DHCP服务器的搭建
呵呵今天我来复习DHCP的搭建了,DHCP的搭建比我想象的要简单,不过估计深究的话也会有很多知识点的,就好像DNS一样,深究的话会扯出一串的知识点。好了言归正传我现在就开始撰写复习笔记
一. 什么是DHCP
Dhcp就是动态主机配置协议,可以自动的去分配IP地址、子网掩码、网关以及DNS等tcp/ip信息。当局域网中电脑十分的多的时候,咱总不能一台一台的去主机旁设IP等信息吧,那不累死了。所以只需要在局域网中设置一台DHCP服务器,通过此服务器就可以动态的给局域网中的每台电脑自动设置IP等信息。
二. DHCP的工作原理
(1)首先我们先介绍几个名字解释:
DHCP客户端:DHCP客户是通过DHCP来获得网络配置参数的internet主机,通常就是普通的用户工作站。
DHCP服务器:DHCP服务器是提供网络参数的给DHCP客户的internet主机
DHCP/BOOTP中继代理:在DHCP客户和服务器之间转发DHCP消息的主机或者路由器
DHCP是基于客户机/服务器模型设计的,DHCP客户和DHCP服务器之间通过收发DHCP消息进行通讯。
作用域:一个完整连续的可用IP地址薄,DHCP服务主要就是通过作用域来管理网络分布、IP地址分配及相关配置参数。
排除范围:排除范围是作用域内从DHCP服务中排除的有限地址序列,排除范围确保在这些范围中的任何地址都不是由网络上的服务器提供给客户端的。其实说白了就是将作用域中的一些IP地址给排除在外使其不能分配给客户端。
地址池:在定义DHCP作用域并应用排除范围后,剩余的地址在作用域内形成的可用地址池,地址池中的地址可以动态分配给DHCP客户端。
租约:客户端可以使用动态分配IP地址的时间。
预约:创建从DHCP服务器到客户机的永久地址租约指定,预约可以保证子网上的特定硬件设备总是使用相同的IP。
(2)工作原理
大致知道一些名字后,我们来说说其其基本原理:
首先DHCP一般是局域网内的一个通讯协议,当客户端没有设定任何网络配置信息时候,他会想其所在的局域网上发出一个广播封包给局域网内的所有主机(其发送的是DHCP DISCVER数据包,为保证服务器能够接收到请求,数据包源地址设定为0.0.0.0,而目的地址为255.255.255.255,以广播形式发送DHCP DISCOVER的信息。),一般主机接收到这个封包后,会直接给予丢弃,但如果局域网中有DHCP服务器,则会自动响应。
当DHCP服务器监听到客户端发出的DHCP DISCOVER广播后,它会从那些还没有租出的地址范围内选择可用的IP及其他TCP/IP设定以DHCP OFFER数据包的形式发送给客户机。
如果客户端收到网络上多台DHCP服务器的响应,客户端会挑选最快的一个DHCP OFFER并向网络发送一个DHCP REQUEST广播封包,告诉所有DHCP服务器它将使用哪一台服务器提供的IP地址。同时,客户端还会向网络发送ARP广播数据包,查询网络上面有没有其他机器使用该IP地址,如果发现该IP地址已经被占用,客户端则会发送一个DHCP DECLINE数据包给DHCP服务器,拒绝接受其DHCP OFFER,并重新发送DHCP REQUEST信息。
注:实际上并不是所有DHCP客户端都会无条件接受DHCP服务器的响应,客户端可以保留自己的一些TCP/IP设定,比如网关、DNS地址等等
将地址分配给客户端后,DHCP服务器会发送一个DHCP ACK消息,以确认IP租约的正式生效,结束完整的DHCP工作过程。
DHCP客户端成功地从服务器取得IP地址之后,一般不需要再发送DHCP DISCOVER信息了,除非其租约已经到期或者IP地址重新设定回0.0.0.0。此时客户端会直接使用已经租用到的IP地址向为其发此IP地址的DHCP服务器发出DHCP REQUEST信息,DHCP服务器会尽量让客户端使用原来的IP地址,如果没有特殊的情况,会直接响应DHCP ACK,允许客户端继续使用该IP地址。如果该地址已经失效或者已经被其他主机使用了,服务器则会响应一个DHCP NACK数据包给客户端,要求其重新执行DHCP DISCOVER。
注意:客户端执行DHCP DISCOVER后,如果没有DHCP服务器响应客户端的请求,客户端会随机使用169.254.0.0/16网段中的一个IP地址配置本机地址。
Ok 大致的过程就是如上所示,上面也是我摘抄的,似乎说的比较详细,简单的说就是在一个存在DHCP服务器的网络环境中,客户端发送一个目标地址为255.255.255.255的广播给网络中的所有主机,其他客户端收到此消息会直接丢弃,而DHCP服务器收到此消息后则会从其地址池中随机选择一个IP给发送此消息的客户端来配置其网络参数,客户端接收到消息后,就开始处理本身的网络参数,包括网关、DNS等等信息,并且会给服务器发送一个确认信息,表示该参数已经被接受了,可别又分给其他客户端。
这里有个地方需要注意一下,当客户端无论是关闭网络接口(ifdown)、重新启动(reboot)、关机(shutdown)等行为都算是脱机,这个时候服务器端会收回IP,并放到自己的备用区中,等待未来使用。但通过前面我们讲述原理知道“DHCP服务器会尽量让客户端使用原来的IP地址,如果没有特殊的情况,会直接响应DHCP ACK,允许客户端继续使用该IP地址”所以当重启网络服务的时候,常常会发现IP地址居然没有改变,原因就在这里。
三. 配置DHCP服务器端
首先当然是要安装DHCP,如果你有yum仓库的话,直接
yum install dhcp就可以实现安装,我先查看下我的主机装了没有呵呵:
[root@linux102 dhcpd]# rpm -qa dhcp
dhcp-3.0.5-21.el5
ok,我已经装过了。那么我们就开始配置吧。配置DHCP服务器大概有以下几个步骤:
首先编辑/etc/dhcpd.conf
配置dhcp一般是配置/etc/dhcpd.conf这个文件,但一般情况下此文件并不存在,需要我们自己手动配置,这里面的东东还蛮多的,自己一个一个敲多费劲,所以我们可以拷贝一个现成的配置文件到etc目录下将其改名即可:
cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-3.0.5/dhcpd.conf.sample /etc/dhcpd.conf
复制好后,我们就在/etc下有这个文件了。
hcpd.conf包括全局配置和局部配置。全局配置可以包含参数或选项,该部分对整个DHCP服务器生效;局部配置通常由声明部分来表示,该部分仅对局部生效,比如只对某个IP作用域生效
dhcpd.conf文件格式:
#全局配置
参数或选项; #全局生效
#局部配置
声明{
参数或选项; #局部生效
}
下来我们将对全局与局部配置的一些常用参数和声明进行解释
1.常用参数:
(1)ddns-update-style (none|interim|ad-hoc)
作用:定义所支持的DNS动态更新类型。
none:表示不支持动态更新
interim:表示DNS互动更新模式
ad-hoc:表示特殊DNS更新模式
因为DHCP 客户端所取得的IP 通常是一直变动的,所以某部主机的主机名与IP 的对应就很难处理。此时DHCP 可以透过ddns 来更新主机名与IP 的对应。
注意:这个选项是必选参数哈,配置文件中必须包含这一个参数并且要放在第一行。
(2)gnore client-updates
作用:忽略客户端更新
(3)default-lease-time number(数字)
作用:定义默认IP租约时间
(4)max-lease-time number(数字)
作用:定义客户端IP租约时间的最大值,当客户端超过租约
间却尚未更新IP 时,最长可以使用该IP 的时间;
注意:(3)、(4)都是以秒为单位的租约时间,该项参数可以作用在全局配置中,也可以作用在局部配置中。
2.常用声明
声明一般用来指定IP作用域、定义为客户端分配的IP地址池等等
声明格式如下:
声明{
选项或参数;
}
常见声明的使用如下:
(1)subnet 网络号netmask 子网掩码{......}
作用:定义作用域,指定子网
注意:网络号必须与DHCP服务器的网络号相同
(2)range 起始IP地址结束IP地址
作用:指定动态IP地址范围
注意:可以在subnet声明中指定多个range,但多个range所定义IP范围不能重复。
3. 常用选项介绍
选项通常用来配置DHCP客户端的可选参数,比如定义客户端的DNS地址、默认网关等等。选项内容都是以option关键字开始滴
常见选项使用如下:
(1)option routers IP地址
作用:为客户端指定默认网关
(2)option subnet-mask 子网掩码
作用:设置客户端的子网掩码
(3)option domain-name-servers IP地址
作用:为客户端指定DNS服务器地址
(4)option broadcasst-address 广播地址:
设定广播地址而已。如果没有设定的话,系统应该会自动依据class A, B, C 的原则来计算出广播地址。
注意:(1)、(2)、(3)选项可以用在全局配置中,也可以用在局部配置中。
ok 大概说完了之后,我们来看看这个配置文件到底是什么样子的
图上的是我自己服务器上的配置,基本上就这么多东西。根据实际情况大家也可以自己添加。
这里稍微多说几句关于dhcp的固定ip获取:
(1)host 主机名{......}
作用:用于定义保留地址
注意:该项通常搭配subnet声明使用。
(2)hardware 类型硬件地址
作用:定义网络接口类型和硬件地址。常用类型为以太网(ethernet),地址为MAC地址。
(3)fixed-address IP地址
作用:定义DHCP客户端指定的IP地址。
注意:(2)、(3)项只能应用于host声明中。
配置到这里,基本上就已经可以正常使用了,但如果服务器上有多个网络接口的时候,往往就会出错。比如192.168.0.0/24是eth0
上的,而192.168.1.0/24是eth1上的,如果DHCP服务器同时监听的是两个接口的话,这个时候我们192.168.1.0/24上的客户端发送了dhcp封包要求,这个时候他取的ip就可能取成192.168.0.0/24网段上的了(服务器设置的是0网段),所以为了防止这类事情发生,我们最好可以设定dhcp的监听端口。如图:
[root@linux102 ]# vi /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd
# Command line options here
DHCPDARGS=“eth0”
配置好后,我们来启动dhcp服务器:
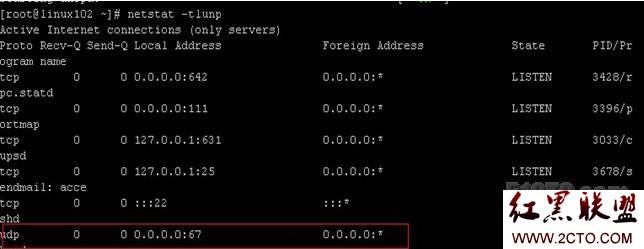
启动好后,我们来观察下端口启动的情况:
DHCP启用的是67号端口,我们看到我的67号端口服务器上已经开启了。
服务器端查询有多少客户端已经向我们申请了ip,以及ip的相关记录可以再此处查询:
[root@linux102 ~]# cat /var/lib/dhcpd/dhcpd.leases
lease 192.168.0.101 { //客户端的ip地址
starts 5 2011/08/05 06:56:02;
ends 5 2011/08/05 12:56:02;
tstp 5 2011/08/05 12:56:02;
binding state free;
hardware ethernet 00:0c:29:5d:41:62;
}
这个其实是租约数据库文件,其是用于保存一系列的租约声明,其中包含客户端的主机名、MAC地址、分配到的IP地址,以及IP地址的有效期等相关信息。这个数据库文件是可编辑的ASCII格式文本文件。每当发生租约变化的时候,都会在文件结尾添加新的租约记录。
DHCP刚安装好后租约数据库文件dhcpd.leases是个空文件
四.客户端的配置
其实客户端也没啥配置的,只要设置成dhcp方式来获取ip就可以了。设置好后,我们重启网络就可以从刚刚配置好的dhcp服务器上来获取ip了呵呵 就这么简单。现在我们在客户端上来观察下其相关参数都是否符合配置:
1.客户端的dns是否符合
[root@linux101 ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
; generated by /sbin/dhclient-script
search linux102
nameserver 192.168.0.102
客户端的dns已经是是我们设定的dns地址了,注意观察哦,这里的
search linux102 就是我们在服务器上设置的“option domain-name”的名称,nameserver 即是我们服务器上设置的地址。所以完全吻合
2.ip是否符合
[root@linux101 ~]# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:5D:41:62
inet addr:192.168.0.101 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
我们服务器上是设置了给客户端绑定ip为192.168.0.101,也符合
3.观察路由
[root@linux101 ~]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
观察发现和我服务器上设置的192.168.0.1是一致的
4.查看端口
Dhcp客户端所用的端口是68,现在我们来检查下:
5.查看客户端所记载的租约记录信息
[root@linux101 dhclient]# cat /var/lib/dhclient/dhclient-eth0.leases
lease {
lease {
interface "eth0"; //所监听的端口
fixed-address 192.168.0.101; //ip地址
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; //所取得的子网掩码
option time-offset -18000;
option routers 192.168.0.1; //路由地址
option dhcp-lease-time 21600; //租约时间
option dhcp-message-type 5;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.102; //dns的地址
option dhcp-server-identifier 192.168.0.102;
option nis-domain "domain.org";
option domain-name "linux102"; //dns主机名称
renew 2 2011/8/9 11:22:19; //下一次预计更新(renew)时间
rebind 2 2011/8/9 13:47:58;
expire 2 2011/8/9 14:32:58;
}
# 这个档案会记录该适配卡所曾经要求过的DHCP 信息!
# 他几乎就与你设定的/etc/dhcpd.conf 类似
Ubuntu下DHCP服务器的配置
(2012-09-13 15:09:03)标签: 杂谈 |
分类:新技术 |
Ubuntu DHCP 服务配置
#安装DHCP服务
sudo apt-get install dhcp3-server
---------------------------------------------
#配置DHCP网卡
emacs /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server
#改为对应网卡
INTERFACES="eth0"
---------------------------------------------
(eth0 可能要设置一个IP地址做网关)
#备份当前配置
sudo cp /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf /etc/dhcp3/dhcpd.conf.bak
#编辑当前配置
sudo vi /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf #删掉所有内容
---------------------------------------------
#emacs /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
ddns-update-style none;
option domain-name "tagpt.mtn";
default-lease-time 14400;
#最小租约14400秒=4小时
max-lease-time 36000;
#最大租约36000秒=10小时
subnet 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
#IP地址起止范围
range 192.168.2.77192.168.2.240;
option subnet-mask255.255.255.0;
#子网掩码 255.255.255.0
option routers192.168.2.10;
#默认网关 192.168.2.10
optionbroadcast-address 192.168.2.255;
#广播地址 192.168.2.255
}
---------------------------------------------
sudo /etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restart
或
service isc-dhcp-server restart
客户端设置为dhcp获取IP即可
Ubuntu 12.10配置DHCP服务
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network service that enables host computers to be automatically assigned settings from a server as opposed to manually configuring each network host. Computers configured to be DHCP clients have no control over the settings they receive from the DHCP server, and the configuration is transparent to the computer's user.
The most common settings provided by a DHCP server to DHCP clients include:
-
IP address and netmask
-
IP address of the default-gateway to use
-
IP adresses of the DNS servers to use
However, a DHCP server can also supply configuration properties such as:
-
Host Name
-
Domain Name
-
Time Server
-
Print Server
The advantage of using DHCP is that changes to the network, for example a change in the address of the DNS server, need only be changed at the DHCP server, and all network hosts will be reconfigured the next time their DHCP clients poll the DHCP server. As an added advantage, it is also easier to integrate new computers into the network, as there is no need to check for the availability of an IP address. Conflicts in IP address allocation are also reduced.
A DHCP server can provide configuration settings using the following methods:
- Manual allocation (MAC address)
-
This method entails using DHCP to identify the unique hardware address of each network card connected to the network and then continually supplying a constant configuration each time the DHCP client makes a request to the DHCP server using that network device. This ensures that a particular address is assigned automatically to that network card, based on it's MAC address.
- Dynamic allocation (address pool)
-
In this method, the DHCP server will assign an IP address from a pool of addresses (sometimes also called a range or scope) for a period of time or lease, that is configured on the server or until the client informs the server that it doesn't need the address anymore. This way, the clients will be receiving their configuration properties dynamically and on a "first come, first served" basis. When a DHCP client is no longer on the network for a specified period, the configuration is expired and released back to the address pool for use by other DHCP Clients. This way, an address cand be leased or used for a period of time. After this period, the client has to renegociate the lease with the server to maintain use of the address.
- Automatic allocation
-
Using this method, the DHCP automatically assigns an IP address permanently to a device, selecting it from a pool of available addresses. Usually DHCP is used to assign a temporary address to a client, but a DHCP server can allow an infinite lease time.
The last two methods can be considered “automatic” because in each case the DHCP server assigns an address with no extra intervention needed. The only difference between them is in how long the IP address is leased, in other words whether a client's address varies over time. Ubuntu is shipped with both DHCP server and client. The server is dhcpd (dynamic host configuration protocol daemon). The client provided with Ubuntu isdhclient and should be installed on all computers required to be automatically configured. Both programs are easy to install and configure and will be automatically started at system boot.
Installation
At a terminal prompt, enter the following command to install dhcpd:
sudo apt-get install isc-dhcp-server
You will probably need to change the default configuration by editing /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf to suit your needs and particular configuration.
You also may need to edit /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server to specify the interfaces dhcpd should listen to.
NOTE: dhcpd's messages are being sent to syslog. Look there for diagnostics messages.
Configuration
The error message the installation ends with might be a little confusing, but the following steps will help you configure the service:
Most commonly, what you want to do is assign an IP address randomly. This can be done with settings as follows:
# minimal sample /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.1.150 192.168.1.200;
option routers 192.168.1.254;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2;
option domain-name "mydomain.example";
}
This will result in the DHCP server giving clients an IP address from the range 192.168.1.150-192.168.1.200. It will lease an IP address for 600 seconds if the client doesn't ask for a specific time frame. Otherwise the maximum (allowed) lease will be 7200 seconds. The server will also "advise" the client to use 192.168.1.254 as the default-gateway and 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.2 as its DNS servers.
After changing the config file you have to restart the dhcpd:
sudo service isc-dhcp-server restart
References
-
The dhcp3-server Ubuntu Wiki page has more information.
-
For more /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf options see the dhcpd.conf man page.
-
ISC dhcp-server
from:https://help.ubuntu.com/12.10/serverguide/dhcp.html
ubuntu 13.04 配置dhcp服务
apt-get install dhcp3-server
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255;
option routers 192.168.1.11;
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8;
option domain-name "mydomain.com";
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.1.101 192.168.1.121;
}
/etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restart
状态文件
/var/lib/dhcp/dhcpd.leases
Ok,整个过程已经全部讲解完毕,现在我们来进行个简单的总结:
基本的DHCP服务器搭建流程:
(1)编辑主配置文件dhcpd.conf,指定IP作用域(指定一个或多个IP地址范围)。
(2)建立租约数据库文件。
(3)重新加载配置文件或重新启动dhcpd服务使配置生效。
DHCP工作流程:
(1)客户端发送广播向服务器申请IP地址。
(2)服务器收到请求后查看主配置文件dhcpd.conf,先根据客户端的MAC地址查看是否为客户端设置了固定IP地址。
(3)如果为客户端设置了固定IP地址则将该IP地址发送给客户端。如果没有设置固定IP地址,则将地址池中的IP地址发送给客户端。
(4)客户端收到服务器回应后,客户端给于服务器回应,告诉服务器已经使用了分配的IP地址。
(5)服务器将相关租约信息存入数据库。