linux(Red Hat)NTP时间同步的配置方法(局域网内)
- NTP跟踪层级安排
- NTP配置数据对单点故障应对能力的评估
- NTP服务器- redhat服务器的配置数据及说明
- NTP客户机-redhat服务器的配置数据及说明
-
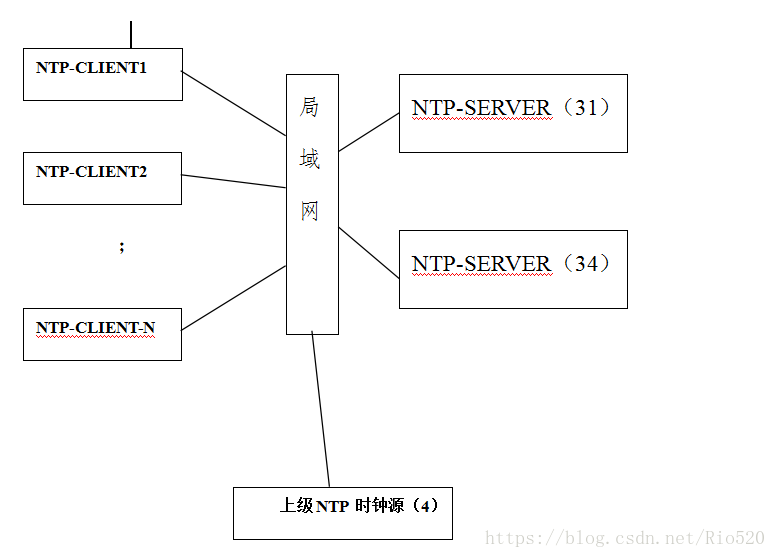
- NTP跟踪层级安排
| 设备 |
第1跟踪时钟源 |
第2跟踪时钟源 |
第3跟踪时钟源 |
网内NTP S/C |
| 192.168.80.31 |
192.168.80.4 prefer |
注1 |
127.127.1.0 |
server |
| 192.168.80.34 |
192.168.80.4 prefer |
注1 |
127.127.1.0 |
server |
| 其他redhat机器 |
192.168.80.31或192.168.80.34 |
192.168.80.34或192.168.80.31 |
127.127.1.0 |
client |
注1:如有其他与192.168.80.4同级的时钟源可用,则NTP的可靠性更佳。
网内所有NTP客户机由自已的NTP算法根据当时NTP服务器及网络状态自行选择NTP服务器:不是192.168.80.31就是192.168.80.34。一旦网内NTP客户机失去了与网内NTP服务器的连接,将会按照自已的时钟频率将系统时间继续走下去,除了可能会造成日志时间和告警时间与标准时间有非常小的偏差外,不会对服务器应用或自身造成任何影响。
-
- NTP配置数据对单点故障应对能力的评估
下面就局域网内系统中相关设备发生单点故障时,各设备的NTP时钟跟踪情况做一分析:
- 上级NTP服务器单机失效但vrrp有效:
| 设备 |
所跟踪的上级NTP服务器 |
能否跟踪上级时钟 |
| 192.168.80.31 |
192.168.80.4 |
能 |
| 192.168.80.34 |
192.168.80.4 |
能 |
| 其他redhat机器 |
192.168.80.31或192.168.80.34 |
能 |
- 上级NTP服务器vrrp失效):
| 设备 |
所跟踪的上级NTP服务器 |
能否跟踪上级时钟 |
| 192.168.80.31 |
127.127.1.0(自身硬件时钟) |
不能 |
| 192.168.80.34 |
127.127.1.0(自身硬件时钟) |
不能 |
| 其他redhat机器 |
192.168.80.31或192.168.80.34 |
能 |
- 局域网内的NTP server_1 (31)失效:
| 设备 |
所跟踪的上级NTP服务器 |
能否跟踪上级时钟 |
| 192.168.80.31 |
|
|
| 192.168.80.34 |
192.168.80.4 |
能 |
| 其他redhat机器 |
192.168.80.34 |
能 |
- 局域网内的NTP server_2 (34)失效:
| 设备 |
所跟踪的上级NTP服务器 |
能否跟踪上级时钟 |
| 192.168.80.31 |
192.168.80.4 |
能 |
| 192.168.80.34 |
|
|
| 其他redhat机器 |
192.168.80.32 |
能 |
- NTP服务器-redhat服务器(31, 34)的配置数据及说明
(注:对NTP服务器的唯一要求是机器上不要跑双机系统。)
- NTP的配置文件(/etc/ntp.conf)的内容:
===============================
#ntp restrict part
restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict 192.168.80.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
restrict 192.168.81.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
#ntp server part
server 192.168.80.4 version 3
server 127.127.1.0
#fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
#ntp other part
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
==============================
- 硬件时间每日有条件地被系统时间更新的配置
(1)创建硬件时间更新脚本:
/root/day_update_hwclock.sh的内容:
===========================
/usr/sbin/ntpq -p > /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
if grep "*192.168.80.4" /root/tmp_ntpq.txt
then
/bin/date >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
/usr/sbin/hwclock --show >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
/usr/sbin/hwclock -w >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
[ $? -eq 0 ] && echo "hwclock -w success" >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
/bin/date >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
/usr/sbin/hwclock --show >> /root/tmp_ntpq.txt 2>&1
else
logger -p alert "[HC]:NTP server lost or NTP service stop"
fi
正常输出结果:
# cat tmp_ntpq.txt
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
===========================================================
*192.168.80.4 127.0.0.1 4 u 763 1024 377 7.651 0.373 2.499
LOCAL(0) .LOCL. 5 l 21 64 377 0.000 0.000 0.001
[root@PC2 sbin]#cat tmp_ntpq.txt
Mon Jan 4 14:19:18 CST 2010
Mon 04 Jan 2010 02:19:18 PM CST -0.015936 seconds
hwclock -w success
Mon Jan 4 14:19:20 CST 2010
Mon 04 Jan 2010 02:19:20 PM CST -0.015907 seconds
[root@ftpnode2 ~]#
=============================
该脚本用于将系统时间去同步硬件时间,以消除硬件时间的累积误差。作为网内NTP服务器,这样做是必须的。因为一旦与上级NTP服务器失去连接后,该网内NTP服务器将使用自身的硬件时钟作为自已的时间跟踪源向网内NTP客户机提供服务,所以NTP服务器的硬件时间必须尽可能接近标准时间。但同步也是有条件的:当本机与上级NTP服务器处在有效跟踪状态时,用本机当前系统时间去更新硬件时间;反之,当本机与上级NTP服务器的同步状态失去时,本机硬件时钟必须保持独立,因为此时系统时间将把本机的硬件时钟作为自已的上级NTP服务器而跟踪,故此时不能再用系统时间去同步硬件时间了。
在本机与上级NTP服务器的同步状态失去的同时,脚本将向局域网内网管告警:本机与上级NTP服务器的连接丢失或本机NTP服务已退出。
(2)在系统cron中增加一条命令,用于每日一次系统自动去做系统时间同步硬件时间的动作:
在/etc/crontab中增加的内容:
=============================
00 12 * * * root /root/ day_update_hwclock.sh
=============================
每日12时0分时自动有条件地做一次硬件时钟的校准。
- NTP服务开机自动启动的配置及相关处理
配置NTP服务在开机时自动启动:
#chkconfig --level 35 ntpd on
配置了NTP服务开机时自动启动后,Linux机器在开机或重启时,系统会首先读取硬件时间作为本机的系统时间,然后启动NTP服务。但作为NTP服务器,这样的启动过程无法保证其以标准时间向NTP客户机提供服务(硬件时间不准确的因素有很多)。所以,必须在系统启动NTP服务之前,把它的系统时间直接校准到上级NTP服务器的时间。其处理方法是:在NTP服务启动脚本/etc/rc.d/init.d/ntpd中"# Start daemons."行(113行)后增加下列命令:
================================
#before NTP service start,system time is reset by its NTP server's time.
NTP_MAX_WAIT_SECOND=120
NTP_SERVER_IP=192.168.80.4
NTP_WAIT_COUNT=0
date > /root/tmp_ntpdate.txt 2>&1
while [ $NTP_WAIT_COUNT -ne $NTP_MAX_WAIT_SECOND ]
do
NTP_PING_STATE=`ping -c1 $NTP_SERVER_IP|grep '1 received'|wc -l`
[ $NTP_PING_STATE -ne 0 ] && break
NTP_WAIT_COUNT=`expr $NTP_WAIT_COUNT + 1`
echo $NTP_WAIT_COUNT >> /root/tmp_ntpdate.txt 2>&1
done
/usr/sbin/ntpdate $NTP_SERVER_IP >> /root/tmp_ntpdate.txt 2>&1
date >> /root/tmp_ntpdate.txt 2>&1
===============================
这样配置以后,NTP服务器在启动后将无需人工介入,直接提供NTP校时服务。
上述1,2,3步的配置和措施能够保证局域网内网内NTP服务器以稳定的时间基准和状态向网内所有NTP客户机提供校时服务,以满足网内RAC架构或其他双机数据库服务器对时间同步的严格要求。
- NTP相关操作命令
(1)系统时间设置及显示命令:
日期设置:#date –s yyyy-mm-dd
时间设置:#date –s hh:mm:ss
显示:#date
(2)硬件时间设置及显示命令:
hwclock --set --date="12/15/2009 15:59:59"
hwclock -r or hwclock --show
(3)系统时间与硬件时间的同步命令:
把硬件时间设置为系统时间:hwclock -w or hwclock --systohc
把系统时间设置为硬件时间:hwclock -s or hwclock --hctosys
(4)将本机系统时间直接设置为对方机器系统时间的命令(注:本机NTP服务必须是关闭的):
#ntpdate 对方机器的IP地址
(5)NTP服务状态查询命令:
# ntpstat
synchronised to NTP server (192.168.80.4 at stratum 6
time correct to within 30 ms
polling server every 64 s
(6)NTP同步过程的单步和连续跟踪命令(注:本机NTP服务必须在运行状态):
单步跟踪命令:
#ntpq –p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
===================================================================
*192.168.80.4 127.0.0.1 4 u 1023 1024 377 9.260 -0.291 1.480
LOCAL(0) .LOCL. 5 l 29 64 377 0.000 0.000 0.001
(7)NTP时钟源的跟踪命令(注:本机NTP服务必须在运行状态):
[root@shouli1 ~]# ntptrace
shouli1: stratum 5, offset -0.000024, synch distance 0.066127
PC1: stratum 4, offset 0.000404, synch distance 0.029184
192.168.80.4: timed out, nothing received
***Request timed out
(8)设备之间的连接状态及两者之间的传输延迟,时间差值(-XX.局域网内表示本机系统时间比对方设备的系统时间快XX.局域网内秒)的查询命令:
(注:本机NTP服务在运行状态或关闭状态均可,但对方设备的NTP服务必须在运行状态)
#ntpdate -d 对方设备的IP地址
[root@PC1 etc]# ntpdate -d 192.168.80.4
4 Dec 16:39:11 ntpdate[27230]: ntpdate [email protected] Mon Jun 4 15:13:13 UTC 2007 (1)
Looking for host 192.168.80.4 and service ntp
host found : 192.168.80.4
transmit(192.168.80.4)
receive(192.168.80.4)
transmit(192.168.80.4)
receive(192.168.80.4)
transmit(192.168.80.4)
receive(192.168.80.4)
transmit(192.168.80.4)
receive(192.168.80.4)
transmit(192.168.80.4)
server 192.168.80.4, port 123
stratum 3, precision -18, leap 00, trust 000
refid [192.168.80.4], delay 0.02632, dispersion 0.00000
transmitted 4, in filter 4
reference time: cec34851.72072e27 Fri, Dec 4 2009 16:35:29.445
originate timestamp: cec3492d.a883ecc1 Fri, Dec 4 2009 16:39:09.658
transmit timestamp: cec3492f.701a79fe Fri, Dec 4 2009 16:39:11.437
filter delay: 0.02641 0.02632 0.02637 0.02634
0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
filter offset: -1.77999 -1.78002 -1.78002 -1.78001
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
delay 0.02632, dispersion 0.00000
offset -1.780027
4 Dec 16:39:11 ntpdate[27230]: step time server 192.168.80.4 offset -1.780027 sec
(9)NTP服务开机自动启动的配置及检查命令:
配置:#chkconfig --level 35 ntpd on
(打开自动启动用“on”;去掉自动启动用“off”)
检查:# chkconfig --list
(10)启动/停止/重启动NTP服务的命令:
service ntpd start|stop|restart
- NTP客户机-redhat服务器的配置及说明
- NTP配置文件(/etc/ntp.conf)
#ntp restrict part
restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict 192.168.80.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
restrict 192.168.81.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
#ntp server part
server 192.168.80.31
server 192.168.80.34
server 127.127.1.0
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
#ntp other part
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
- NTP服务开机自动启动的配置
均配置为NTP服务自动启动。但不做重启特殊处理,即在系统重启时不做系统时间直接校准(需评估)。
- 定时(每日一次)将系统时间无条件写入硬件时钟
在系统cron(/etc/crontab)中增加一条命令: -------------------------------------------------
01 0 * * * root /sbin/hwclock -w
- NTP相关操作命令
同NTP服务器的相关操作命令。