c++与python基础编程算法汇总|数组|字符串|链表|递归
目录
0、做题技巧总结
0.1 c++
0.2 python
一、数组
1.1 判断数组整数存在
整数存在c++
整数存在python
1.2 旋转数组最小数字
python旋转数组最小数字
c++旋转数组最小数字
1.3 调整数组顺序
c++数组奇数位于偶数前
1.4 数组中出现超过一半的数
c++数组中出现超过一半的数
1.5 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
1.6 最小的k个数
c++最小的k个数
1.7 子序列最大和
c++子序列最大和
1.8 整数1出现的次数
c++整数1出现的次数
1.9 顺时针打印矩阵
c++顺时针打印矩阵
1.10 和为S的两个数
c++和为S的两个数
1.11 构建乘积数组
c++构建乘积数组
二、字符串
2.1 字符串插入
c++符串插入
python字符串插入
2.2 字符串转为整数
c++字符串转为整数
2.3 第一个只出现一次的字符
c++只出现一次的字符
2.4 左旋转字符串
c++左旋转字符串
三、链表
3.1 链表中的值倒序
链表中的值倒序python
c++链表中的值倒序
3.2 链表的倒数第k个节点
倒数k个节点python
倒数第k个节点c++
3.3 反转链表
python反转链表
c++反转链表
3.4 链表的公共节点
六、递归
6.1 斐波那契数列
c++
python
6.2 青蛙跳台阶
青蛙跳台阶python
青蛙跳台阶c++
6.3 变态跳台阶
变态跳台阶c++
变态跳台阶python
6.4 合成排序链表
c++合成排序链表
python合成排序链表
6.5 覆盖矩形
python覆盖矩形
c++覆盖矩形
0、做题技巧总结
使用变量的时候,务必复制粘贴,在线答题界面没有IDE那么方便自动补全,有必要用复制粘贴补全。
0.1 c++
习惯之后c++必须加分号;因为python总是记不得加分号
c语言变量必须先声明后使用
0.2 python
缩进并不会像IDE里面那样自动缩进,所以需要运用四个空格,或者四个删除。
一、数组
1.1 判断数组整数存在
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
整数存在c++
涉及到数组的遍历,运用到了一个包,vector包的操作,如果不会vector的话,会因为语言的问题影响到算法。
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector > array) {
bool target_exist=false;
for(vector>::iterator current_row_it=array.begin(); current_row_it != array.end(); ++current_row_it){
for(int current_col=0; current_col<(*current_row_it).size(); ++current_col){
if(target==(*current_row_it)[current_col])target_exist=true;
}
}
return target_exist;
}
}; 可以设置一个vector
除了写法注意意外,还需要注意下面这些:
- 向量的.begin表示初始数组,.end表示最终的数组。
- *iterator表示数组的内部,是一个一维数组。
- 注意表示函数的时候,array.begin之后需要加括号,array.end之后需要加括号,size之后也需要加括号
- 可以用row_iterator
整数存在python
class Solution:
# array 二维列表
def Find(self, target, array):
# write code here
target_exist=False
for row_idx in range(len(array)):
for col_idx in range(len(array[row_idx])):
if array[row_idx][col_idx]==target:
target_exist=True
return target_exist输入为list变量,对此,我们可以用 in range(len(变量))来进行遍历。python经常使用,会比较熟悉。
真实出题的时候,应该会给出输入变量的类型。
1.2 旋转数组最小数字
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
python旋转数组最小数字
知道min函数特别简单
class Solution:
def minNumberInRotateArray(self, rotateArray):
if(len(rotateArray)==0):
return 0
return min(rotateArray)c++旋转数组最小数字
c++与python类似,sort函数即可实现。
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberInRotateArray(vector rotateArray) {
sort(rotateArray.begin(),rotateArray.end());
return rotateArray[0];
}
}; 可以再用复杂的解法解一遍:
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberInRotateArray(vector rotateArray) {
int array_size=rotateArray.size();
if(array_size==0)return 0;
int min=rotateArray[0];
for(int idx=0;idxrotateArray[idx])min=rotateArray[idx];
}
return min;
}
}; 1.3 调整数组顺序
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
解析:可以利用类似于冒泡排序法的思路来做。
c++数组奇数位于偶数前
上限可以变化。
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector &array) {
int array_size=array.size();
if(array_size==0||array_size==1)return;
for(int idx_out=0;idx_out 1.4 数组中出现超过一半的数
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
c++数组中出现超过一半的数
思路清晰基本一遍编成。需要注意的是,可以加一个mask增加运行效率,即使用过的数字可以设为false
class Solution {
public:
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector numbers) {
int num_size=numbers.size();
if(num_size<1)return 0;
vector mask(num_size);
for(int idx=0;idxthrehood)return current_num;
}
}
return 0;
}
}; 1.5 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
class Solution {
public:
int GetNumberOfK(vector data ,int k) {
int data_size=data.size();
if(data_size<1)return 0;
int times=0;
for(int idx=0;idx 1.6 最小的k个数
输入n个整数,找出其中最小的K个数。例如输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4,。
解析:可以类似于冒泡排序法。
c++最小的k个数
class Solution {
public:
vector GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector input, int k) {
vector min_num;
int input_size=input.size();
if(input_size<1||input_sizemin_idx;loc_idx--){
if(input[loc_idx] 1.7 子序列最大和
HZ偶尔会拿些专业问题来忽悠那些非计算机专业的同学。今天测试组开完会后,他又发话了:在古老的一维模式识别中,常常需要计算连续子向量的最大和,当向量全为正数的时候,问题很好解决。但是,如果向量中包含负数,是否应该包含某个负数,并期望旁边的正数会弥补它呢?例如:{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},连续子向量的最大和为8(从第0个开始,到第3个为止)。给一个数组,返回它的最大连续子序列的和,你会不会被他忽悠住?(子向量的长度至少是1)
解析:需要弄清楚题意,是连续的子序列即可,不需要从头开始,两个for循环即可实现。
c++子序列最大和
class Solution {
public:
int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector array) {
int array_size=array.size();
if(array_size<1)return 0;
int max=array[0];
int sum=0;
for(int idx=0;idxmax)?sum:max;
}
}
return max;
}
}; 1.8 整数1出现的次数
求出1~13的整数中1出现的次数,并算出100~1300的整数中1出现的次数?为此他特别数了一下1~13中包含1的数字有1、10、11、12、13因此共出现6次,但是对于后面问题他就没辙了。ACMer希望你们帮帮他,并把问题更加普遍化,可以很快的求出任意非负整数区间中1出现的次数(从1 到 n 中1出现的次数)。
c++整数1出现的次数
c++中int值的除法相当于去尾法。
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n)
{
int times_one=0;
for(int current_num=1;current_num<=n;current_num++){
int calcu_num=current_num;
while(calcu_num>0){
if(calcu_num%10==1)times_one++;
calcu_num=calcu_num/10;
}
}
return times_one;
}
};要注意循环用的值,与变量的值不是一个值。
1.9 顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10
c++顺时针打印矩阵
这题有更简单的方法,这个方法先放在这。
class Solution {
public:
vector printMatrix(vector > matrix) {
vector matrix_value;
int row_size=matrix.size();
int col_size=matrix[0].size();
if(row_size<1||col_size<1)return matrix_value;
int left_wall=-1;int right_wall=col_size;
int up_wall=-1;int down_wall=row_size;
int row_loc=0;int col_loc=0;
while(matrix_value.size()left_wall)){
for(;row_locup_wall)&&(col_loc>left_wall)){
for(;col_loc>left_wall;col_loc--)
matrix_value.push_back(matrix[row_loc][col_loc]);
down_wall--;col_loc++;row_loc--;
}
if((row_loc==down_wall-1)&&(col_loc==left_wall+1)&&(row_loc>up_wall)&&(col_locup_wall;row_loc--)
matrix_value.push_back(matrix[row_loc][col_loc]);
left_wall++;row_loc++;col_loc++;
}
}
return matrix_value;
}
}; 或者。三个if之中语句均为:
if(row_loc
1.10 和为S的两个数
题目描述
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字S,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是S,如果有多对数字的和等于S,输出两个数的乘积最小的。
输出描述: 对应每个测试案例,输出两个数,小的先输出
c++和为S的两个数
class Solution {
public:
vector FindNumbersWithSum(vector array,int sum) {
vector two_number;
int array_size=array.size();
if(array_size<2)return two_number;
int small_num;int big_num;int product;
bool is_exist=false;
for(int former_idx=0;former_idxbig_num)?small_num:big_num);
}
return two_number;
}
}; 1.11 构建乘积数组
给定一个数组A[0,1,...,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,...,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1]*A[i+1]*...*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
c++构建乘积数组
class Solution {
public:
vector multiply(const vector& A) {
vector multiply_vec;
int vector_size=A.size();
if(vector_size<1)return multiply_vec;
int multiply;
for(int idx=0;idx 1.12 数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
c++数组中重复的数字
class Solution {
public:
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number
// otherwise false
bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) {
if(numbers==NULL||length<1)return false;
for(int idx=0;idx=length)return false;
}
for(int idx=0;idx
二、字符串
2.1 字符串插入
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
c++符串插入
(实际编译的时候发现不能用malloc这样的函数,即不能创建新的数组,只能在原有数组基础之上进行更改)
从前往后会变动自身,从后往前排列即可。
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length) {
int num_space=0;
int old_length=0;
for(int idx=0; str[idx]!='\0'; idx++){
if(str[idx]==' ')num_space++;
old_length++;
}
int new_length=old_length+2*num_space;
str[new_length+1]='\0';
for( ;new_length!=-1; new_length--){
str[new_length]=str[old_length];
if(str[old_length]==' '){
str[new_length]='0';
str[new_length-1]='2';
str[new_length-2]='%';
new_length=new_length-2;
}
old_length--;
}
}
};需要注意字符串最后一个为 ‘\0’
python字符串插入
python如果了解字符串的操作的话,非常简单,简单的+号即可实现。
class Solution:
# s 源字符串
def replaceSpace(self, s):
# write code here
new_idx=0
new_s=''
for char_element in s:
if(char_element==' '):
new_s=new_s+'%20'
else:
new_s=new_s+char_element
return new_s2.2 字符串转为整数
将一个字符串转换成一个整数(实现Integer.valueOf(string)的功能,但是string不符合数字要求时返回0),要求不能使用字符串转换整数的库函数。 数值为0或者字符串不是一个合法的数值则返回0。
示例1,输入 +2147483647
1a33
输出 2147483647
0
注意:这种题有时候不能运用strlen函数。
c++字符串转为整数
需要考虑正负号,比如第一个为+或者-
class Solution {
public:
int StrToInt(string str) {
bool sign=false;
int idx=0;
if(str[0]=='+'||str[0]=='-'){
sign=true;
idx=1;
}
int value=0;
for(;str[idx]!='\0';idx++){
if(str[idx]<'0'||str[idx]>'9')return 0;
else{
value=10*value+str[idx]-'0';
}
}
if(sign)value=(str[0]=='+')?value:-value;
return value;
}
};2.3 第一个只出现一次的字符
在一个字符串(0<=字符串长度<=10000,全部由字母组成)中找到第一个只出现一次的字符,并返回它的位置, 如果没有则返回 -1(需要区分大小写).
c++只出现一次的字符
class Solution {
public:
int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) {
int loc_idx=0;
while(str[loc_idx]!='\0'){
for(int search_loc=0;str[search_loc]!='\0';search_loc++){
if(str[loc_idx]==str[search_loc]&&loc_idx!=search_loc){
break;
}
if(str[search_loc+1]=='\0')
return loc_idx;
}
loc_idx++;
}
return -1;
}
};2.4 左旋转字符串
汇编语言中有一种移位指令叫做循环左移(ROL),现在有个简单的任务,就是用字符串模拟这个指令的运算结果。对于一个给定的字符序列S,请你把其循环左移K位后的序列输出。例如,字符序列S=”abcXYZdef”,要求输出循环左移3位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。是不是很简单?OK,搞定它!
c++左旋转字符串
解决这题的时候,发现一个问题,如果在原来字符串增加长度的话,第二个字符串直接对第一个字符串取地址。但是实际运行的时候,如果先第二个字符串对第一个取地址,则什么时候取地址,值是什么时候的值。很奇怪。应该先增加长度,再取地址,这样就没问题了。可能string有长度的记录?底层的原理值得实验。
class Solution {
public:
string LeftRotateString(string str, int n) {
int str_length=0;
while(str[str_length]!='\0')str_length++;
if(str_length<1)return str;
// positive n
int shift_num=n%str_length;
// string new_str=&str[shift_num];
for(int idx=0;idx
三、链表
链表对于c++来说是一个节省效率的东西,但是对于python来说只能使得问题复杂化,并不能起到优化效率和内存的作用。只是我们必须掌握python链表的编发,以便做题。
3.1 链表中的值倒序
链表中的值倒序python
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3]
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
# write code here
value_list=[]
while(listNode):
value_list.append(listNode.val)
listNode=listNode.next
return value_list[::-1]需要将链表中的值写入list之中。可以倒着写。
注意最后一个数组倒序列的表述,开始位置:结束位置:step , numpy和list格式都可以这么写。
还有while(listNode):而不是while(listNode.next):这个必须实际推导一下
c++链表中的值倒序
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* node_ptr=head;
vector val_vector;
for( ; node_ptr!=NULL; node_ptr=node_ptr->next){
val_vector.insert(val_vector.begin(),node_ptr->val);
}
// reverse vector
return val_vector;
}
}; 难度不难,但是需要对vector这个工具进行熟练运用。
比如insert命令。
然后就是链表的遍历。
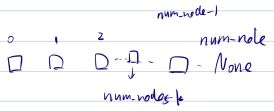
3.2 链表的倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
倒数k个节点python
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self, head, k):
# write code here
num_nodes=0
cur_node=head
while(cur_node!=None):
cur_node=cur_node.next
num_nodes=num_nodes+1
if(num_nodes-k<0):
return
cur_node=head
for idx in range(0,num_nodes-k):
cur_node=cur_node.next
return cur_nodec++总是存在内存超限的问题,需要继续做。
倒数第k个节点c++
思路清晰即可
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
if(pListHead==NULL)return NULL;
int list_size=0;
ListNode* node_ptr=pListHead;
while(node_ptr!=NULL){
node_ptr=node_ptr->next;
list_size++;
}
int idx_back_k=list_size-k;
if(idx_back_k<0)return NULL;
node_ptr=pListHead;
for(int idx=0;idxnext;
}
return node_ptr;
}
}; 可以采用剑指offer中的快慢指针来解。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
ListNode* fast_ptr=pListHead;
ListNode* slow_ptr=pListHead;
for(int idx=0;idxnext;
}
while(fast_ptr!=NULL){
fast_ptr=fast_ptr->next;
slow_ptr=slow_ptr->next;
}
return slow_ptr;
}
};
3.3 反转链表
反转链表需要将之前的链表进行反转。因为内存限制,c++代码最好不要引入新的变量。数据结构的题,有必要画出相应的图方便不出错与理解。
python反转链表
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
# write code here
if(pHead==None):
return
seq_node=pHead
inv_node=ListNode(pHead.val)
while(seq_node.next!=None):
seq_node=seq_node.next
inv_node_new=ListNode(seq_node.val)
inv_node_new.next=inv_node
inv_node=inv_node_new
return inv_nodec++反转链表
一定要考虑程序鲁棒性,即如果空链表的话,返回NULL,不要直接return。
并且需要少量的内存占用,尽量运用已有的节点。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==NULL)return NULL;
ListNode* pre_node=new ListNode(pHead->val);
ListNode* cur_node=pHead->next;
ListNode* next_node=cur_node;
while(next_node!=NULL){
next_node=cur_node->next;
cur_node->next=pre_node;
pre_node=cur_node;
cur_node=next_node;
}
return pre_node;
}
};3.4 链表的公共节点
找到两个链表公共节点,思路清晰即可,注意非void函数一定要返回值。且第一个链表固定一个节点时候,第二个链表需要从头开始。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(pHead1==NULL||pHead2==NULL)return NULL;
ListNode* node_1=pHead1;
ListNode* node_2;
while(node_1!=NULL){
node_2=pHead2;
while(node_2!=NULL){
if(node_1==node_2)return node_1;
node_2=node_2->next;
}
node_1=node_1->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
六、递归
递归可能存在递归后内存超限的问题,因此必须使用前馈的运算来实现。
6.1 斐波那契数列
递归总显示内存超限,因此需要前向运算。
从0开始,0,1,1,2,3,
c++
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
if(n==0)return 0;
if(n==1)return 1;
if(n==2)return 1;
int sum_1=1;
int sum_2=1;
int sum;
for(int idx=3;idx<=n;idx++){
sum=sum_1+sum_2;
sum_1=sum_2;
sum_2=sum;
}
return sum;
}
};python
class Solution:
def Fibonacci(self, n):
# write code here
if(n==0):
return 0
if(n==1):
return 1
sum_1=0
sum_2=1
sum=1
for idx in range(2,n+1):
sum=sum_2+sum_1
sum_1=sum_2
sum_2=sum
return sumpython的结尾位置,写成n+1,其实只到n,还有range后面需要是小括号。python的上界的问题需要额外注意。
range用法:https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-range.html
6.2 青蛙跳台阶
类似于斐波那契数列是一个递归的问题。只有一个台阶的时候跳法是1,只有两个台阶的时候跳法是2,如果n个台阶的出后,跳法是n-1个台阶和n-2个台阶的跳法的加和。
青蛙跳台阶python
同时需要注意range的用法,上限的参数为上限+1
class Solution:
def jumpFloor(self, number):
# write code here
if(number==1):
return 1
if(number==2):
return 2
sum_1=1
sum_2=2
sum_num=sum_1+sum_2
for n in range(3,number+1):
sum_num=sum_1+sum_2
sum_1=sum_2
sum_2=sum_num
return sum_num青蛙跳台阶c++
类似于python
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloor(int number) {
if(number==0||number==1||number==2)return number;
int sum_1=1;
int sum_2=2;
int sum_num=sum_1+sum_2;
for(int floor=3;floor<=number;floor++){
sum_num=sum_1+sum_2;
sum_1=sum_2;
sum_2=sum_num;
}
return sum_num;
}
};6.3 变态跳台阶
这种可以理解为,第n中跳法,是前面n-1,n-2,,,,,所有的跳法之和再加上一次性跳完这种跳法
就是sum(n-1,n-2,n-3,,,1)+1
推导一下,(1,1)(2,2)(3,4)(4,8),即 method=2^(floor-1)
有指数实现的:c之中有个math.h的头函数,如果没有那个头函数可能要跟下面这样实现了
变态跳台阶c++
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloorII(int number) {
if(number==0||number==1||number==2)return number;
// 2^nunber-1
int exp=2;
for(int floor=3;floor<=number;floor++){
exp=2*exp;
}
return exp;
}
};这里,需要知道c++的次方操作是pow,则很快即可做出来(^号可能不可用。math.h可能已经在编译器之中了。所以直接调用pow即可)
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloorII(int number) {
if(number==0||number==1)return number;
return pow(2,number-1);
}
};变态跳台阶python
超级简单,这个只要知道python的乘方操作是**肯定可以做出来
class Solution:
def jumpFloorII(self, number):
# write code here
return 2**(number-1)
6.4 合成排序链表
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
c++合成排序链表
其他递归为了避免内存超限,因此无法确实使用递归,这个确实使用了递归。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2)
{
if(pHead1==NULL)return pHead2;
if(pHead2==NULL)return pHead1;
if((pHead1->val)<(pHead2->val)){
pHead1->next=Merge(pHead1->next,pHead2);
return pHead1;
}
else{
pHead2->next=Merge(pHead1,pHead2->next);
return pHead2;
}
}
};python合成排序链表
与c++一样,用递归很简单
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if(pHead1==None):
return pHead2
if(pHead2==None):
return pHead1
if(pHead1.val6.5 覆盖矩形
我们可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
解析:还是递归的方法,多一个矩形相当于一个或者两个的方法的和。
python覆盖矩形
注意python的或运算符号是or,与c++区分。
class Solution:
def rectCover(self, number):
# write code here
if((number==0)or(number==1)or(number==2)):
return number
method_1=2
method_2=1
method=method_2+method_1
for idx in range(3,number+1):
method=method_2+method_1
method_2=method_1
method_1=method
return methodc++覆盖矩形
class Solution {
public:
int rectCover(int number) {
if(number==0||number==1||number==2)return number;
int method_minus_1=2;
int method_minus_2=1;
int method=method_minus_1+method_minus_2;
for(int idx=3;idx<=number;idx++){
method=method_minus_1+method_minus_2;
method_minus_2=method_minus_1;
method_minus_1=method;
}
return method;
}
};