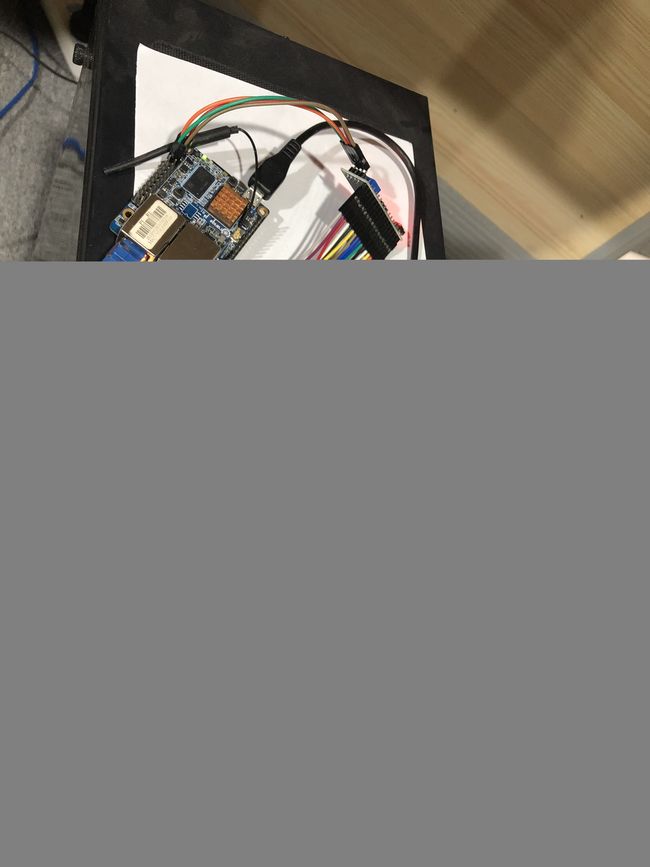
Orange Pi 通过I2C总线连接LCD1602
Orange Pi 通过I2C总线连接LCD1602
前言
上一节通过Orange Pi gpio 直接控制1602,可以看出来缺点非常明显:Orange Pi IO 口占用过多
因为Orange Pi的GPIO口非常有限,所以这一章就来解决这个问题,采用 i2c转LCD1602的转接板( PCF85741)来减少Orange Pi 的GPIO占用
一、硬件及连线:
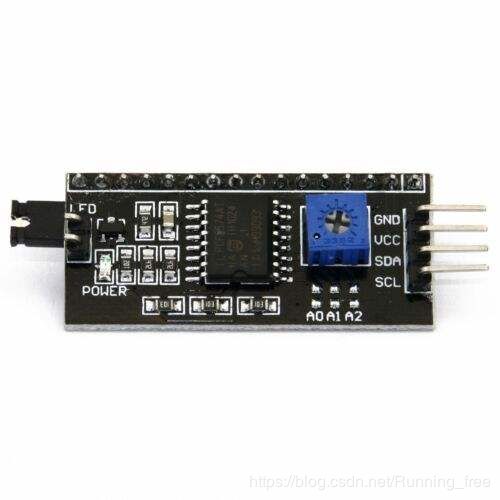
模块长这样子,网上找的图:

和1602连在一起是这样子,这个是焊接在一起的,也可以用杜邦线连接起来

有了这货之后,连接香橙派就只需要两根数据线就可以了,如果不算电源线的话,加上电源线一共也才四根线,清爽多了
连线也是so easy,下面奉上接线方式(物理接口):
:---PCF85741---: :---Orange Pi---:
GND-------------06 GROUND
VCC-------------04 5V
SDA-------------03 SDA1
SCL-------------05 SDA1
好了,完成上面的接线工作,就可以通电了。
连接电源打开树莓派,显示屏就会亮,同时在第一行显示一排黑方块。如果看不到黑方块或黑方块不明显,请调节i2c模块上的可调电阻,直到黑方块清晰显示。如果调节可调电阻还看不到方块,则可能你的连接有问题了,请检查连接,包括检查显示屏的引脚有没有虚焊。
二、使能I2C
由于我的系统是armbian的,比较方便,如果你装的是orangepi官网提供的ubuntu,建议你不要折腾了,换回armbian会让你省很多事。这是我含泪踩过的坑啊,内核都重新编译过了,心酸
废话不多说,先看看默认有没有使能i2c:
ls /dev | grep i2c
什么都没有,看来是没有使能i2c啊
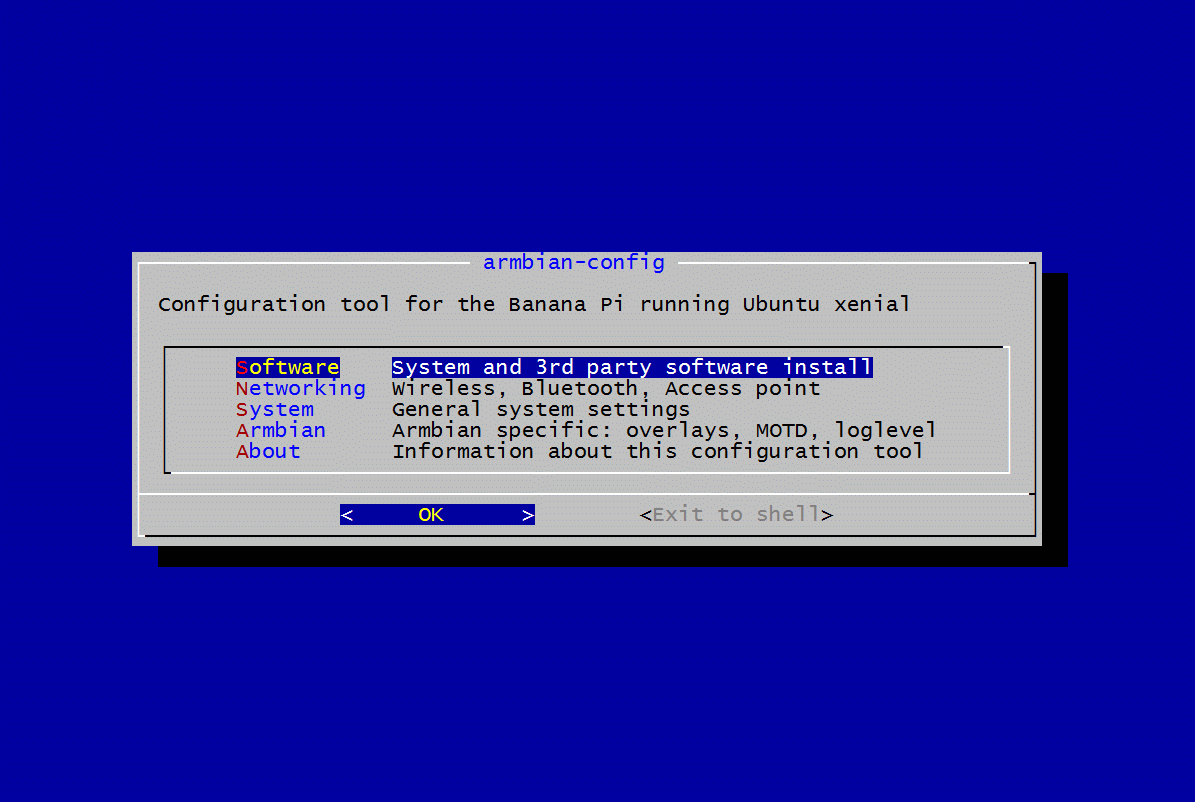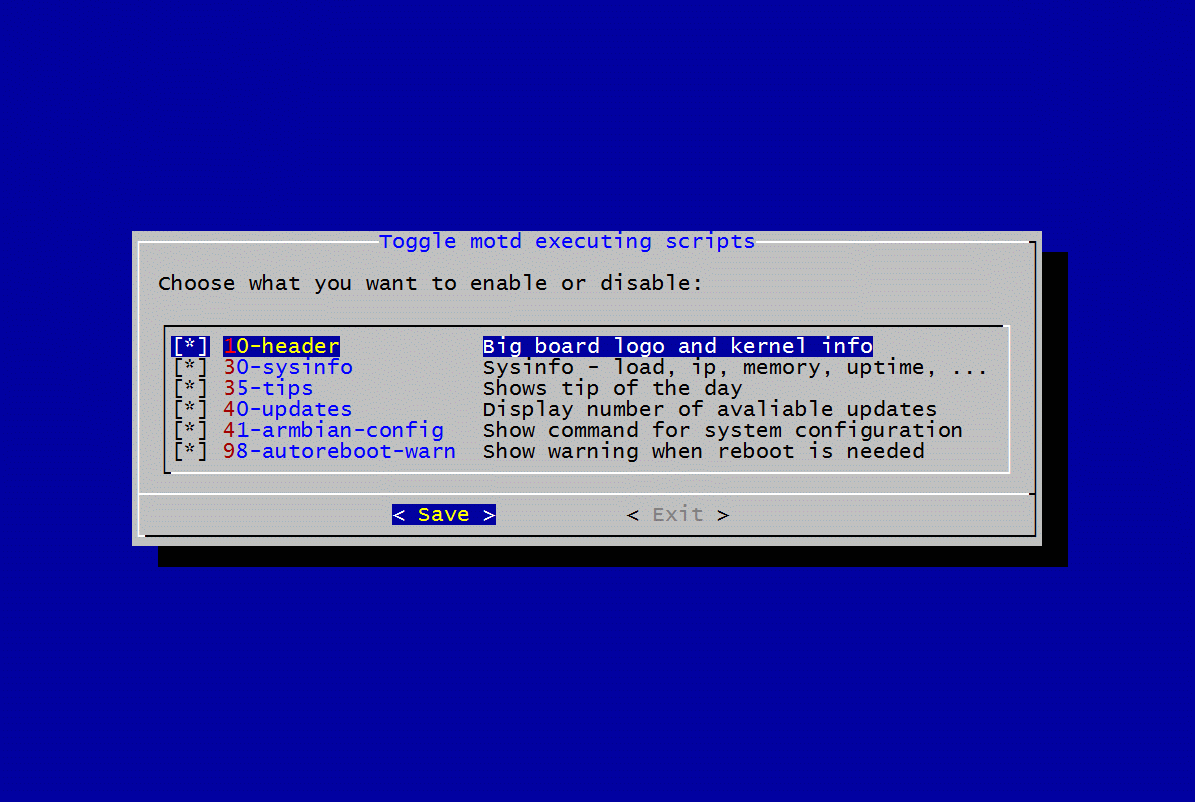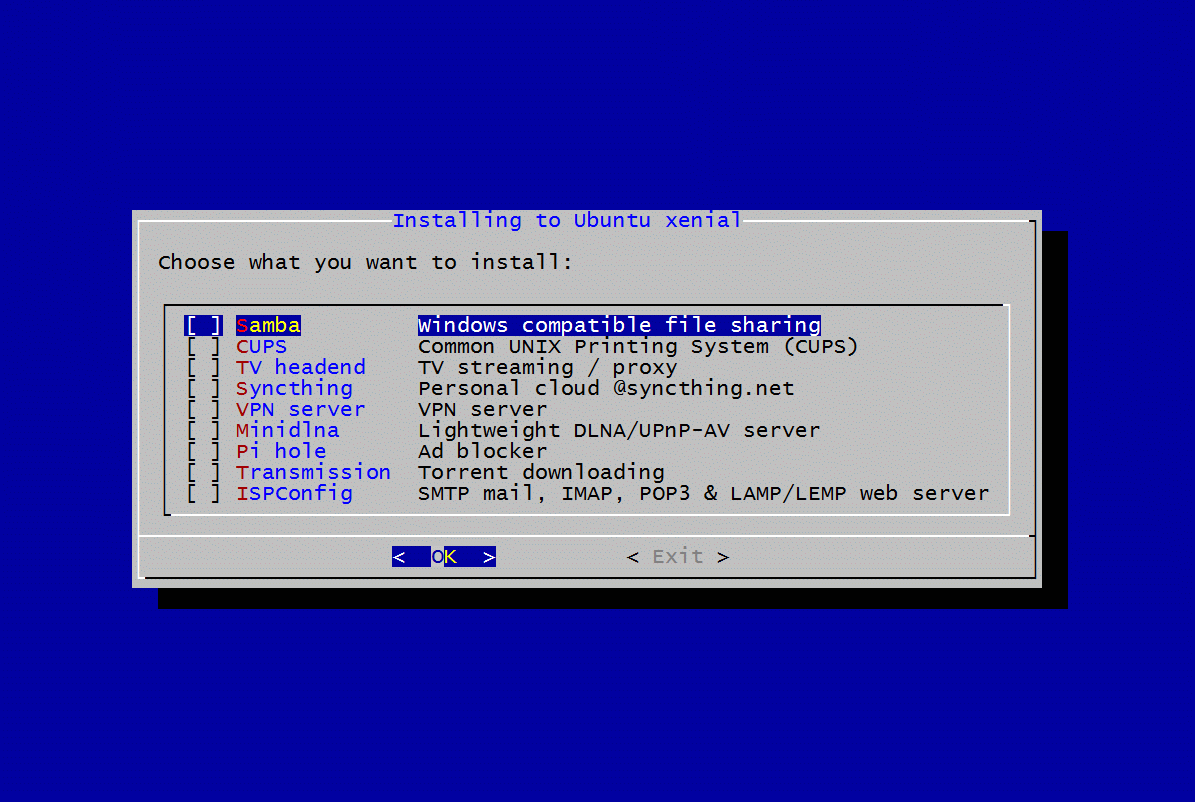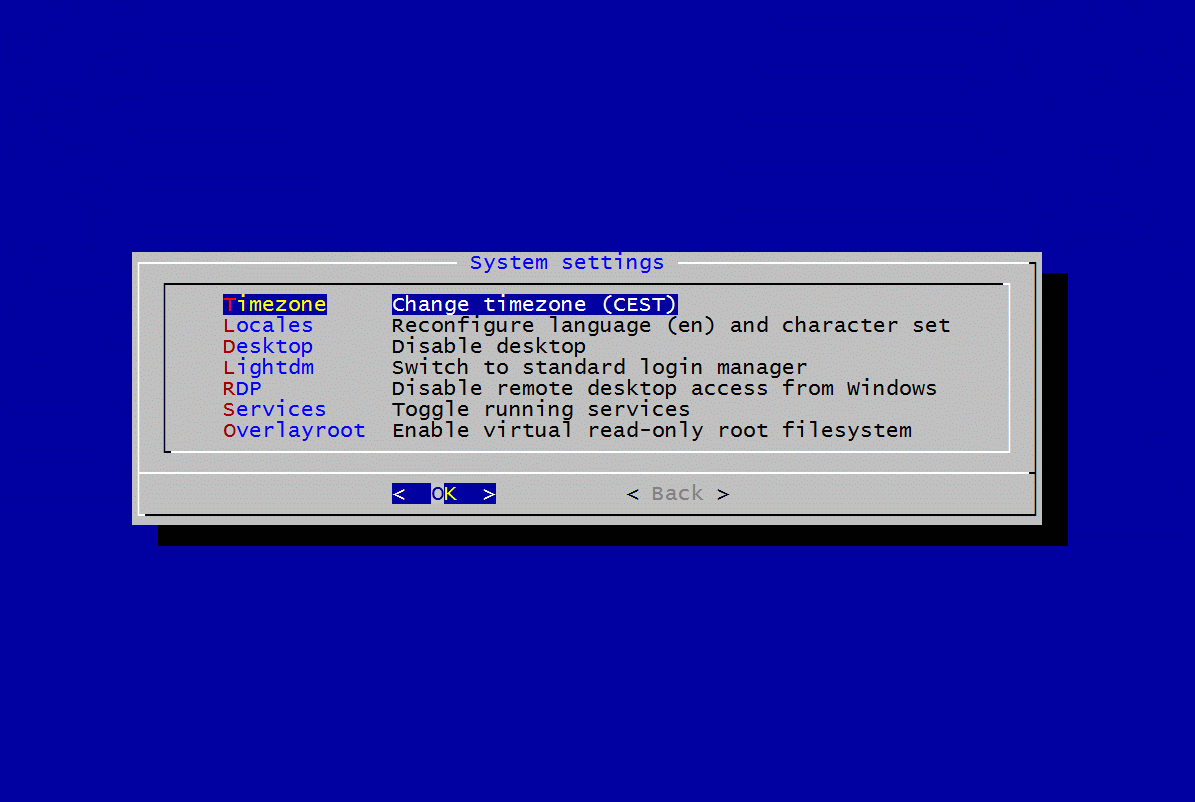
接下来开启i2c,armbian有一个非常好用的工具,类似树莓派的raspi-config,它就是armbian-config
sudo armbian-config
忘了截图了,依次进入:system>>HardWare>>[ ]i2c0 ,按空格键选中i2c0,变成[* ]i2c0这样子,
然后选中save,reboot即可
再执行:
ls /dev | grep i2c
打印出 i2c-0 了,说明开启成功,接下来看一下i2c设备地址:
root@orangepi:~# sudo apt install i2c-tools
root@orangepi:~# i2cdetect -y 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 27 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
可以看到我的i2c设备地址是0x27
这说明 已经成功连接了 LCD1602 。接下来就可以用 Python 控制 LCD1602 显示信息了。
三、驱动程序:
python驱动i2c需要python-smbus,先安装一下:
sudo apt-get install python3-smbus
接下来我们熟悉的套路,上代码,如下:
vim i2c_1602_test.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
'''
BIT D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
| | | | | | | |
LCD D7 D6 D5 D4 BackLight En Rw Rs
'''
import time
import smbus
import sys
Bl = 0B00001000 # backlight 0:off 1:on
En = 0B00000100 # Enable bit
Rw = 0B00000010 # Read/Write bit 0:write 1:read
Rs = 0B00000001 # Register select bit 0:cmd 1:data
LCD_WIDTH = 16 # Maximum characters per line
LCD_LINE_1 = 0x80 # LCD RAM address for the 1st line
LCD_LINE_2 = 0xC0 # LCD RAM address for the 2nd line
debug = 0
#创建一个smbus实例
BUS = smbus.SMBus(0) # 0 代表 /dev/i2c-0, 1 代表 /dev/i2c-1 ,具体看使用的树莓派那个I2C来决定
LCD_ADDR = 0x27 #sudo i2cdetect -y -a 0
def main():
global debug
if len(sys.argv)>1:
debug = 1
print("turn on debug,welcom!")
else:
debug = 0
init_lcd()
while True:
show_on_lcd(LCD_LINE_1, 0, '1234567890123456')
show_on_lcd(LCD_LINE_2, 0, 'abcdefghijklmnop')
time.sleep(3) # 3 second delay
show_on_lcd(LCD_LINE_1, 0, 'blog.csdn.net')
show_on_lcd(LCD_LINE_2, 0, 'Running_free')
time.sleep(3) # 3 second delay
def send_command(comm):
if debug:
print("****************now send sommand******************")
print("now send command >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>",hex(comm),"---",bin(comm))
# Send bit7-4 firstly
buf = comm & 0xF0 | Bl | En
if debug:
print(" high: ",bin(buf)),
# buf |= (Bl | En) # BL = 1, EN = 1, RW = 0, RS = 0
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
time.sleep(0.002)
buf &= 0xFB # EN = 0
if debug:
print(" high_en: ",bin(buf)),
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
# Send bit3-0 secondly
buf = ((comm & 0x0F) << 4)| Bl | En
if debug:
print(" low: ",bin(buf)),
# buf |= (Bl | En) # BL = 1, EN = 1, RW = 0, RS = 0
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
time.sleep(0.002)
buf &= 0xFB # EN = 0
if debug:
print(" low_en: ",bin(buf),"end<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<")
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
def send_data(data):
if debug:
print("****************now send data******************")
print("now send data --------------",hex(data),"---",bin(data))
# Send bit7-4 firstly
buf = data & 0xF0 | Bl | En | Rs
if debug:
print(" high: ",bin(buf)),
# buf |= (Bl | En | Rs) # BL = 1, EN = 1, RW = 0, RS = 1
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
time.sleep(0.002)
buf &= 0xFB # EN = 0
if debug:
print(" high_en: ",bin(buf)),
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
# Send bit3-0 secondly
buf = ((data & 0x0F) << 4)| Bl | En | Rs
if debug:
print(" low: ",bin(buf)),
# buf |= (Bl | En | Rs) # BL = 1, EN = 1, RW = 0, RS = 1
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
time.sleep(0.002)
buf &= 0xFB # EN = 0
if debug:
print(" low_en: ",bin(buf),"end------------------")
BUS.write_byte(LCD_ADDR ,buf)
def init_lcd():
if debug:
print("****************now init******************")
send_command(0x33) # Must initialize to 8-line mode at first
time.sleep(0.005)
send_command(0x32) # Then initialize to 4-line mode
time.sleep(0.005)
send_command(0x06) # Cursor move direction
time.sleep(0.005)
send_command(0x0C) # Enable display without cursor
time.sleep(0.005)
send_command(0x28) # 2 Lines & 5*7 dots
time.sleep(0.005)
send_command(0x01) # Clear Screen
time.sleep(0.005)
def clear_lcd():
if debug:
print("****************now clear******************")
send_command(0x01) # Clear Screen
def show_on_lcd(line,table,message):
if debug:
print("****************now show on lcd******************")
# Send string to display
message = message.ljust(LCD_WIDTH," ")
send_command(line)
for i in range(LCD_WIDTH):
send_data(ord(message[i]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
#except KeyboardInterrupt:
except:
pass
finally:
clear_lcd()
show_on_lcd(LCD_LINE_1, 0, 'Goodbye!')
BUS.close()
加了debug方便调试,运行python3 i2c_1602_test.py 后面不跟参数不打印debug信息,如果想打印debug信息,只需要后面跟一个参数即可,任何参数都ok,例:python3 i2c_1602_test.py 1 或者 python3 i2c_1602_test.py debug
#仅运行
python3 i2c_1602_test.py
#运行并打印debug信息
python3 i2c_1602_test.py debug
总结
如果1602没有显示,请检查线路是否有故障,杜邦线容易松动导致接触不良,传输数据就会出现问题,含着泪踩过的坑啊
