目录
- 一、背景
- 二、概念
- 1、定义
- 2、方法
- 2.1、排序方法
- 2.2、查找/替换方法
- 三、斗地主实例
- 3.1、代码结构
- 3.2、常量定义
- 3.3、单只牌类
- 3.4、玩家类
- 3.5、主程序
- 四、深入理解
一、背景
最近在学习数据结构和算法的过程中频繁用到了Collections工具类,这是开发中的一把利器,简化了许多涉及集合的编码,该文将通过实例对此工具类进入深入剖析。
二、概念
1、定义
java.util.Collections
是一个包装类。它包含有各种有关集合操作的静态多态方法。此类不能实例化,就像一个工具类,服务于Java的集合框架。
public class Collections {
// 默认构造方法私有化,不允许实例化.
private Collections() {
}
...
}
2、方法
Collections的方法都为静态方法,主要分为以下几类:该文主要对排序、查找/替换等方法进行解析。

2.1、排序方法
- 方法定义:
// 反转
public static void reverse(List list)
// 随机排序
public static void shuffle(List list)
// 按自然排序的升序排序
public static void sort(List list, Comparator c)
// 交换两个索引位置的元素
public static void swap(List list, int i, int j)
// 旋转
public static void rotate(List list, int distance)
2.2、查找/替换方法
// 二分查找
int binarySearch(List> list, T key)
// 根据定制排序,返回最大元素
int max(Collection coll, Comparator c)
// 根据定制排序,返回最小元素
int min(Collection coll, Comparator c)
// 统计元素出现次数
int frequency(Collection c, Object o),统计元素出现次数
// 统计targe在list中第一次出现的索引
int indexOfSubList(List list, List target)
// 用新元素替换旧元素
boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal)
三、斗地主实例
3.1、代码结构
3.2、常量定义
- 用集合的方式定义扑克牌的花色、牌面数字、大小王。
/**
* 扑克牌常量定义
* * @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-05
*/
public class Constant {
// 纸牌花色:黑桃,红心,梅花,方块
final static List COLORS = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(new String[]{"♢", "♣", "♡", "♠"}));
// 牌面数字
final static List NUMBERS = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(new String[]{"3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q", "K", "A", "2"}));
// 大王小王
final static List JOKER = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(new String[]{"小王","大王"}));
}
3.3、单只牌类
- 在单只牌类的定义中,重写了会影响到牌面大小的compareTo比较方法:
-- 如果是"王"的两只牌的比较,则"大王"大于"小王";
-- 如果是"王"与“数字牌”之间的比较,则"王"大于“数字牌”;
-- 如果是“数字牌”相互之间的比较,数字大的牌则牌面大,如果数字相同,则按花色比较(♢<♣< ♡< ♠)(虽然斗地主不按花色排列大小,但程序会按花色大小进行理牌)。
/**
* 单只牌
* * @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-05
*/
public class Card implements Comparable {
// 花色
private String color = "";
//数字
private String number = "";
public Card() {
}
public Card(String color, String number) {
this.color = color;
this.number = number;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getNumber() {
return this.number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.color + this.number;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Card) {
int thisColorIndex = Constant.COLORS.indexOf(this.getColor());
int anotherColorIndex = Constant.COLORS.indexOf(((Card) o).getColor());
int thisNumberIndex = Constant.NUMBERS.indexOf(this.getNumber());
int anotherNumberIndex = Constant.NUMBERS.indexOf(((Card) o).getNumber());
// 大小王之间相互比较: 大王大于小王
if ("JOKER".equals(this.color) && "JOKER".equals(((Card) o).getColor())) {
return thisColorIndex > anotherColorIndex ? 1 : -1;
}
// 大小王与数字牌之间相互比较:大小王大于数字牌
if ("JOKER".equals(this.color) && !"JOKER".equals(((Card) o).getColor())) {
return 1;
}
if (!"JOKER".equals(this.color) && "JOKER".equals(((Card) o).getColor())) {
return -1;
}
// 数字牌之间相互比较: 数字不相等,数字大则牌面大;数字相等 ,花色大则牌面大
if (thisNumberIndex == anotherNumberIndex) {
return thisColorIndex > anotherColorIndex ? 1 : -1;
} else {
return thisNumberIndex > anotherNumberIndex ? 1 : -1;
}
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
3.4、玩家类
- 玩家类中主要定义了抓牌、洗牌、理牌、找牌、获取最大最小牌、统计炸弹数等成员方法,在这些成员方法中,我们广泛应用了Collections工具类的静态方法。
/**
1. 玩家
2. * @author zhuhuix
3. @date 2020-06-05
*/
public class Player {
// 玩家姓名
private String name;
// 玩家类型:农民/地主
private String type;
// 抓到的牌
private List cards;
public Player(String name, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.cards = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 洗牌 shuffle
public void shuffle() {
Collections.shuffle(this.cards);
}
// 理牌 sort
public void sort() {
Collections.sort(this.cards, Card::compareTo);
}
// 抓牌
public void draw(Card card) {
this.cards.add(card);
}
// 出牌
public void play(Card card) {
this.cards.remove(card);
}
// 找出最大牌 max
public Card max() {
return Collections.max(this.cards, Card::compareTo);
}
// 找出最小牌 min
public Card min() {
return Collections.min(this.cards, Card::compareTo);
}
// 找到指定牌的位置 binarySearch
public int binarySearch(Card card) {
return Collections.binarySearch(this.cards, card, Card::compareTo);
}
// 统计有几手炸弹 frequency
public int frequency() {
int count = 0;
List numbers= new ArrayList<>();
List colors= new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < this.cards.size(); i++) {
colors.add(this.cards.get(i).getColor());
numbers.add(this.cards.get(i).getNumber());
}
for (int j = 0; j < Constant.NUMBERS.size(); j++) {
if (Collections.frequency(numbers, Constant.NUMBERS.get(j)) == 4) {
count++;
}
}
if (Collections.frequency(colors, "JOKER") == 2) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public List getCards() {
return cards;
}
public void setCards(List cards) {
this.cards = cards;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder poker = new StringBuilder("[");
Iterator iterator = this.cards.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
poker.append(iterator.next().toString() + ",");
}
poker.setCharAt(poker.length() - 1, ']');
return this.getType() + ":" + this.getName() + "拿到" + this.cards.size() + "张牌:" + poker;
}
3.5、主程序
- 生成一整副牌;
- 设置3个玩家,其中两个为农民,一个为地主;
- 3人轮流抓牌,地主多拿三张牌;
- 玩家理牌看牌(找到最大牌最小牌);
- 判断大王是否在地主手上?
- 统计各个玩家手上有几个炸弹?
/**
* 斗地主的主程序
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-6-5
*/
public class PlayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 生成一副扑克牌
Poker poker = new Poker();
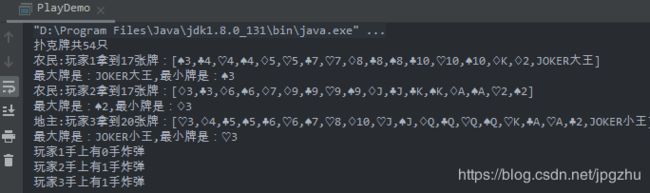
System.out.println("扑克牌共" + poker.getCardCount() + "只");
// 设置三个玩家,并设定两人为农民,一个为地主
int playCount = 3;
Player player1 = new Player("玩家1", "农民");
Player player2 = new Player("玩家2", "农民");
Player player3 = new Player("玩家3", "地主");
// 三个玩家按顺序抓牌
int i;
for (i = 0; i < poker.getCardCount() - playCount; i++) {
if (i % playCount == 0) {
player1.draw(poker.getCards().get(i));
} else if (i % playCount == 1) {
player2.draw(poker.getCards().get(i));
} else if (i % playCount == 2) {
player3.draw(poker.getCards().get(i));
}
}
// 地主拿剩余底牌
while (i < poker.getCardCount()) {
player3.draw(poker.getCards().get(i));
i++;
}
// 展示三个玩家洗牌后手上的牌面及最大和最小的牌
player1.sort();
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println("最大牌是:"+player1.max().toString()+",最小牌是:"+player1.min().toString());
player2.sort();
System.out.println(player2.toString());
System.out.println("最大牌是:"+player2.max().toString()+",最小牌是:"+player2.min().toString());
player3.sort();
System.out.println(player3.toString());
System.out.println("最大牌是:"+player3.max().toString()+",最小牌是:"+player3.min().toString());
// 大王是否在地主手里
if (player3.binarySearch(new Card("JOKER","大王"))>=0){
System.out.println("大王在"+player3.getType()+player3.getName()+"手里");
}
// 统计有几手炸弹
System.out.println(player1.getName()+"手上有"+player1.frequency()+"手炸弹");
System.out.println(player2.getName()+"手上有"+player2.frequency()+"手炸弹");
System.out.println(player3.getName()+"手上有"+player2.frequency()+"手炸弹");
}
}
四、深入理解
- 我们对其中的一些方法进行源码跟踪
-- shuffle
public static void shuffle(List list, Random rnd) {
int size = list.size();
if (size < SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(list, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));
} else {
//将集合转化成数组
Object arr[] = list.toArray();
// 通过随机数随机交换数组元素位置
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(arr, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));
// 通过迭代器将打乱顺序的数组赋值给集合
ListIterator it = list.listIterator();
for (int i=0; i-- sort
public static void sort(List list, Comparator c) {
list.sort(c);
}
...
default void sort(Comparator c) {
Object[] a = this.toArray();
//调用数组工具类的排序方法--该方法为改进过的归并排序
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator i = this.listIterator();
for (Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
}
-- min/max
public static T min(Collection coll, Comparator comp) {
if (comp==null)
return (T)min((Collection) coll);
Iterator i = coll.iterator();
T candidate = i.next();
// 通过迭代器循环比较,找到最小的
while (i.hasNext()) {
T next = i.next();
if (comp.compare(next, candidate) < 0)
candidate = next;
}
return candidate;
}
public static T max(Collection coll, Comparator comp) {
if (comp==null)
return (T)max((Collection) coll);
Iterator i = coll.iterator();
T candidate = i.next();
// 通过迭代器循环比较,找到最大的
while (i.hasNext()) {
T next = i.next();
if (comp.compare(next, candidate) > 0)
candidate = next;
}
return candidate;
}
-- binarySearch
public static int binarySearch(List list, T key, Comparator c) {
if (c==null)
return binarySearch((List>) list, key);
if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size() int iteratorBinarySearch(List l, T key, Comparator c) {
int low = 0;
int high = l.size()-1;
ListIterator i = l.listIterator();
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
T midVal = get(i, mid);
int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found
}