pn0 + alp * real(XX.* conj(XX));
pn = pn0;
% pn = (1 - alp) * pn + alp * M * pn0;
% ---------------------- Filtering
XFm(:,1) = XX;
for mm=0:(M-1)
m=mm+1;
YFb(:,m) = XFm(:,m) .* WFb(:,m);
end
yfk = sum(YFb,2);
tmp = [yfk ; flipud(conj(yfk(2:N)))];
ykt = real(ifft(tmp));
ykfb = ykt(end-N+1:end);
% ---------------------- Error estimation
ekfb = dk - ykfb;
%if sum(abs(ekfb)) < sum(abs(dk))
%ekfb = dk - ykfb;
% erfb(pos:pos+N-1) = ekfb;
%else
%ekfb = dk;
% erfb(pos:pos+N-1) = dk;
%end
%(kk-1)*(N*2)+1
erfb(pos:pos+N-1) = ekfb;
tmp = fft([zm;ekfb]); % FD version for cancelling part (overlap-save)
Ek = tmp(1:N+1);
% ------------------------ Adaptation
%Ek2 = Ek ./(M*pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
Ek2 = Ek ./(pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
absEf = max(abs(Ek2), threshold);
absEf = ones(N+1,1)*threshold./absEf;
Ek2 = Ek2.*absEf;
mEk = mufb.*Ek2;
PP = conj(XFm).*(ones(M,1) * mEk')';
tmp = [PP ; flipud(conj(PP(2:N,:)))];
IFPP = real(ifft(tmp));
PH = IFPP(1:N,:);
tmp = fft([PH;zeros(N,M)]);
FPH = tmp(1:N+1,:);
WFb = WFb + FPH;
% if mod(kk, 10*mult) == 0
WFbEn = sum(real(WFb.*conj(WFb)));
%WFbEn = sum(abs(WFb));
[tmp, dIdx] = max(WFbEn);
WFbD = sum(abs(WFb(:, dIdx)),2);
%WFbD = WFbD / (mean(WFbD) + 1e-10);
WFbD = min(max(WFbD, 0.5), 4);
% end
dIdxV(kk) = dIdx;
% NLP
if (NLPon)
ee = [eo;ekfb];
eo = ekfb;
window = wins;
if fs == 8000
gamma = 0.9;
else
gamma = 0.93;
end
tmp = fft(xx.*window);
xf = tmp(1:N+1);
tmp = fft(dd.*window);
df = tmp(1:N+1);
tmp = fft(ee.*window);
ef = tmp(1:N+1);
xfwm(:,1) = xf;
xf = xfwm(:,dIdx);
%fprintf(1,'%d: %f\n', kk, xf(4));
dfm(:,1) = df;
SxOld = Sx;
Se = gamma*Se + (1-gamma)*real(ef.*conj(ef));
Sd = gamma*Sd + (1-gamma)*real(df.*conj(df));
Sx = gamma*Sx + (1 - gamma)*real(xf.*conj(xf));
%xRatio = real(xfwm(:,1).*conj(xfwm(:,1))) ./ ...
% (real(xfwm(:,2).*conj(xfwm(:,2))) + 1e-10);
%xRatio = Sx ./ (SxOld + 1e-10);
%SLx = log(1/(N+1)*sum(xRatio)) - 1/(N+1)*sum(log(xRatio));
%SLxV(kk) = SLx;
% freqSm = 0.9;
% Sx = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sx);
% Sx(end:1) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sx(end:1));
% Se = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Se);
% Se(end:1) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Se(end:1));
% Sd = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sd);
% Sd(end:1) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sd(end:1));
%SeFast = ef.*conj(ef);
%SdFast = df.*conj(df);
%SxFast = xf.*conj(xf);
%cohedFast = 0.9*cohedFast + 0.1*SeFast ./ (SdFast + 1e-10);
%cohedFast(find(cohedFast > 1)) = 1;
%cohedFast(find(cohedFast > 1)) = 1 ./ cohedFast(find(cohedFast>1));
%cohedFastAvg(kk) = mean(cohedFast(echoBandRange));
%cohedFastAvg(kk) = min(cohedFast);
%cohxdFast = 0.8*cohxdFast + 0.2*log(SdFast ./ (SxFast + 1e-10));
%cohxdFastAvg(kk) = mean(cohxdFast(echoBandRange));
% coherence
Sxd = gamma*Sxd + (1 - gamma)*xf.*conj(df);
Sed = gamma*Sed + (1-gamma)*ef.*conj(df);
% Sxd = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sxd);
% Sxd(end:1) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sxd(end:1));
% Sed = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sed);
% Sed(end:1) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], Sed(end:1));
cohed = real(Sed.*conj(Sed))./(Se.*Sd + 1e-10);
cohedAvg(kk) = mean(cohed(echoBandRange));
%cohedAvg(kk) = cohed(6);
%cohedAvg(kk) = min(cohed);
cohxd = real(Sxd.*conj(Sxd))./(Sx.*Sd + 1e-10);
freqSm = 0.6;
cohxd(2:end) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], cohxd(2:end));
cohxd(end:2) = filter(freqSm, [1 -(1-freqSm)], cohxd(end:2));
cohxdAvg(kk) = mean(cohxd(echoBandRange));
%cohxdAvg(kk) = (cohxd(32));
%cohxdAvg(kk) = max(cohxd);
%xf = xfm(:,dIdx);
%SxBad = gamma*SxBad + (1 - gamma)*real(xf.*conj(xf));
%SxdBad = gamma*SxdBad + (1 - gamma)*xf.*conj(df);
%cohxdBad = real(SxdBad.*conj(SxdBad))./(SxBad.*Sd + 0.01);
%cohxdAvgBad(kk) = mean(cohxdBad);
%for j=1:N+1
% mutInf(j) = 0.9*mutInf(j) + 0.1*information(abs(xfm(j,:)), abs(dfm(j,:)));
%end
%mutInfAvg(kk) = mean(mutInf);
%hnled = cohedFast;
%xIdx = find(cohxd > 1 - cohed);
%hnled(xIdx) = 1 - cohxd(xIdx);
%hnled = 1 - max(cohxd, 1-cohedFast);
hnled = min(1 - cohxd, cohed);
%hnled = 1 - cohxd;
%hnled = max(1 - (cohxd + (1-cohedFast)), 0);
%hnled = 1 - max(cohxd, 1-cohed);
if kk > 1
cohxdSlow(kk,:) = 0.99*cohxdSlow(kk-1,:) + 0.01*cohxd';
cohedSlow(kk,:) = 0.99*cohedSlow(kk-1,:) + 0.01*(1-cohed)';
end
if 0
%if kk > 50
%idx = find(hnled > 0.3);
hnlMax = hnlMax*0.9999;
%hnlMax(idx) = max(hnlMax(idx), hnled(idx));
hnlMax = max(hnlMax, hnled);
%overdrive(idx) = max(log(hnlMax(idx))/log(0.99), 1);
avgHnl = mean(hnlMax(echoBandRange));
if avgHnl > 0.3
overdrive = max(log(avgHnl)/log(0.99), 1);
end
weight(4:end) = max(hnlMax) - hnlMax(4:end);
end
%[hg, gidx] = max(hnled);
%fnrg = Sx(gidx) / (Sd(gidx) + 1e-10);
%[tmp, bidx] = find((Sx / Sd + 1e-10) > fnrg);
%hnled(bidx) = hg;
%cohed1 = mean(cohed(cohRange)); % range depends on bandwidth
%cohed1 = cohed1^2;
%echoBands(kk) = length(find(cohed(echoBandRange) < 0.25))/length(echoBandRange);
%if (fbSupp == 0)
% if (echoBands(kk) > 0.8)
% fbSupp = 1;
% end
%else
% if (echoBands(kk) < 0.6)
% fbSupp = 0;
% end
%end
%overdrive(kk) = 7.5*echoBands(kk) + 0.5;
% Factor by which to weight other bands
%if (cohed1 < 0.1)
% w = 0.8 - cohed1*10*0.4;
%else
% w = 0.4;
%end
% Weight coherence subbands
%hnled = w*cohed1 + (1 - w)*cohed;
%hnled = (hnled).^2;
%cohed(floor(N/2):end) = cohed(floor(N/2):end).^2;
%if fbSupp == 1
% cohed = zeros(size(cohed));
%end
%cohed = cohed.^overdrive(kk);
%hnled = gamma*hnled + (1 - gamma)*cohed;
% Additional hf suppression
%hnledp = [hnledp ; mean(hnled)];
%hnled(floor(N/2):end) = hnled(floor(N/2):end).^2;
%ef = ef.*((weight*(min(1 - hnled)).^2 + (1 - weight).*(1 - hnled)).^2);
cohedMean = mean(cohed(echoBandRange));
%aggrFact = 4*(1-mean(hnled(echoBandRange))) + 1;
%[hnlSort, hnlSortIdx] = sort(hnled(echoBandRange));
[hnlSort, hnlSortIdx] = sort(1-cohxd(echoBandRange));
[xSort, xSortIdx] = sort(Sx);
%aggrFact = (1-mean(hnled(echoBandRange)));
%hnlSortQ = hnlSort(qIdx);
hnlSortQ = mean(1 - cohxd(echoBandRange));
%hnlSortQ = mean(1 - cohxd);
[hnlSort2, hnlSortIdx2] = sort(hnled(echoBandRange));
%[hnlSort2, hnlSortIdx2] = sort(hnled);
hnlQuant = 0.75;
hnlQuantLow = 0.5;
qIdx = floor(hnlQuant*length(hnlSort2));
qIdxLow = floor(hnlQuantLow*length(hnlSort2));
hnlPrefAvg = hnlSort2(qIdx);
hnlPrefAvgLow = hnlSort2(qIdxLow);
%hnlPrefAvgLow = mean(hnled);
%hnlPrefAvg = max(hnlSort2);
%hnlPrefAvgLow = min(hnlSort2);
%hnlPref = hnled(echoBandRange);
%hnlPrefAvg = mean(hnlPref(xSortIdx((0.5*length(xSortIdx)):end)));
%hnlPrefAvg = min(hnlPrefAvg, hnlSortQ);
%hnlSortQIdx = hnlSortIdx(qIdx);
%SeQ = Se(qIdx + echoBandRange(1) - 1);
%SdQ = Sd(qIdx + echoBandRange(1) - 1);
%SeQ = Se(qIdxLow + echoBandRange(1) - 1);
%SdQ = Sd(qIdxLow + echoBandRange(1) - 1);
%propLow = length(find(hnlSort < 0.1))/length(hnlSort);
%aggrFact = min((1 - hnlSortQ)/2, 0.5);
%aggrTerm = 1/aggrFact;
%hnlg = mean(hnled(echoBandRange));
%hnlg = hnlSortQ;
%if suppState == 0
% if hnlg < 0.05
% suppState = 2;
% transCtr = 0;
% elseif hnlg < 0.75
% suppState = 1;
% transCtr = 0;
% end
%elseif suppState == 1
% if hnlg > 0.8
% suppState = 0;
% transCtr = 0;
% elseif hnlg < 0.05
% suppState = 2;
% transCtr = 0;
% end
%else
% if hnlg > 0.8
% suppState = 0;
% transCtr = 0;
% elseif hnlg > 0.25
% suppState = 1;
% transCtr = 0;
% end
%end
%if kk > 50
if cohedMean > 0.98 & hnlSortQ > 0.9
%if suppState == 1
% hnled = 0.5*hnled + 0.5*cohed;
% %hnlSortQ = 0.5*hnlSortQ + 0.5*cohedMean;
% hnlPrefAvg = 0.5*hnlPrefAvg + 0.5*cohedMean;
%else
% hnled = cohed;
% %hnlSortQ = cohedMean;
% hnlPrefAvg = cohedMean;
%end
suppState = 0;
elseif cohedMean < 0.95 | hnlSortQ < 0.8
%if suppState == 0
% hnled = 0.5*hnled + 0.5*cohed;
% %hnlSortQ = 0.5*hnlSortQ + 0.5*cohedMean;
% hnlPrefAvg = 0.5*hnlPrefAvg + 0.5*cohedMean;
%end
suppState = 1;
end
if hnlSortQ < cohxdLocalMin & hnlSortQ < 0.75
cohxdLocalMin = hnlSortQ;
end
if cohxdLocalMin == 1
ovrd = 3;
hnled = 1-cohxd;
hnlPrefAvg = hnlSortQ;
hnlPrefAvgLow = hnlSortQ;
end
if suppState == 0
hnled = cohed;
hnlPrefAvg = cohedMean;
hnlPrefAvgLow = cohedMean;
end
%if hnlPrefAvg < hnlLocalMin & hnlPrefAvg < 0.6
if hnlPrefAvgLow < hnlLocalMin & hnlPrefAvgLow < 0.6
%hnlLocalMin = hnlPrefAvg;
%hnlMin = hnlPrefAvg;
hnlLocalMin = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlMin = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlNewMin = 1;
hnlMinCtr = 0;
if hnlMinCtr == 0
hnlMinCtr = hnlMinCtr + 1;
else
hnlMinCtr = 0;
hnlMin = hnlLocalMin;
SeLocalMin = SeQ;
SdLocalMin = SdQ;
SeLocalAvg = 0;
minCtr = 0;
ovrd = max(log(0.0001)/log(hnlMin), 2);
divergeFact = hnlLocalMin;
end
end
if hnlNewMin == 1
hnlMinCtr = hnlMinCtr + 1;
end
if hnlMinCtr == 2
hnlNewMin = 0;
hnlMinCtr = 0;
%ovrd = max(log(0.0001)/log(hnlMin), 2);
% ovrd = max(log(0.00001)/(log(hnlMin + 1e-10) + 1e-10), 3);
ovrd = max(log(0.00000001)/(log(hnlMin + 1e-10) + 1e-10), 5);
%ovrd = max(log(0.0001)/log(hnlPrefAvg), 2);
%ovrd = max(log(0.001)/log(hnlMin), 2);
end
hnlLocalMin = min(hnlLocalMin + 0.0008/mult, 1);
cohxdLocalMin = min(cohxdLocalMin + 0.0004/mult, 1);
%divergeFact = hnlSortQ;
%if minCtr > 0 & hnlLocalMin < 1
% hnlMin = hnlLocalMin;
% %SeMin = 0.9*SeMin + 0.1*sqrt(SeLocalMin);
% SdMin = sqrt(SdLocalMin);
% %SeMin = sqrt(SeLocalMin)*hnlSortQ;
% SeMin = sqrt(SeLocalMin);
% %ovrd = log(100/SeMin)/log(hnlSortQ);
% %ovrd = log(100/SeMin)/log(hnlSortQ);
% ovrd = log(0.01)/log(hnlMin);
% ovrd = max(ovrd, 2);
% ovrdPos = hnlSortQIdx;
% %ovrd = max(ovrd, 1);
% %SeMin = sqrt(SeLocalAvg/5);
% minCtr = 0;
%else
% %SeLocalMin = 0.9*SeLocalMin +0.1*SeQ;
% SeLocalAvg = SeLocalAvg + SeQ;
% minCtr = minCtr + 1;
%end
if ovrd < ovrdSm
ovrdSm = 0.99*ovrdSm + 0.01*ovrd;
else
ovrdSm = 0.9*ovrdSm + 0.1*ovrd;
end
%end
% ekEn = sum(real(ekfb.^2));
% dkEn = sum(real(dk.^2));
ekEn = sum(Se);
dkEn = sum(Sd);
if divergeState == 0
if ekEn > dkEn
ef = df;
divergeState = 1;
%hnlPrefAvg = hnlSortQ;
%hnled = (1 - cohxd);
end
else
%if ekEn*1.1 < dkEn
%if ekEn*1.26 < dkEn
if ekEn*1.05 < dkEn
divergeState = 0;
else
ef = df;
end
end
if ekEn > dkEn*19.95
WFb=zeros(N+1,M); % Block-based FD NLMS
end
ekEnV(kk) = ekEn;
dkEnV(kk) = dkEn;
hnlLocalMinV(kk) = hnlLocalMin;
cohxdLocalMinV(kk) = cohxdLocalMin;
hnlMinV(kk) = hnlMin;
%cohxdMaxLocal = max(cohxdSlow(kk,:));
%if kk > 50
%cohxdMaxLocal = 1-hnlSortQ;
%if cohxdMaxLocal > 0.5
% %if cohxdMaxLocal > cohxdMax
% odScale = max(log(cohxdMaxLocal)/log(0.95), 1);
% %overdrive(7:end) = max(log(cohxdSlow(kk,7:end))/log(0.9), 1);
% cohxdMax = cohxdMaxLocal;
% end
%end
%end
%cohxdMax = cohxdMax*0.999;
%overdriveM(kk,:) = max(overdrive, 1);
%aggrFact = 0.25;
aggrFact = 0.3;
%aggrFact = 0.5*propLow;
%if fs == 8000
% wCurve = [0 ; 0 ; aggrFact*sqrt(linspace(0,1,N-1))' + 0.1];
%else
% wCurve = [0; 0; 0; aggrFact*sqrt(linspace(0,1,N-2))' + 0.1];
%end
wCurve = [0; aggrFact*sqrt(linspace(0,1,N))' + 0.1];
% For sync with C
%if fs == 8000
% wCurve = wCurve(2:end);
%else
% wCurve = wCurve(1:end-1);
%end
%weight = aggrFact*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1)'));
%weight = aggrFact*wCurve;
weight = wCurve;
%weight = aggrFact*ones(N+1,1);
%weight = zeros(N+1,1);
%hnled = weight.*min(hnled) + (1 - weight).*hnled;
%hnled = weight.*min(mean(hnled(echoBandRange)), hnled) + (1 - weight).*hnled;
%hnled = weight.*min(hnlSortQ, hnled) + (1 - weight).*hnled;
%hnlSortQV(kk) = mean(hnled);
%hnlPrefAvgV(kk) = mean(hnled(echoBandRange));
hnled = weight.*min(hnlPrefAvg, hnled) + (1 - weight).*hnled;
%od = aggrFact*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1)') + aggrTerm);
%od = 4*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1)') + 1/4);
%ovrdFact = (ovrdSm - 1) / sqrt(ovrdPos/(N+1));
%ovrdFact = ovrdSm / sqrt(echoBandRange(floor(length(echoBandRange)/2))/(N+1));
%od = ovrdFact*sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1))' + 1;
%od = ovrdSm*ones(N+1,1).*abs(WFb(:,dIdx))/(max(abs(WFb(:,dIdx)))+1e-10);
%od = ovrdSm*ones(N+1,1);
%od = ovrdSm*WFbD.*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1))' + 1);
od = ovrdSm*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1))' + 1);
%od = 4*(sqrt(linspace(0,1,N+1))' + 1);
%od = 2*ones(N+1,1);
%od = 2*ones(N+1,1);
%sshift = ((1-hnled)*2-1).^3+1;
sshift = ones(N+1,1);
hnled = hnled.^(od.*sshift);
%if hnlg > 0.75
%if (suppState ~= 0)
% transCtr = 0;
%end
% suppState = 0;
%elseif hnlg < 0.6 & hnlg > 0.2
% suppState = 1;
%elseif hnlg < 0.1
%hnled = zeros(N+1, 1);
%if (suppState ~= 2)
% transCtr = 0;
%end
% suppState = 2;
%else
% if (suppState ~= 2)
% transCtr = 0;
% end
% suppState = 2;
%end
%if suppState == 0
% hnled = ones(N+1, 1);
%elseif suppState == 2
% hnled = zeros(N+1, 1);
%end
%hnled(find(hnled < 0.1)) = 0;
%hnled = hnled.^2;
%if transCtr < 5
%hnl = 0.75*hnl + 0.25*hnled;
% transCtr = transCtr + 1;
%else
hnl = hnled;
%end
%hnled(find(hnled < 0.05)) = 0;
ef = ef.*(hnl);
%ef = ef.*(min(1 - cohxd, cohed).^2);
%ef = ef.*((1-cohxd).^2);
ovrdV(kk) = ovrdSm;
%ovrdV(kk) = dIdx;
%ovrdV(kk) = divergeFact;
%hnledAvg(kk) = 1-mean(1-cohedFast(echoBandRange));
hnledAvg(kk) = 1-mean(1-cohed(echoBandRange));
hnlxdAvg(kk) = 1-mean(cohxd(echoBandRange));
%hnlxdAvg(kk) = cohxd(5);
%hnlSortQV(kk) = mean(hnled);
hnlSortQV(kk) = hnlPrefAvgLow;
hnlPrefAvgV(kk) = hnlPrefAvg;
%hnlAvg(kk) = propLow;
%ef(N/2:end) = 0;
%ner = (sum(Sd) ./ (sum(Se.*(hnl.^2)) + 1e-10));
% Comfort noise
if (CNon)
snn=sqrt(Sym);
snn(1)=0; % Reject LF noise
Un=snn.*exp(j*2*pi.*[0;rand(N-1,1);0]);
% Weight comfort noise by suppression
Un = sqrt(1-hnled.^2).*Un;
Fmix = ef + Un;
else
Fmix = ef;
end
% Overlap and add in time domain for smoothness
tmp = [Fmix ; flipud(conj(Fmix(2:N)))];
mixw = wins.*real(ifft(tmp));
mola = mbuf(end-N+1:end) + mixw(1:N);
mbuf = mixw;
ercn(pos:pos+N-1) = mola;%%%%%-------------you can hear the effect by sound(10*ercn,16000),add by Shichaog
end % NLPon
% Filter update
% Ek2 = Ek ./(12*pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
% Ek2 = Ek2 * divergeFact;
Ek2 = Ek ./(pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
%Ek2 = Ek ./(100*pn + 0.001); % Normalized error
%divergeIdx = find(abs(Ek) > abs(DD));
%divergeIdx = find(Se > Sd);
%threshMod = threshold*ones(N+1,1);
%if length(divergeIdx) > 0
%if sum(abs(Ek)) > sum(abs(DD))
%WFb(divergeIdx,:) = WFb(divergeIdx,:) .* repmat(sqrt(Sd(divergeIdx)./(Se(divergeIdx)+1e-10))),1,M);
%Ek2(divergeIdx) = Ek2(divergeIdx) .* sqrt(Sd(divergeIdx)./(Se(divergeIdx)+1e-10));
%Ek2(divergeIdx) = Ek2(divergeIdx) .* abs(DD(divergeIdx))./(abs(Ek(divergeIdx))+1e-10);
%WFb(divergeIdx,:) = WFbOld(divergeIdx,:);
%WFb = WFbOld;
%threshMod(divergeIdx) = threshMod(divergeIdx) .* abs(DD(divergeIdx))./(abs(Ek(divergeIdx))+1e-10);
% threshMod(divergeIdx) = threshMod(divergeIdx) .* sqrt(Sd(divergeIdx)./(Se(divergeIdx)+1e-10));
%end
%absEf = max(abs(Ek2), threshold);
%absEf = ones(N+1,1)*threshold./absEf;
%absEf = max(abs(Ek2), threshMod);
%absEf = threshMod./absEf;
%Ek2 = Ek2.*absEf;
%if sum(Se) <= sum(Sd)
% mEk = mufb.*Ek2;
% PP = conj(XFm).*(ones(M,1) * mEk')';
% tmp = [PP ; flipud(conj(PP(2:N,:)))];
% IFPP = real(ifft(tmp));
% PH = IFPP(1:N,:);
% tmp = fft([PH;zeros(N,M)]);
% FPH = tmp(1:N+1,:);
% %WFbOld = WFb;
% WFb = WFb + FPH;
%else
% WF = WFbOld;
%end
% Shift old FFTs
XFm(:,2:end) = XFm(:,1:end-1);
YFm(:,2:end) = YFm(:,1:end-1);
xfwm(:,2:end) = xfwm(:,1:end-1);
dfm(:,2:end) = dfm(:,1:end-1);
%if mod(kk, floor(Nb/50)) == 0
% fprintf(1, '.');
%end
if mod(kk, floor(Nb/100)) == 0
%if mod(kk, floor(Nb/500)) == 0
%progressbar(kk/Nb);
%figure(5)
%plot(abs(WFb));
%legend('1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10','11','12');
%title(kk*N/fs);
%figure(6)
%plot(WFbD);
%figure(6)
%plot(threshMod)
%if length(divergeIdx) > 0
% plot(abs(DD))
% hold on
% plot(abs(Ek), 'r')
% hold off
%plot(min(sqrt(Sd./(Se+1e-10)),1))
%axis([0 N 0 1]);
%end
%figure(6)
%plot(cohedFast);
%axis([1 N+1 0 1]);
%plot(WFbEn);
%figure(7)
%plot(weight);
%plot([cohxd 1-cohed]);
%plot([cohxd 1-cohed 1-cohedFast hnled]);
%plot([cohxd cohxdFast/max(cohxdFast)]);
%legend('cohxd', '1-cohed', '1-cohedFast');
%axis([1 65 0 1]);
%pause(0.5);
%overdrive
end
end
%progressbar(1);
%figure(2);
%plot([feat(:,1) feat(:,2)+1 feat(:,3)+2 mfeat+3]);
%plot([feat(:,1) mfeat+1]);
%figure(3);
%plot(10*log10([dri erifb erifb3 ericn]));
%legend('Near-end','Error','Post NLP','Final',4);
% Compensate for delay
%ercn=[ercn(N+1:end);zeros(N,1)];
%ercn_=[ercn_(N+1:end);zeros(N,1)];
%figure(11);
%plot(cohxdSlow);
%figure(12);
%surf(cohxdSlow);
%shading interp;
%figure(13);
%plot(overdriveM);
%figure(14);
%surf(overdriveM);
%shading interp;
figure(10);
t = (0:Nb)*N/fs;
rrinSubSamp = rrin(N*(1:(Nb+1)));
plot(t, rrinSubSamp/max(abs(rrinSubSamp)),'b');
hold on
plot(t, hnledAvg, 'r');
plot(t, hnlxdAvg, 'g');
plot(t, hnlSortQV, 'y');
plot(t, hnlLocalMinV, 'k');
plot(t, cohxdLocalMinV, 'c');
plot(t, hnlPrefAvgV, 'm');
%plot(t, cohxdAvg, 'r');
%plot(cohxdFastAvg, 'r');
%plot(cohxdAvgBad, 'k');
%plot(t, cohedAvg, 'k');
%plot(t, 1-cohedFastAvg, 'k');
%plot(ssin(N*(1:floor(length(ssin)/N)))/max(abs(ssin)));
%plot(echoBands,'r');
%plot(overdrive, 'g');
%plot(erfb(N*(1:floor(length(erfb)/N)))/max(abs(erfb)));
hold off
%tight x;
% figure(11)
% plot(t, ovrdV);
%tightx;
%plot(mfeat,'r');
%plot(1-cohxyp_,'r');
%plot(Hnlxydp,'y');
%plot(hnledp,'k');
%plot(Hnlxydp, 'c');
%plot(ccohpd_,'k');
%plot(supplot_, 'g');
%plot(ones(length(mfeat),1)*rr1_, 'k');
%plot(ones(length(mfeat),1)*rr2_, 'k');
%plot(N*(1:length(feat)), feat);
%plot(Sep_,'r');
%axis([1 floor(length(erfb)/N) -1 1])
%hold off
%plot(10*log10([Se_, Sx_, Seu_, real(sf_.*conj(sf_))]));
%legend('Se','Sx','Seu','S');
%figure(5)
%plot([ercn ercn_]);
% figure(12)
% plot(t, dIdxV);
%plot(t, SLxV);
%tightx;
%figure(13)
%plot(t, [ekEnV dkEnV]);
%plot(t, dkEnV./(ekEnV+1e-10));
%tightx;
%close(hh);
%spclab(fs,ssin,erfb,ercn,'outxd.pcm');
%spclab(fs,rrin,ssin,erfb,1.78*ercn,'vqeOut-1.pcm');
%spclab(fs,erfb,'aecOutLp.pcm');
%spclab(fs,rrin,ssin,erfb,1.78*ercn,'aecOut25.pcm','vqeOut-1.pcm');
%spclab(fs,rrin,ssin,erfb,ercn,'aecOut-mba.pcm');
%spclab(fs,rrin,ssin,erfb,ercn,'aecOut.pcm');
%spclab(fs, ssin, erfb, ercn, 'out0.pcm');
#speex AEC算法
和WebRTC一样也是采用频域分块自适应滤波方法,不同的是权重调整的方式变化,我这边测试效果是计算量比WebRTC的大,且效果调节的没有WebRTC的好。这里也给出speex的源代码和测试方法。
% Copyright (C) 2012 Waves Audio LTD
% Copyright (C) 2003-2008 Jean-Marc Valin
%
% File: speex_mdf.m
% Echo canceller based on the MDF algorithm (see below)
%
% Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
% modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
% met:
%
% 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
% this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
%
% 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
% notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
% documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
%
% 3. The name of the author may not be used to endorse or promote products
% derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
%
% THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR
% IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
% OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
% DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
% INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
% (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
% SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
% HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT,
% STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
% ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
% POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
%
% Notes from original mdf.c:
%
% The echo canceller is based on the MDF algorithm described in:
%
% J. S. Soo, K. K. Pang Multidelay block frequency adaptive filter,
% IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process., Vol. ASSP-38, No. 2,
% February 1990.
%
% We use the Alternatively Updated MDF (AUMDF) variant. Robustness to
% double-talk is achieved using a variable learning rate as described in:
%
% Valin, J.-M., On Adjusting the Learning Rate in Frequency Domain Echo
% Cancellation With Double-Talk. IEEE Transactions on Audio,
% Speech and Language Processing, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 1030-1034, 2007.
% http://people.xiph.org/~jm/papers/valin_taslp2006.pdf
%
% There is no explicit double-talk detection, but a continuous variation
% in the learning rate based on residual echo, double-talk and background
% noise.
%
% Another kludge that seems to work good: when performing the weight
% update, we only move half the way toward the "goal" this seems to
% reduce the effect of quantization noise in the update phase. This
% can be seen as applying a gradient descent on a "soft constraint"
% instead of having a hard constraint.
%
% Notes for this file:
%
% Usage:
%
% speex_mdf_out = speex_mdf(Fs, u, d, filter_length, frame_size, dbg_var_name);
%
% Fs sample rate
% u speaker signal, column vector in range [-1; 1]
% d microphone signal, column vector in range [-1; 1]
% filter_length typically 250ms, i.e. 4096 @ 16k FS
% must be a power of 2
% frame_size typically 8ms, i.e. 128 @ 16k Fs
% must be a power of 2
% dbg_var_name internal state variable name to trace.
% Default: 'st.leak_estimate'.
%
% Jonathan Rouach
%
function speex_mdf_out = speex_mdf(Fs, u, d, filter_length, frame_size, dbg_var_name)
fprintf('Starting Speex MDF (PBFDAF) algorithm.\n');
st = speex_echo_state_init_mc_mdf(frame_size, filter_length, 1, 1, Fs);
% which variable to trace
if nargin<6
dbg_var_name = 'st.leak_estimate';
end
dbg = init_dbg(st, length(u));
[e, dbg] = main_loop(st, float_to_short(u), float_to_short(d), dbg);
speex_mdf_out.e = e/32768.0;
speex_mdf_out.var1 = dbg.var1;
function x = float_to_short(x)
x = x*32768.0;
x(x< -32767.5) = -32768;
x(x> 32766.5) = 32767;
x = floor(0.5+x);
end
function [e, dbg] = main_loop(st, u, d, dbg)
e = zeros(size(u));
y = zeros(size(u));
% prepare waitbar
try h_wb = waitbar(0, 'Processing...'); catch; end
end_point = length(u);
for n = 1:st.frame_size:end_point
nStep = floor(n/st.frame_size)+1;
if mod(nStep, 128)==0 && update_waitbar_check_wasclosed(h_wb, n, end_point, st.sampling_rate)
break;
end
u_frame = u(n:n+st.frame_size-1);
d_frame = d(n:n+st.frame_size-1);
[out, st] = speex_echo_cancellation_mdf(st, d_frame, u_frame);
e(n:n+st.frame_size-1) = out*2;
y(n:n+st.frame_size-1) = d_frame - out;
dbg.var1(:, nStep) = reshape( eval(dbg_var_name), numel(eval(dbg_var_name)), 1);
end
try close(h_wb); catch; end
end
function st = speex_echo_state_init_mc_mdf(frame_size, filter_length, nb_mic, nb_speakers, sample_rate)
st.K = nb_speakers;
st.C = nb_mic;
C=st.C;
K=st.K;
st.frame_size = frame_size;
st.window_size = 2*frame_size;
N = st.window_size;
st.M = fix((filter_length+st.frame_size-1)/frame_size);
M = st.M;
st.cancel_count=0;
st.sum_adapt = 0;
st.saturated = 0;
st.screwed_up = 0;
% /* This is the default sampling rate */
st.sampling_rate = sample_rate;
st.spec_average = (st.frame_size)/( st.sampling_rate);
st.beta0 = (2.0*st.frame_size)/st.sampling_rate;
st.beta_max = (.5*st.frame_size)/st.sampling_rate;
st.leak_estimate = 0;
st.e = zeros(N, C);
st.x = zeros(N, K);
st.input = zeros(st.frame_size, C);
st.y = zeros(N, C);
st.last_y = zeros(N, C);
st.Yf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Rf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Xf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Yh = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Eh = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.X = zeros(N, K, M+1);
st.Y = zeros(N, C);
st.E = zeros(N, C);
st.W = zeros(N, K, M, C);
st.foreground = zeros(N, K, M, C);
st.PHI = zeros(frame_size+1, 1);
st.power = zeros(frame_size+1, 1);
st.power_1 = ones((frame_size+1), 1);
st.window = zeros(N, 1);
st.prop = zeros(M, 1);
st.wtmp = zeros(N, 1);
st.window = .5-.5*cos(2*pi*((1:N)'-1)/N);
% /* Ratio of ~10 between adaptation rate of first and last block */
decay = exp(-1/M);
st.prop(1, 1) = .7;
for i=2:M
st.prop(i, 1) = st.prop(i-1, 1) * decay;
end
st.prop = (.8 * st.prop)./sum(st.prop);
st.memX = zeros(K, 1);
st.memD = zeros(C, 1);
st.memE = zeros(C, 1);
st.preemph = .98;
if (st.sampling_rate<12000)
st.notch_radius = .9;
elseif (st.sampling_rate<24000)
st.notch_radius = .982;
else
st.notch_radius = .992;
end
st.notch_mem = zeros(2*C, 1);
st.adapted = 0;
st.Pey = 1;
st.Pyy = 1;
st.Davg1 = 0; st.Davg2 = 0;
st.Dvar1 = 0; st.Dvar2 = 0;
end
function dbg = init_dbg(st, len)
dbg.var1 = zeros(numel(eval(dbg_var_name)), fix(len/st.frame_size));
end
function [out, st] = speex_echo_cancellation_mdf(st, in, far_end)
N = st.window_size;
M = st.M;
C = st.C;
K = st.K;
Pey_cur = 1;
Pyy_cur = 1;
out = zeros(st.frame_size, C);
st.cancel_count = st.cancel_count + 1;
%ss=.35/M;
ss = 0.5/M;
ss_1 = 1-ss;
for chan = 1:C
% Apply a notch filter to make sure DC doesn't end up causing problems
[st.input(:, chan), st.notch_mem(:, chan)] = filter_dc_notch16(in(:, chan), st.notch_radius, st.frame_size, st.notch_mem(:, chan));
% Copy input data to buffer and apply pre-emphasis
for i=1:st.frame_size
tmp32 = st.input(i, chan)- (st.preemph* st.memD(chan));
st.memD(chan) = st.input(i, chan);
st.input(i, chan) = tmp32;
end
end
for speak = 1:K
for i =1:st.frame_size
st.x(i, speak) = st.x(i+st.frame_size, speak);
tmp32 = far_end(i, speak) - st.preemph * st.memX(speak);
st.x(i+st.frame_size, speak) = tmp32;
st.memX(speak) = far_end(i, speak);
end
end
% Shift memory
st.X = circshift(st.X, [0, 0, 1]);
for speak = 1:K
% Convert x (echo input) to frequency domain
% MATLAB_MATCH: we divide by N to get values as in speex
st.X(:, speak, 1) = fft(st.x(:, speak)) /N;
end
Sxx = 0;
for speak = 1:K
Sxx = Sxx + sum(st.x(st.frame_size+1:end, speak).^2);
st.Xf = abs(st.X(1:st.frame_size+1, speak, 1)).^2;
end
Sff = 0;
for chan = 1:C
% Compute foreground filter
st.Y(:, chan) = 0;
for speak=1:K
for j=1:M
st.Y(:, chan) = st.Y(:, chan) + st.X(:, speak, j) .* st.foreground(:, speak, j, chan);
end
end
% MATLAB_MATCH: we multiply by N to get values as in speex
st.e(:, chan) = ifft(st.Y(:, chan)) * N;
st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan) = st.input(:, chan) - st.e(st.frame_size+1:end, chan);
% st.e : [out foreground | leak foreground ]
Sff = Sff + sum(abs(st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan)).^2);
end
% Adjust proportional adaption rate */
if (st.adapted)
st.prop = mdf_adjust_prop (st.W, N, M, C, K);
end
% Compute weight gradient */
if (st.saturated == 0)
for chan = 1:C
for speak = 1:K
for j=M:-1:1
st.PHI = [st.power_1; st.power_1(end-1:-1:2)] .* st.prop(j) .* conj(st.X(:, speak, (j+1))) .* st.E(:, chan);
st.W(:, j) = st.W(:, j) + st.PHI;
end
end
end
else
st.saturated = st.saturated -1;
end
%FIXME: MC conversion required */
% Update weight to prevent circular convolution (MDF / AUMDF)
for chan = 1:C
for speak = 1:K
for j = 1:M
% This is a variant of the Alternatively Updated MDF (AUMDF) */
% Remove the "if" to make this an MDF filter */
if (j==1 || mod(2+st.cancel_count,(M-1)) == j)
st.wtmp = ifft(st.W(:, speak, j, chan));
st.wtmp(st.frame_size+1:N) = 0;
st.W(:, speak, j, chan) = fft(st.wtmp);
end
end
end
end
% So we can use power_spectrum_accum */
st.Yf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Rf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Xf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
Dbf = 0;
for chan = 1:C
st.Y(:, chan) = 0;
for speak=1:K
for j=1:M
st.Y(:, chan) = st.Y(:, chan) + st.X(:, speak, j) .* st.W(:, speak, j, chan);
end
end
% MATLAB_MATCH: we multiply by N to get values as in speex
st.y(:,chan) = ifft(st.Y(:,chan)) * N;
% st.y : [ ~ | leak background ]
end
See = 0;
% Difference in response, this is used to estimate the variance of our residual power estimate */
for chan = 1:C
st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan) = st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan) - st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan);
Dbf = Dbf + 10 + sum(abs(st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan)).^2);
st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan) = st.input(:, chan) - st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan);
% st.e : [ out background | leak foreground ]
See = See + sum(abs(st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan)).^2);
end
% Logic for updating the foreground filter */
% For two time windows, compute the mean of the energy difference, as well as the variance */
VAR1_UPDATE = .5;
VAR2_UPDATE = .25;
VAR_BACKTRACK = 4;
MIN_LEAK = .005;
st.Davg1 = .6*st.Davg1 + .4*(Sff-See);
st.Davg2 = .85*st.Davg2 + .15*(Sff-See);
st.Dvar1 = .36*st.Dvar1 + .16*Sff*Dbf;
st.Dvar2 = .7225*st.Dvar2 + .0225*Sff*Dbf;
update_foreground = 0;
% Check if we have a statistically significant reduction in the residual echo */
% Note that this is *not* Gaussian, so we need to be careful about the longer tail */
if (Sff-See)*abs(Sff-See) > (Sff*Dbf)
update_foreground = 1;
elseif (st.Davg1* abs(st.Davg1) > (VAR1_UPDATE*st.Dvar1))
update_foreground = 1;
elseif (st.Davg2* abs(st.Davg2) > (VAR2_UPDATE*(st.Dvar2)))
update_foreground = 1;
end
% Do we update? */
if (update_foreground)
st.Davg1 = 0;
st.Davg2 = 0;
st.Dvar1 = 0;
st.Dvar2 = 0;
st.foreground = st.W;
% Apply a smooth transition so as to not introduce blocking artifacts */
for chan = 1:C
st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan) = (st.window(st.frame_size+1:N) .* st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan)) + (st.window(1:st.frame_size) .* st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan));
end
else
reset_background=0;
% Otherwise, check if the background filter is significantly worse */
if (-(Sff-See)*abs(Sff-See)> VAR_BACKTRACK*(Sff*Dbf))
reset_background = 1;
end
if ((-st.Davg1 * abs(st.Davg1))> (VAR_BACKTRACK*st.Dvar1))
reset_background = 1;
end
if ((-st.Davg2* abs(st.Davg2))> (VAR_BACKTRACK*st.Dvar2))
reset_background = 1;
end
if (reset_background)
% Copy foreground filter to background filter */
st.W = st.foreground;
% We also need to copy the output so as to get correct adaptation */
for chan = 1:C
st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan) = st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan);
st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan) = st.input(:, chan) - st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan);
end
See = Sff;
st.Davg1 = 0;
st.Davg2 = 0;
st.Dvar1 = 0;
st.Dvar2 = 0;
end
end
Sey = 0;
Syy = 0;
Sdd = 0;
for chan = 1:C
% Compute error signal (for the output with de-emphasis) */
for i=1:st.frame_size
tmp_out = st.input(i, chan)- st.e(i+st.frame_size, chan);
tmp_out = tmp_out + st.preemph * st.memE(chan);
% This is an arbitrary test for saturation in the microphone signal */
if (in(i,chan) <= -32000 || in(i,chan) >= 32000)
if (st.saturated == 0)
st.saturated = 1;
end
end
out(i, chan) = tmp_out;
st.memE(chan) = tmp_out;
end
% Compute error signal (filter update version) */
st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan) = st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan);
st.e(1:st.frame_size, chan) = 0;
% st.e : [ zeros | out background ]
% Compute a bunch of correlations */
% FIXME: bad merge */
Sey = Sey + sum(st.e(st.frame_size+1:N, chan) .* st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan));
Syy = Syy + sum(st.y(st.frame_size+1:N, chan).^2);
Sdd = Sdd + sum(st.input.^2);
% Convert error to frequency domain */
% MATLAB_MATCH: we divide by N to get values as in speex
st.E = fft(st.e) / N;
st.y(1:st.frame_size, chan) = 0;
% MATLAB_MATCH: we divide by N to get values as in speex
st.Y = fft(st.y) / N;
% Compute power spectrum of echo (X), error (E) and filter response (Y) */
st.Rf = abs(st.E(1:st.frame_size+1,chan)).^2;
st.Yf = abs(st.Y(1:st.frame_size+1,chan)).^2;
end
% Do some sanity check */
if (~(Syy>=0 && Sxx>=0 && See >= 0))
% Things have gone really bad */
st.screwed_up = st.screwed_up + 50;
out = out*0;
elseif Sff > Sdd+ N*10000
% AEC seems to add lots of echo instead of removing it, let's see if it will improve */
st.screwed_up = st.screwed_up + 1;
else
% Everything's fine */
st.screwed_up=0;
end
if (st.screwed_up>=50)
disp('Screwed up, full reset');
st = speex_echo_state_reset_mdf(st);
end
% Add a small noise floor to make sure not to have problems when dividing */
See = max(See, N* 100);
for speak = 1:K
Sxx = Sxx + sum(st.x(st.frame_size+1:end, speak).^2);
st.Xf = abs(st.X(1:st.frame_size+1, speak, 1)).^2;
end
% Smooth far end energy estimate over time */
st.power = ss_1*st.power+ 1 + ss*st.Xf;
% Compute filtered spectra and (cross-)correlations */
Eh_cur = st.Rf - st.Eh;
Yh_cur = st.Yf - st.Yh;
Pey_cur = Pey_cur + sum(Eh_cur.*Yh_cur) ;
Pyy_cur = Pyy_cur + sum(Yh_cur.^2);
st.Eh = (1-st.spec_average)*st.Eh + st.spec_average*st.Rf;
st.Yh = (1-st.spec_average)*st.Yh + st.spec_average*st.Yf;
Pyy = sqrt(Pyy_cur);
Pey = Pey_cur/Pyy;
% Compute correlation updatete rate */
tmp32 = st.beta0*Syy;
if (tmp32 > st.beta_max*See)
tmp32 = st.beta_max*See;
end
alpha = tmp32/ See;
alpha_1 = 1- alpha;
% Update correlations (recursive average) */
st.Pey = alpha_1*st.Pey + alpha*Pey;
st.Pyy = alpha_1*st.Pyy + alpha*Pyy;
if st.Pyy<1
st.Pyy =1;
end
% We don't really hope to get better than 33 dB (MIN_LEAK-3dB) attenuation anyway */
if st.Pey< MIN_LEAK * st.Pyy
st.Pey = MIN_LEAK * st.Pyy;
end
if (st.Pey> st.Pyy)
st.Pey = st.Pyy;
end
% leak_estimate is the linear regression result */
st.leak_estimate = st.Pey/st.Pyy;
% This looks like a stupid bug, but it's right (because we convert from Q14 to Q15) */
if (st.leak_estimate > 16383)
st.leak_estimate = 32767;
end
% Compute Residual to Error Ratio */
RER = (.0001*Sxx + 3.*st.leak_estimate*Syy) / See;
% Check for y in e (lower bound on RER) */
if (RER < Sey*Sey/(1+See*Syy))
RER = Sey*Sey/(1+See*Syy);
end
if (RER > .5)
RER = .5;
end
% We consider that the filter has had minimal adaptation if the following is true*/
if (~st.adapted && st.sum_adapt > M && st.leak_estimate*Syy > .03*Syy)
st.adapted = 1;
end
if (st.adapted)
% Normal learning rate calculation once we're past the minimal adaptation phase */
for i=1:st.frame_size+1
% Compute frequency-domain adaptation mask */
r = st.leak_estimate*st.Yf(i);
e = st.Rf(i)+1;
if (r>.5*e)
r = .5*e;
end
r = 0.7*r + 0.3*(RER*e);
%st.power_1[i] = adapt_rate*r/(e*(1+st.power[i]));*/
st.power_1(i) = (r/(e*st.power(i)+10));
end
else
% Temporary adaption rate if filter is not yet adapted enough */
adapt_rate=0;
if (Sxx > N* 1000)
tmp32 = 0.25* Sxx;
if (tmp32 > .25*See)
tmp32 = .25*See;
end
adapt_rate = tmp32/ See;
end
st.power_1 = adapt_rate./(st.power+10);
% How much have we adapted so far? */
st.sum_adapt = st.sum_adapt+adapt_rate;
end
% FIXME: MC conversion required */
st.last_y(1:st.frame_size) = st.last_y(st.frame_size+1:N);
if (st.adapted)
% If the filter is adapted, take the filtered echo */
st.last_y(st.frame_size+1:N) = in-out;
end
end
function [out,mem] = filter_dc_notch16(in, radius, len, mem)
out = zeros(size(in));
den2 = radius*radius + .7*(1-radius)*(1-radius);
for i=1:len
vin = in(i);
vout = mem(1) + vin;
mem(1) = mem(2) + 2*(-vin + radius*vout);
mem(2) = vin - (den2*vout);
out(i) = radius*vout;
end
end
function prop = mdf_adjust_prop(W, N, M, C, K)
prop = zeros(M,1);
for i=1:M
tmp = 1;
for chan=1:C
for speak=1:K
tmp = tmp + sum(abs(W(1:N/2+1, K, i, C)).^2);
end
end
prop(i) = sqrt(tmp);
end
max_sum = max(prop, 1);
prop = prop + .1*max_sum;
prop_sum = 1+sum(prop);
prop = .99*prop / prop_sum;
end
% Resets echo canceller state */
function st = speex_echo_state_reset_mdf(st)
st.cancel_count=0;
st.screwed_up = 0;
N = st.window_size;
M = st.M;
C=st.C;
K=st.K;
st.e = zeros(N, C);
st.x = zeros(N, K);
st.input = zeros(st.frame_size, C);
st.y = zeros(N, C);
st.last_y = zeros(N, C);
st.Yf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Rf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Xf = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Yh = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.Eh = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.X = zeros(N, K, M+1);
st.Y = zeros(N, C);
st.E = zeros(N, C);
st.W = zeros(N, K, M, C);
st.foreground = zeros(N, K, M, C);
st.PHI = zeros(N, 1);
st.power = zeros(st.frame_size+1, 1);
st.power_1 = ones((st.frame_size+1), 1);
st.window = zeros(N, 1);
st.prop = zeros(M, 1);
st.wtmp = zeros(N, 1);
st.memX = zeros(K, 1);
st.memD = zeros(C, 1);
st.memE = zeros(C, 1);
st.saturated = 0;
st.adapted = 0;
st.sum_adapt = 0;
st.Pey = 1;
st.Pyy = 1;
st.Davg1 = 0;
st.Davg2 = 0;
st.Dvar1 = 0;
st.Dvar2 = 0;
end
function was_closed = update_waitbar_check_wasclosed(h, n, end_point, Fs)
was_closed = 0;
% update waitbar
try
waitbar(n/end_point, h, ['Processing... ', num2str(n/Fs, '%.2f'), 's / ', num2str(end_point/Fs, '%.2f'), 's' ]);
catch ME
% if it's no longer there (closed by user)
if (strcmp(ME.identifier(1:length('MATLAB:waitbar:')), 'MATLAB:waitbar:'))
was_closed = 1; % then get out of the loop
end
end
end
end
##测试方法
首先需要自己读取文件并设置相关的初始值
给出自己的一个样例
fid=fopen('near.pcm', 'rb'); % Load far end
ssin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
fid=fopen('far.pcm', 'rb'); % Load fnear end
rrin=fread(fid,inf,'float32');
ssin=ssin(1:4096*200);
rrin=rrin(1:4096*200);
Fs=16000;
filter_length=4096;
frame_size=128;
speex_mdf_out = speex_mdf(Fs, rrin, ssin, filter_length, frame_size);
执行完之后,需要播放出来听:
sound(speex_mdf_out.e,16000)
##代码里名词术语
RERL:ERL+ERLE
RERL:residual_echo_return_loss
ERL:echo_return_loss
ERLE:echo_return_loss_enhancement
psd:power spectral density 功率谱密度
x: far end
d: near end
e: error
s: psd
nlp:non-linear processing
