剑指offer题解(Java实现)—— 面试题7:重建二叉树
文章目录
- 前言
- 题目描述
- 解题思路
- 总结
- 后记
前言
本系列的文章为笔者学习《剑指offer第二版》后的笔记整理以及Java实现,解法不保证与书上一致。
另外,我最近在系统整理一些 Java 后台方面的面试题和参考答案,有找工作需求的童鞋,欢迎关注我的 Github 仓库,如果觉得不错可以点个 star 关注 :
- 1、awesome-java-interview
- 2、awesome-java-notes
题目描述
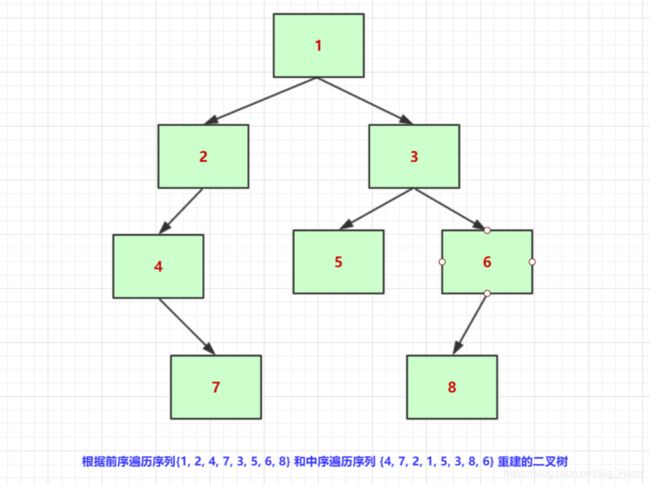
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建如下图所示的二叉树并输出它的头节点。二叉树节点的定义如下:
private class BinaryTreeNode {
int val;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
BinaryTreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
解题思路
在二叉树中,前序遍历的第一个节点即为树的根节点。根据二叉树的前序遍历序列确定了根节点后,遍历中序遍历序列可以找到根节点的位置,然后根据二叉树中序遍历的特点可知,根节点左边的节点即为左子树的所有节点,而根节点右边的节点即为右子树的所有节点。
根据上述遍历我们可以分别找到了左右子树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,很显然,我们也可以用同样的方法分别构建左、右子树。也就是说,接下来完全可以不断地递归去实现。
比如输入前序遍历序列 {1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8} 和中序遍历序列 {4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6}。由前序序列可知根结点是 1,于是从中序序列可知,{4, 7, 2} 属于根结点 1 的左子树,有 3 个结点;{5, 3 ,8, 6} 属于根结点 1 的右子树。回到前序序列,除开第一个根结点,其后 3 个结点 {2, 4, 7} 就是左子树,余下的 {3, 5, 6 ,8} 是右子树。按照这些关系可以精确地将数组分解成两个子数组,递归地对两个数组进行同样的操作即可。
package com.offers.chapter2.question07;
/**
* 输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树并返回它的头节点。
* 假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
*
* @author Rotor
* @since 2019/9/30 16:39
*/
public class ReConstructBinaryTree {
/**
* 二叉树节点类
*/
private static class BinaryTreeNode {
int val;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
BinaryTreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
/**
* @param preorder 前序遍历序列
* @param inorder 中序遍历序列
* @return 树的根节点
*/
public static BinaryTreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
// 合法性判断,前序遍历和后序遍历连个数组不能为空并且节点的数目应该相同
if (preorder == null || inorder == null || preorder.length != inorder.length || inorder.length < 1) {
return null;
}
return contructTree(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
/**
* @param preorder 前序遍历序列
* @param startPreorder 前序遍历的起始位置(左指针)
* @param endPreorder 前序遍历序列的结束位置(右指针)
* @param inorder 中序遍历序列
* @param startInorder 中序遍历的起始位置(左指针)
* @param endInorder 中序遍历的结束位置(右指针)
* @return 树的根节点
*/
private static BinaryTreeNode contructTree(int[] preorder, int startPreorder, int endPreorder,
int[] inorder, int startInorder, int endInorder) {
// 前序序列或中序序列起始位置大于结束位置,说明不能再继续递归分解成子数组了,返回空子树给父节点
if (startPreorder > endPreorder || startInorder > endInorder) {
return null;
}
// 前序序列的第一个节点的值就是根节点的值
int rootvalue = preorder[startPreorder];
// 创建根节点
BinaryTreeNode root = new BinaryTreeNode(rootvalue);
// 遍历中序遍历序列,找到中序序列中根节点的位置
int rootIndex = startInorder;
while (rootIndex <= endInorder && inorder[rootIndex] != rootvalue) {
rootIndex++;
}
// 如果遍历整个中序遍历序列都没有找到根节点,说明输入了无效参数
if (rootIndex > endInorder) {
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid input");
}
// 左子树的长度
int leftLength = rootIndex - startInorder;
int leftPreorderEnd = startPreorder + leftLength;
/**
* 构建左子树
* 左子树对应的前序遍历序列中的位置为:[startPreorder + 1, startPreorder + rootIndex - startInorder]
* 左子树对应的中序遍历序列中的位置为:[startInorder, rootIndex - 1]
*/
root.left = contructTree(preorder, startPreorder + 1, leftPreorderEnd, inorder, startInorder, rootIndex - 1);
/**
* 构建右子树
* 右子树对应的前序遍历序列中的位置为:[startPreorder + rootIndex - startInorder + 1, endPreorder]
* 右子树对应的中序遍历序列中的位置为:[rootIndex + 1, endInorder]
*/
root.right = contructTree(preorder, leftPreorderEnd + 1, endPreorder, inorder, rootIndex + 1, endInorder);
// 返回树的根节点
return root;
}
// 中序遍历二叉树
public static void printTree(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
printTree(root.right);
}
}
// 普通二叉树
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / / \
// 4 5 6
// \ /
// 7 8
private static void test1() {
int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8};
int[] inorder = {4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
// 所有结点都没有右子结点
// 1
// /
// 2
// /
// 3
// /
// 4
// /
// 5
private static void test2() {
int[] preorder = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] inorder = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
// 所有结点都没有左子结点
// 1
// \
// 2
// \
// 3
// \
// 4
// \
// 5
private static void test3() {
int[] preorder = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] inorder = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
// 树中只有一个结点
private static void test4() {
int[] preorder = {1};
int[] inorder = {1};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
// 完全二叉树
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
private static void test5() {
int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int[] inorder = {4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
// 输入空指针
private static void test6() {
reConstructBinaryTree(null, null);
}
// 输入的两个序列不匹配
private static void test7() {
int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int[] inorder = {4, 2, 8, 1, 6, 3, 7};
BinaryTreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder);
printTree(root);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
System.out.println();
test2();
System.out.println();
test3();
System.out.println();
test4();
System.out.println();
test5();
System.out.println();
test6();
System.out.println();
test7();
}
}
【注】代码测试用例参开来源:https://github.com/Wang-Jun-Chao/coding-interviews/blob/master/src/Test06.java
总结
- 在构建二叉树时,我们可以将构建二叉树地大问题分解成构建左、右子树地两个小问题;
- 很显然,可以发现小问题和大问题在本质上是一样地,因此可以用递归的方式解决。
后记
如果你同我一样想要努力学好数据结构与算法、想要刷 LeetCode 和剑指 offer,欢迎关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:awesome-java-notes