java1.8源码之ArrayList源码解读
文章目录
- 一、ArrayList概述
- 1.1 ArrayList简介
- 1.2 ArrayList数据结构
- 二、ArrayList源码分析
- 2.1 ArrayList继承结构和层次关系
- 2.2 类的属性
- 2.3 构造方法
- 2.4 主要方法
- 2.4.1 get()方法
- 2.4.2 set()方法
- 2.4.3 add()方法
- 2.4.4 remove()方法
- 2.4.5 indexOf()和lastIndexOf()方法
- 2.4.6 clear()方法
- 三、总结
一、ArrayList概述
1.1 ArrayList简介
ArrayList经常用,今天对它的源码探究一二。
一上来顶部有一大串注释,顶部注释参考了这篇博客内容如下:
List接口的大小可变数组的实现。实现了所有可选列表操作,并允许包括null在内的所有元素。除了实现List接口外,此类还提供一些方法来操作内部用来存储列表的数组的大小。(此类大致上等同于Vector类,除了此类是不同步的。)
size、isEmpty、get、set、iterator和listIterator操作都以固定时间运行。add操作以分摊的固定时间运行,也就是说,添加n个元素需要O(n)时间。其他所有操作都以线性时间运行(大体上讲)。与用于LinkedList实现的常数因子相比,此实现的常数因子较低。
每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量。该容量是指用来存储列表元素的数组的大小。它总是至少等于列表的大小。随着向ArrayList中不断添加元素,其容量也自动增长。并未指定增长策略的细节,因为这不只是添加元素会带来分摊固定时间开销那样简单。
在添加大量元素前,应用程序可以使用ensureCapacity操作来增加ArrayList实例的容量。这可以减少递增式再分配的数量。
注意,此实现不是同步的。如果多个线程同时访问一个ArrayList实例,而其中至少一个线程从结构上修改了列表,那么它必须保持外部同步。(结构上的修改是指任何添加或删除一个或多个元素的操作,或者显式调整底层数组的大小;仅仅设置元素的值不是结构上的修改。)这一般通过对自然封装该列表的对象进行同步操作来完成。如果不存在这样的对象,则应该使用Collections.synchronizedList方法将该列表“包装”起来。这最好在创建时完成,以防止意外对列表进行不同步的访问:
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(…));
此类的iterator和listIterator方法返回的迭代器是快速失败的:在创建迭代器之后,除非通过迭代器自身的remove或add方法从结构上对列表进行修改,否则在任何时间以任何方式对列表进行修改,迭代器都会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,面对并发的修改,迭代器很快就会完全失败,而不是冒着在将来某个不确定时间发生任意不确定行为的风险。
注意,迭代器的快速失败行为无法得到保证,因为一般来说,不可能对是否出现不同步并发修改做出任何硬性保证。快速失败迭代器会尽最大努力抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,为提高这类迭代器的正确性而编写一个依赖于此异常的程序是错误的做法:迭代器的快速失败行为应该仅用于检测bug。
此类是Java Collections Framework的成员。
顶部的注释给我们透露了几点重要信息:ArrayList是List接口的大小可变数组的实现;ArrayList允许null元素;ArrayList的容量可以自动增长;ArrayList不是同步的;ArrayList的iterator和listIterator方法返回的迭代器是fail-fast的
1.2 ArrayList数据结构
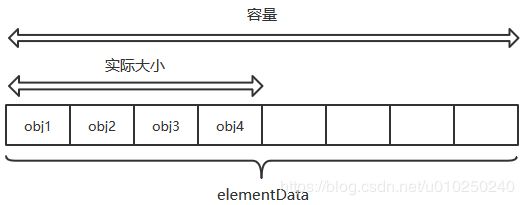
容量:CAPACITY ; 实际大小:size;
ArrayList底层的数据结构就是数组,数组元素类型为Object类型,即可以存放所有类型数据。我们对ArrayList类的实例的所有的操作底层都是基于数组的。
二、ArrayList源码分析
2.1 ArrayList继承结构和层次关系
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- ArrayList:说明ArrayList支持泛型。
- extends AbstractList :继承了AbstractList。为什么要先继承AbstractList,而让AbstractList先实现List?而不是让ArrayList直接实现List?
这里是有一个思想,接口中全都是抽象的方法,而抽象类中可以有抽象方法,还可以有具体的实现方法,正是利用了这一点,让AbstractList是实现接口中一些通用的方法,而具体的类, 如ArrayList就继承这个AbstractList类,拿到一些通用的方法,然后自己在实现一些自己特有的方法,这样一来,让代码更简洁,就继承结构最底层的类中通用的方法都抽取出来,先一起实现了,减少重复代码。所以一般看到一个类上面还有一个抽象类,应该就是这个作用。 - 实现了List接口:ArrayList的父类AbstractList也实现了List接口,那为什么子类ArrayList还是去实现一遍呢?collection 的作者Josh说他写这代码的时候觉得这个会有用处,但是其实并没什么用,但因为没什么影响,就一直留到了现在。
- 实现了RandomAccess接口:表明ArrayList支持快速(通常是固定时间)随机访问。在ArrayList中,我们可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象,这就是快速随机访问。
- 实现了Cloneable接口:实现了该接口,就可以使用Object.Clone()方法了。
- implements java.io.Serializable:表明该类具有序列化功能,该类可以被序列化,什么是序列化?简单的说,就是能够从类变成字节流传输,然后还能从字节流变成原来的类。
2.2 类的属性
// 序列化id
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity. 默认的初始化容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
* 指定该ArrayList容量为0时,返回该空数组。
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* 当调用无参构造方法,返回的是该数组。刚创建一个ArrayList 时,其内数据量为0。
* 它与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的区别就是:该数组是默认返回的,而EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是在用户指定容量为0时返回。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* 保存添加到ArrayList中的元素。
* ArrayList的容量就是该数组的长度。
* 该值为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 时,当第一次添加元素进入ArrayList中时,数组将扩容值DEFAULT_CAPACITY。
* 被标记为transient,在对象被序列化的时候不会被序列化。
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* ArrayList的实际大小(数组包含的元素个数/实际数据的数量)默认为0
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
/**
* 分派给arrays的最大容量
* 为什么要减去8呢?
* 因为某些VM会在数组中保留一些头字,尝试分配这个最大存储容量,可能会导致array容量大于VM的limit,最终导致OutOfMemoryError。
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//备注:MAX.VALUE为0x7fffffff,转换成十进制就是2147483647,也就是数组的最大长度是2147483639;
2.3 构造方法
ArrayList提供了三种构造方法:
- ArrayList(int initialCapacity):构造一个指定容量为capacity的空ArrayList。这是一个带初始容量大小的有参构造函数。
- 初始容量大于0,实例化数组,将自定义的容量大小当成初始化elementData的大小
- 初始容量等于0,将空数组赋给elementData
- 初始容量小于0,抛异常
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
* 构造具有指定初始容量的空List
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list (list的初始化容量)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity is negative
* 如果指定的初始容量为负,抛出异常
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
- ArrayList():构造一个初始容量为 10 的空列表。如果我们创建ArrayList对象的时候不传入参数,则使用此无参构造方法创建ArrayList对象。从前面我们可以知道DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是一个空的Object[],将elementData初始化,elementData也是个Object[]类型。空的Object[]会给默认容量10。但是这里我们并没有看到数组的容量变为10啊,那么什么时候会被初始化为10的数组呢?答案是有元素被加入时(add方法).当进行第一次add的时候,elementData将会变成默认的长度:10。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
* 构造一个初始容量为10的空列表
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
- ArrayList(Collection c):构造一个包含指定 collection 的元素的列表,这些元素是按照该 collection 的迭代器返回它们的顺序排列的。第二个有参构造方法构造时赋的值是它的父类Collection对象。
- 将collection对象转换成数组,然后将数组的地址的赋给elementData。
- 如果数组的实际大小等于0(c中没有元素),将空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA赋值给elementData
- 如果size的值大于0,则执行Arrays.copy方法,把collection对象的内容(可以理解为深拷贝)copy到elementData中。
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*构造一个包含指定 collection 的元素的列表,这些元素是按照该 collection 的迭代器返回它们的顺序排列的。
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* 其元素将放置在此列表中的 collection
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 如果指定的 collection 为 null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//每个集合的toarray()的实现方法不一样,所以需要判断一下,如果不是Object[].class类型,那么就需要使用ArrayList中的方法去改造一下。
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//copyOf(要复制的数组,要返回的副本的长度,要返回的副本的类)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
ArrayList的构造方法就做一件事情,就是初始化一下储存数据的容器,其实本质上就是一个数组,在其中就叫elementData。
2.4 主要方法
2.4.1 get()方法
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
* 返回list中指定位置的元素
* @param index index of the element to return 要返回的元素的索引
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
位于list中指定位置的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);//越界检查
return elementData(index);//返回索引为index的元素
}
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
检查指定索引是否在范围内。如果不在,抛出一个运行时异常。
这个方法不检查索引是否为负数,它总是在数组访问之前立即优先使用,
如果给出的索引index>=size,抛出一个越界异常
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
// Positional Access Operations 位置访问操作
// 返回索引为index的元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
从代码中可以看到,因为ArrayList底层是数组,所以它的get方法非常简单,先是判断一下有没有越界(索引小于0或者大于等于数组实际长度,错误信息返回索引和数组的实际长度),之后就直接通过数组下标来获取元素。
2.4.2 set()方法
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
* 用指定的元素替换列表中指定位置的元素。
* @param index index of the element to replace 要替换的元素的索引
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position 要存储在指定位置的元素
* @return the element previously at the specified position 先前位于指定位置的元素(返回被替换的元素)
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 如果参数指定索引index>=size,抛出一个越界异常
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
//检查索引是否越界。如果参数指定索引index>=size,抛出一个越界异常
rangeCheck(index);
//记录被替换的元素(旧值)
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//替换元素(新值)
elementData[index] = element;
//返回被替换的元素
return oldValue;
}
确保set的位置小于当前数组的长度(size)并且大于0,获取指定位置(index)元素,然后放到oldValue存放,将需要设置的元素放到指定的位置(index)上,然后将原来位置上的元素oldValue返回给用户。
2.4.3 add()方法
add的方法有两个,一个是带一个参数的,一个是带两个参数的。
- boolean add(E e)方法
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾
* @param e element to be appended to this list 被添加到list的元素
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//确认list容量,如果不够,容量加1。注意:只加1,保证资源不被浪费
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将元素e放在size的位置上,并且size++
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//数组容量检查,不够时则进行扩容,只供类内部使用
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
// 若elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,则取minCapacity为DEFAULT_CAPACITY和参数minCapacity之间的最大值。DEFAULT_CAPACITY在此之前已经定义为默认的初始化容量是10。
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
//数组容量检查,不够时则进行扩容,只供类内部使用
// minCapacity 想要的最小容量
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
//最小容量>数组缓冲区当前长度
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);//扩容
}
这个add 方法是在list的末尾添加一个元素。
size是数组中数据的个数,因为要添加一个元素,所以size+1,先判断size+1的这个个数数组能否放得下。calculateCapacity方法用来计算容量。判断初始化的elementData是不是空的数组,如果是空数组长度size就是0,否则数组长度就不是0。
- 如果elementData元素是空的,就是第一次添加元素,minCapacity=size+1,其实就是等于1,空的数组没有长度就存放不了,所以就将minCapacity变成10,也就是默认容量的大小。也就是elementData数组的此时需要的最小容量为变10了,此时ensureExplicitCapacity()方法中的minCapacity就是10。到此只是说elementData数组需要的容量至少是10,还没有改变elementData的大小。
- 如果elementData数组中的元素不是空的,那么它此时需要的最小容量就是原先的数组长度加1,minCapacity代表着elementData中元素增加之后的实际数据个数。
- 要始终记住minCapacity = size+1,在ensureExplicitCapacity()方法中,首先操作数自增1,再把需要的最小空间容量与数组当前实际长度进行比较:
- 如果elementData中的元素是空的,它现在需要的容量是10,但是elementData.length为0,所以要扩容。
- 如果elementData数组中的元素不是空的,若它添加一个元素后需要的容量比原数组长度大,就需要扩容,否则就不需要扩容。
我们接着往下看,ArrayList能自动扩展大小的关键方法就在下面的grow()方法里:
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*扩容,保证ArrayList至少能存储minCapacity个元素
* 第一次扩容,逻辑为newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);即在原有的容量基础上增加一半。
第一次扩容后,如果容量还是小于minCapacity,就将容量扩充为minCapacity。
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// 获取当前数组的容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 扩容。新的容量=当前容量+当前容量/2.即将当前容量增加一半(当前容量增加1.5倍)。
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//如果扩容后的容量还是小于想要的最小容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
//将扩容后的容量再次扩容为想要的最小容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//elementData就空数组的时候,length=0,那么oldCapacity=0,newCapacity=0,在这里就是真正的初始化elementData的大小了,就是为10.
//如果扩容后的容量大于临界值,则进行大容量分配
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//新的容量大小已经确定好了,就copy数组,改变容量大小。
//copyof(原数组,新的数组长度)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
//进行大容量分配
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//如果minCapacity<0,抛出异常
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
//如果想要的容量大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,则分配Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则分配MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
综合以上在list末尾追加数据的方法,如果原数组是空的,添加1个元素时数组容量变为10,如果原数组不为空,追加元素时容量变为原来的1.5倍。如果扩容后的容量大于分配给ArrayList的容量,判断需要的容量是否比分派的容量大,是就把Integer.MAX_VALUE:2147483647赋值给minCapacity,否就用MAX_ARRAY_SIZE:2147483639。
我们调用add方法时,函数调用过程如下:
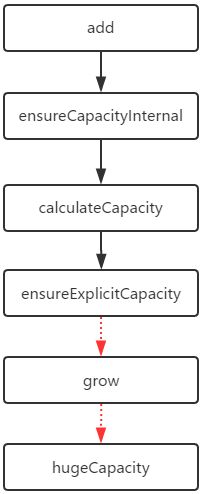
程序调用add,如果需要扩容就可能会调用到grow,grow可能会调用hugeCapacity。
例1(扩容的情况):
List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<Integer>();
lists.add(8);
初始化lists大小为0,调用的ArrayList()的空参构造函数,那么在调用lists.add(8)方法时,经过的步骤如下:
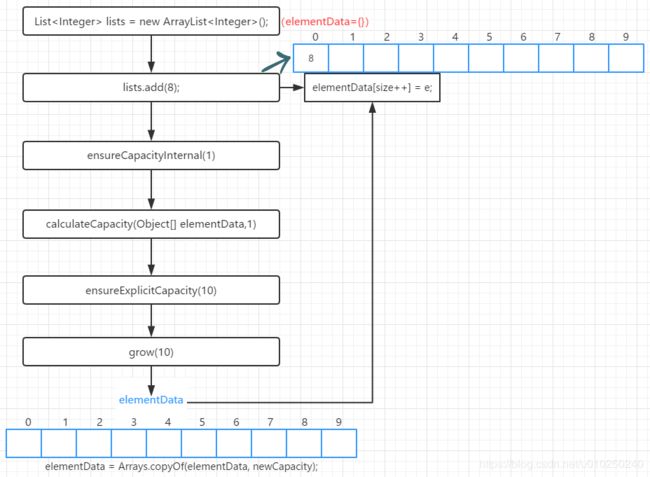
我们可以看到,在add方法之前开始elementData = {};调用add方法时会继续调用,直至grow,最后elementData的大小变为10,之后再返回到add函数,把8放在elementData[0]中。
例2(不扩容的情况):
List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<Integer>(6);
lists.add(8);
调用的ArrayList(int)型构造函数,initialCapacity 等于 6,elementData = new Object[6],elementData被初始化为大小为6的Object数组,在调用add(8)方法时,具体的步骤如下:

在调用add方法之前,elementData的大小已经为6,之后再进行传递,不会进行扩容处理。
- void add(int index, E element)方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*将指定元素插入到列表中的指定位置。将当前位于该位置的元素(如果有的话)和随后的任何元素向右移动(将一个元素添加到它们的索引中)。
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* 要插入指定元素的索引(即将插入元素的位置)
* @param element element to be inserted 即将插入的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 如果索引超出size
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//越界检查
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//确认list容量,如果不够,容量加1。注意:只加1,保证资源不被浪费
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 对数组进行复制处理,目的就是空出index的位置插入element,并将index后的元素位移一个位置
//在插入元素之前,要先将index之后的元素都往后移一位
//arraycopy(原数组,源数组中的起始位置,目标数组,目标数据中的起始位置,要复制的数组元素的数量)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//将指定的index位置赋值为element
elementData[index] = element;
//实际容量+1
size++;
}
/**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)//插入的位置不能大于size 和小于0,如果是就报越界异常
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
在指定的位置添加元素,也就是插入元素。
举例:在索引2处添加元素e,大概过程如下:
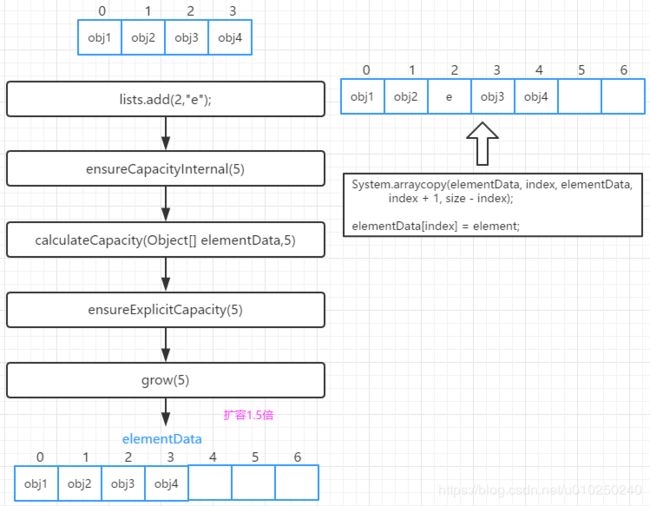
add(int index, E e)需要先对元素进行移动,然后完成插入操作。
2.4.4 remove()方法
- 根据索引remove,通过删除指定位置上的元素
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*删除list中位置为指定索引index的元素
* 索引之后的元素向左移一位
* @param index the index of the element to be removed 被删除元素的索引
* @return the element that was removed from the list 被删除的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 如果参数指定索引index>=size,抛出一个越界异常
*/
public E remove(int index) {
//检查索引是否越界。如果参数指定索引index>=size,抛出一个越界异常
rangeCheck(index);
//结构性修改次数+1
modCount++;
//记录索引处的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 删除指定元素后,需要左移的元素个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
//如果有需要左移的元素,就移动(移动后,该删除的元素就已经被覆盖了)
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// size减一,然后将索引为size-1处的元素置为null。为了让GC起作用,必须显式的为最后一个位置赋null值
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
//返回被删除的元素
return oldValue;
}
从中我们可以看到根据索引删除元素的步骤:
- 进行越界检查
- 记录修改次数(modCount 可以用来检测快速失败的一种标志。)
- 通过索引找到要删除的元素
- 计算要移动的位数
- 移动元素(其实是覆盖掉要删除的元素)
- 将–size上的位置赋值为null,让gc(垃圾回收机制)更快的回收它。
- 返回被删除的元素
- 根据对象remove
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* i such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))
* (if such an element exists). Returns true if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*从列表中删除指定元素的第一个出现项,
如果它存在的话。如果列表不包含该元素,它将保持不变。更正式地说,删除索引最低的元素...
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return true if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
私有的remove方法,该方法跳过边界检查,并且不返回已删除的值。
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//arraycopy(原数组,源数组中的起始位置,目标数组,目标数据中的起始位置,要复制的数组元素的数量)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
循环遍历所有对象,得到对象所在索引位置,然后调用fastRemove方法,执行remove操作。
定位到需要remove的元素索引,先将index后面的元素往前面移动一位(调用System.arraycooy实现),然后将最后一个元素置空。
这里最主要是知道arrayList可以存储null值。
- removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
* 从该列表中删除索引位于两者之间的所有元素,包含fromIndex,但是不包含toIndex,
* 将任何后续元素向左移动(减少它们的索引)
* 这个调用通过{@code (toIndex - fromIndex)}元素缩短列表。
*(如果{@code toIndex==fromIndex},此操作无效。)
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* fromIndex >= size() ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;//被删除的索引后面的个数
//arraycopy(原数组,源数组中的起始位置,目标数组,目标数据中的起始位置,要复制的数组元素的数量)
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// clear to let GC do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);//新数组的长度
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
size = newSize;
}
此方法删除fromIndex到toIndex之间的全部元素,把toIndex以后的元素移动(size-toIndex)位,把左移后空的元素置为null好让垃圾回收机制回收内存,最后把新数组的大小赋值给size。
可以对比下jdk11的写法:
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
outOfBoundsMsg(fromIndex, toIndex));
}
modCount++;
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi);
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
- removeAll(Collection c) 和retainAll(Collection c)
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
//删除指定集合中的所有元素
return batchRemove(c, false, 0, size);
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
//检测两个集合是否有交集
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement, final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);//非空检查
final Object[] es = elementData;//原集合
int r;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from;; r++) {//from等于0,end等于size
if (r == end)
return false;
//判断集合c中是否包含原集合中的当前元素
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
//如果包含则跳出循环
break;
}
int w = r++;//w等于0
try {
for (Object e; r < end; r++)//r等于1
//判断集合c中是否包含原集合中的当前元素
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement)
//如果包含则直接保存
es[w++] = e;
} catch (Throwable ex) {// 如果 c.contains() 抛出异常
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,even if c.contains() throws.
// 复制剩余的元素,将剩下的元素都赋值给原集合
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r);
//w为当前集合的length
w += end - r;
throw ex;
} finally {
modCount += end - w;
//这里有两个用途,在removeAll()时,w一直为0,就直接跟clear一样,全是为null。 //retainAll():没有一个交集返回true,有交集但不全交也返回true,而两个集合相等的时候,返回false,所以不能根据返回值来确认两个集合是否有交集,而是通过原集合的大小是否发生改变来判断,如果原集合中还有元素,则代表有交集,而元集合没有元素了,说明两个集合没有交集。
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
}
return true;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
int indexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
//一开始start为0,end等于size
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
//移除元素的核心操作
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
//arraycopy(原数组,源数组中的起始位置,目标数组,目标数据中的起始位置,要复制的数组元素的数量)
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi);
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
1、boolean retainAll(Collection c)
仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)。换句话说,移除此 collection 中未包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素。
2、list.retainAll(list2):
(1)如果集合list=list2即两个集合元素完全一样 返回值为false;
(2)list包含于list2中 返回值为false;
(3)其他 返回值为true。
理解:如果集合A数组的大小没有改变,则返回false。如果集合A和集合B是完全相同的集合,也会返回false。即使两个集合没有交集,也会返回true。
当集合A的大小改变的时候返回的是True,大小没有改变的时候返回的是False。通过判断集合的大小,来确定是否存在交集。不能通过方法返回的True和False来判断。
3、实际上该方法是指:如果集合list中的元素都在集合list2中则list中的元素不做移除操作,反之如果只要有一个不在list2中则会进行移除操作。
即:list进行移除操作返回值为:true,反之返回值则为false。
2.4.5 indexOf()和lastIndexOf()方法
//返回此列表中指定元素的第一个出现项的索引,如果该列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) { // 查找的元素为空
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) // 遍历数组,找到第一个为空的元素,返回下标
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else { // 查找的元素不为空
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) // 遍历数组,找到第一个和指定元素相等的元素,返回下标
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//返回此列表中指定元素的最后一次出现的索引,如果该列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
2.4.6 clear()方法
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
从列表中删除所有元素。该调用返回后,列表将为空。
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
三、总结
1)arrayList可以存放null。
2)arrayList本质上就是一个elementData数组。
3)arrayList区别于数组的地方在于能够自动扩展大小,其中关键的方法就是gorw()方法。
4)arrayList中removeAll(collection c)和clear()的区别就是removeAll可以删除批量指定的元素,而clear是全是删除集合中的元素。
5)arrayList由于本质是数组,所以它在数据的查询方面会很快,而在插入删除这些方面,性能下降很多,有移动很多数据才能达到应有的效果。
6)arrayList实现了RandomAccess,所以在遍历它的时候推荐使用for循环。
