内核源码IO多路复用之select
1. 简介:
本文将基于内核2.6.32版本,了解select运作的原理。
2. 数据结构:
select基于位图的,因此对于三种事件(读写超时)的位图集合都是使用unsigned long的数组来表示。
__kernel_fd_set就是fd_set,其内在就是一个数组,每个unsigned long在不同机器上表示长度不同,总大小1024,写死在内核,因此如果修改select监听的总fd数需要重新编译内核。
这里出现的几个宏比较常用到,__NFDBITS表示一个unsigned long能表示多少个位,__FD_SETSIZE表示监听的fd数量,__FD_SET_LONGS表示unsigned long数组的大小。对应FD的事件置位只要将相应的位图置位即可。
select中监听的fd应该都是fd号小于1024的,位图的使用都是直接使用fd号当做位图的下标进行处理的,如果fd号大于1024可能会导致异常。
#undef __NFDBITS
#define __NFDBITS (8 * sizeof(unsigned long))
#undef __FD_SETSIZE
#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024
#undef __FDSET_LONGS
#define __FDSET_LONGS (__FD_SETSIZE/__NFDBITS)
#undef __FDELT
#define __FDELT(d) ((d) / __NFDBITS)
#undef __FDMASK
#define __FDMASK(d) (1UL << ((d) % __NFDBITS))
typedef struct {
unsigned long fds_bits [__FDSET_LONGS];
} __kernel_fd_set;函数系统调用的入口在fs/select.c中,系统调用处主要是对超时时间的处理,从用户空间拷贝到内核空间,并检查其合法性。主要流程在core_sys_select。函数poll_select_copy_remaining主要对结果数据进行处理,把数据从内核空间拷贝回用户空间。
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(select, int, n, fd_set __user *, inp, fd_set __user *, outp,
fd_set __user *, exp, struct timeval __user *, tvp)
{
struct timespec end_time, *to = NULL;
struct timeval tv;
int ret;
if (tvp) {
if (copy_from_user(&tv, tvp, sizeof(tv)))
return -EFAULT;
to = &end_time;
/* 检查超时的合法性。 */
if (poll_select_set_timeout(to,
tv.tv_sec + (tv.tv_usec / USEC_PER_SEC),
(tv.tv_usec % USEC_PER_SEC) * NSEC_PER_USEC))
return -EINVAL;
}
/* 实际处理函数。 */
ret = core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, to);
/* 数据后处理。 */
ret = poll_select_copy_remaining(&end_time, tvp, 1, ret);
return ret;
}int core_sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp,
fd_set __user *exp, struct timespec *end_time)
{
/*
* Scaleable version of the fd_set.
*/
/* 需要六个位图,分别表示用户输入的读写异常和输出给用户的读写异常。 */
typedef struct {
unsigned long *in, *out, *ex;
unsigned long *res_in, *res_out, *res_ex;
} fd_set_bits;
fd_set_bits fds;
void *bits;
int ret, max_fds;
unsigned int size;
struct fdtable *fdt;
/* Allocate small arguments on the stack to save memory and be faster */
/* 在栈上开一个栈,fds会先尝试使用栈,如果大小超过栈再去堆上分配内存。 */
#define FRONTEND_STACK_ALLOC 256
#define SELECT_STACK_ALLOC FRONTEND_STACK_ALLOC
long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)];
ret = -EINVAL;
if (n < 0)
goto out_nofds;
/* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */
rcu_read_lock();
fdt = files_fdtable(current->files);
max_fds = fdt->max_fds;
rcu_read_unlock();
if (n > max_fds)
n = max_fds;
/*
* We need 6 bitmaps (in/out/ex for both incoming and outgoing),
* since we used fdset we need to allocate memory in units of
* long-words.
*/
size = FDS_BYTES(n);
bits = stack_fds;
/* 栈大小不够。 */
if (size > sizeof(stack_fds) / 6) {
/* Not enough space in on-stack array; must use kmalloc */
ret = -ENOMEM;
bits = kmalloc(6 * size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bits)
goto out_nofds;
}
/* 分配六个位图的空间。 */
fds.in = bits;
fds.out = bits + size;
fds.ex = bits + 2*size;
fds.res_in = bits + 3*size;
fds.res_out = bits + 4*size;
fds.res_ex = bits + 5*size;
/* 从用户空间把用户输入的fdset拷贝至fds的输入位图。 */
if ((ret = get_fd_set(n, inp, fds.in)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, outp, fds.out)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, exp, fds.ex)))
goto out;
/* 初始化fds的输出位图。 */
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_in);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_out);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_ex);
/* select实际处理逻辑。 */
ret = do_select(n, &fds, end_time);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
if (!ret) {
ret = -ERESTARTNOHAND;
if (signal_pending(current))
goto out;
ret = 0;
}
/* 将输出位图拷贝至用户空间。 */
if (set_fd_set(n, inp, fds.res_in) ||
set_fd_set(n, outp, fds.res_out) ||
set_fd_set(n, exp, fds.res_ex))
ret = -EFAULT;
/* 释放资源。 */
out:
if (bits != stack_fds)
kfree(bits);
out_nofds:
return ret;
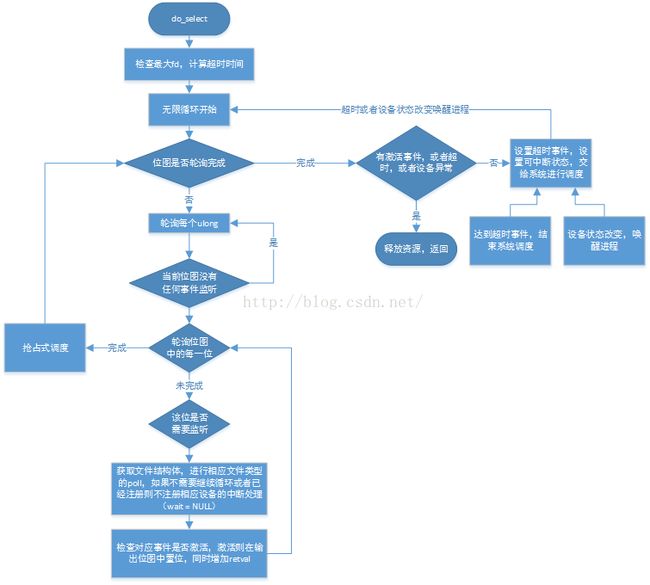
}实际的select执行在do_select中,首先检查了所监听的文件描述符是否合法(是否打开),然后在一个主循环中遍历所有的位图,遍历过程由一个两层循环组成,外层循环为一个unsigned long单位,内层循环为一个bit单位。当该位有事件需要监听时,会通过该文件的poll函数去尝试获取该文件的状态,并注册相应的唤醒函数给设备(如果已经确认要退出循环则只查询状态不注册,如超时为0,或者已经注册,则不重复注册),并根据该状态和用户所监听的事件类型进行比对,相同则在相应的返回位图中置位。
在每一个unsigned long的位图轮询完成的时候,会发起条件调度cond_sched,防止大量的轮询占据操作系统,以降低系统时延[1]。
当每一轮轮询完成时,如果有事件或者信号触发,或者达到定时时间会中断轮询,返回结果。如果还没有结果且没有超时,这时候会出让调度权,将select设置成可中断任务,然后根据超时时间进行调度,这时候唤醒select有两种方式:
一种是超时,但是没有任何所监听的fd被唤醒,这时候下一次轮询每个fd结果后以timeout结束select。
一种是设备唤醒,设置触发标志位,下一次轮询时候根据每个fd结果判断是否有结果可以返回(如果唤醒了但不是关注事件是否进入一个大循环去拼命轮询?因为此时trigger标志已经被置位,在poll_schedule_timeout中不会进行调度)。
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, struct timespec *end_time)
{
ktime_t expire, *to = NULL;
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i, timed_out = 0;
unsigned long slack = 0;
rcu_read_lock();
/* 根据三个输入集合、最大监听fd数量以及系统中打开的fd进行简单的检查
* 重新计算最大的监听fd数量。
* 如果监听的fd不是打开的状态,则返回-EBADFD。 */
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
/* 初始化等待钩子。 */
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
/* 超时计算。 */
if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) {
wait = NULL;
timed_out = 1;
}
if (end_time && !timed_out)
slack = estimate_accuracy(end_time);
retval = 0;
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
/* 外层循环,遍历每个unsigned long。
* i表示当前的位,在外层循环中没有直接改变(除了当前unsigned long无事件)
* 在内层循环遍历时候增加。 */
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) {
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
/* 当前这个unsigned long中所有监听的fd的总位图。 */
all_bits = in | out | ex;
/* 当前这个unsinged long未监听任何fd。 */
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS;
continue;
}
/* 内层循环,遍历单个unsigned long中的每一位。 */
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) {
int fput_needed;
/* 遍历结束。 */
if (i >= n)
break;
/* 当前位不在监听的事件中。 */
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
/* 获取该位的文件结构体。 */
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
f_op = file->f_op;
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll) {
/* 对应文件系统类型的poll函数,如tcp_poll。
* 获取该fd的poll状态。 */
wait_key_set(wait, in, out, bit);
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, wait);
}
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
/* 看看该fd所获取的事件和监听的事件类型是否一致。
* 是就在相应的返回位图中标记,增加返回值。 */
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit;
retval++;
wait = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
wait = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
wait = NULL;
}
}
}
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
/* 开启条件调度。 */
cond_resched();
}
wait = NULL;
/* 有事件或信号触发了,或者达到超时时间了,退出无限循环。 */
if (retval || timed_out || signal_pending(current))
break;
if (table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
/* 设置超时时间,设置可中断,主动交出调度权,由内核进行调度,
* 等到下一次调度回到该函数时候进行下一次循环。 */
/*
* If this is the first loop and we have a timeout
* given, then we convert to ktime_t and set the to
* pointer to the expiry value.
*/
if (end_time && !to) {
expire = timespec_to_ktime(*end_time);
to = &expire;
}
if (!poll_schedule_timeout(&table, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,
to, slack))
timed_out = 1;
}
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}4. do_select简要流程图:
5. 参考文献:
[1]. 内核cond_sched http://blog.csdn.net/su_linux/article/details/15500053
[2]. fd->poll解释 http://blog.csdn.net/lizhiguo0532/article/details/6568969
[3]. poll的唤醒 http://blog.csdn.net/lizhiguo0532/article/details/6568968