java中队列---Queue
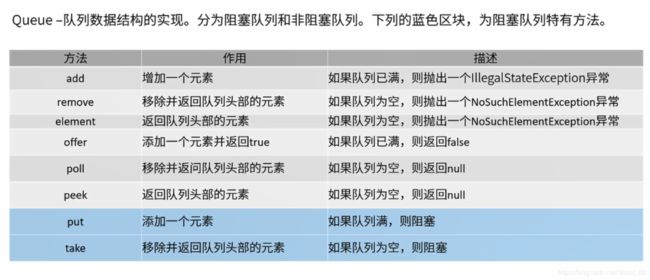
Queue-API
ConcurrentLinkedQueue非阻塞队列-先进先出
示例代码:
package com.study.juc.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
// 优势:无锁。
// 注意:批量操作不提供原子保证 addAll, removeAll, retainAll, containsAll, equals, and toArray
// 坑: size()方法每次都是遍历整个链表,最好不要频繁调用
// 如果没有阻塞要求,用这个挺好的(堆积数据)
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 不需要指定容量,addAll
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();
// 1秒消费数据一个
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("取到数据:" + queue.poll()); // poll非阻塞 没有数据则返回null
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(3000L); // 让前面的线程跑起来
// 生产者
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.offer(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // offer非阻塞,满了返回false
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "塞入完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 中的size()方法谨慎使用,数据量大的时候,性能效率是很低的。它是通过循环遍历的方式实现的。假设里面有1W条数据,每调用一次就要循环1W次。
看源码:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue .size()源码:
public int size() {
int count = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p))
if (p.item != null)
// Collection.size() spec says to max out
if (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
break;
return count;
}
如果只是想判断队列中是否有数据,只需要调用ConcurrentLinkedQueue 提供的isEmpty()方法
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first() == null;
}
ArrayBlockingQueue
它是基于数组的阻塞循环队列, 此队列按 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。
示例代码:
package com.study.juc.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
// 它是基于数组的阻塞循环队列, 此队列按 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。
public class ArrayBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 构造时需要指定容量(量力而行),可以选择是否需要公平(最先进入阻塞的,先操作)
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3, false);
// 1秒消费数据一个
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("取到数据:" + queue.poll()); // poll非阻塞
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(3000L); // 让前面的线程跑起来
// 三个线程塞数据
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // put阻塞(如果当前的队列已经塞满了数据,线程不会继续往下执行,等待其他线程把
// 队列的数据拿出去// )
// queue.offer(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // offer非阻塞,满了返回false
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "塞入完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
构造时需要指定容量(量力而行),可以选择是否需要公平(最先进入阻塞的,先操作)
put阻塞(如果当前的队列已经塞满了数据,线程不会继续往下执行,等待其他线程把 队列的数据拿出去// )从源码可知。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
//判断是否满了,否则进行阻塞。
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
insert(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
queue.offer(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // offer非阻塞,满了返回false,从源码可知。
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//判断队列是否满了,满了则返回false
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
insert(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
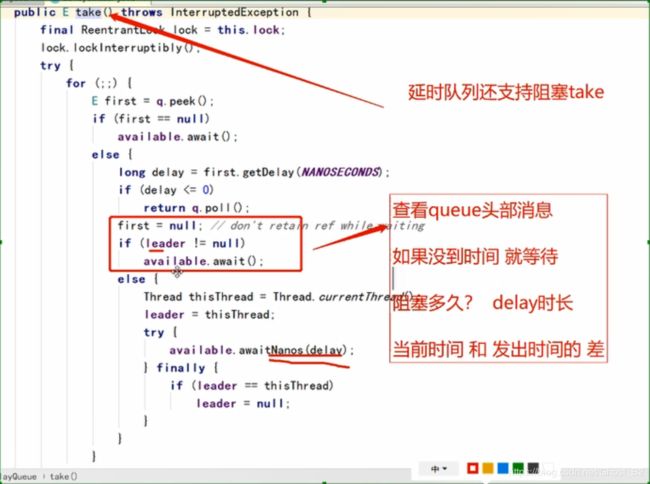
take()方法 当队列中不存在数据的时候,则进行阻塞等待,直到有其他线程插入数据。
从源码可知。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return extract();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
LinkedBlockingQueue
它是基于链表的队列,此队列按 FIFO(先进先出)排序元素。
package com.study.juc.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
// 它是基于链表的队列,此队列按 FIFO(先进先出)排序元素。
// 如果有阻塞需求,用这个。类似生产者消费者场景
public class LinkedBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 构造时可以指定容量,默认Integer.MAX_VALUE
LinkedBlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>(3);
// 1秒消费数据一个
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("取到数据:" + queue.poll()); // poll非阻塞
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(3000L); // 让前面的线程跑起来
// 三个线程塞数据
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// queue.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // put阻塞
queue.offer(Thread.currentThread().getName()); // offer非阻塞,满了返回false
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "塞入完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
PriorityQueue
是一个带优先级的 队列,而不是先进先出队列。
元素按优先级顺序被移除,该队列也没有上限
没有容量限制的,自动扩容
虽然此队列逻辑上是无界的,但是由于资源被耗尽,所以试图执行添加操作可能会导致 OutOfMemoryError)。
代码示例:
package com.study.juc.queue;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
// 是一个带优先级的 队列,而不是先进先出队列。
// 元素按优先级顺序被移除,该队列也没有上限
// 没有容量限制的,自动扩容
// 虽然此队列逻辑上是无界的,但是由于资源被耗尽,所以试图执行添加操作可能会导致 OutOfMemoryError),
// 但是如果队列为空,
// 那么取元素的操作take就会阻塞,所以它的检索操作take是受阻的。另外,
// 入该队列中的元素要具有比较能力
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 可以设置比对方式
PriorityQueue<String> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override //
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// 实际就是 元素之间的 比对。
return 0;
}
});
priorityQueue.add("c");
priorityQueue.add("a");
priorityQueue.add("b");
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());
PriorityQueue<MessageObject> MessageObjectQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<MessageObject>() {
@Override
public int compare(MessageObject o1, MessageObject o2) {
return o1.order > o2.order ? -1 : 1;
}
});
}
}
class MessageObject {
String content;
int order;
}
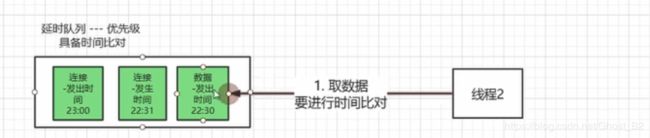
DelayQueue
延时队列具有2个特性:
1、排序(对时间的进行排序22:30 22:31 23:00)
2、时间上的比对(比如:设置的时间为22:30才触发,现在是21:00是取不出来数据的)
示例代码:
package com.study.juc.queue;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
// (基于PriorityQueue来实现的)是一个存放Delayed 元素的无界阻塞队列,
// 只有在延迟期满时才能从中提取元素。该队列的头部是延迟期满后保存时间最长的 Delayed 元素。
// 如果延迟都还没有期满,则队列没有头部,并且poll将返回null。
// 当一个元素的 getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) 方法返回一个小于或等于零的值时,
// 则出现期满,poll就以移除这个元素了。此队列不允许使用 null 元素。
public class DelayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DelayQueue<Message> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<Message>();
// 这条消息5秒后发送
Message message = new Message("message - 00001", new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 5000L));
delayQueue.add(message);
while (true) {
System.out.println(delayQueue.poll());
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
// 线程池中的定时调度就是这样实现的
}
}
// 实现Delayed接口的元素才能存到DelayQueue
class Message implements Delayed {
// 判断当前这个元素,是不是已经到了需要被拿出来的时间
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
// 默认纳秒
long duration = sendTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
return TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.convert(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return o.getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) > this.getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) ? 1 : -1;
}
String content;
Date sendTime;
/**
* @param content 消息内容
* @param sendTime 定时发送
*/
public Message(String content, Date sendTime) {
this.content = content;
this.sendTime = sendTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Message{" +
"content='" + content + '\'' +
", sendTime=" + sendTime +
'}';
}
}