[一]SpringCloud微服务入门
[一]SpringCloud微服务入门
1架构演进和分布式系统基础
1.1微服务核心基础
- 网关:路由转发+过滤器
- 服务注册发现:调用和被调用方的信息维护
- 配置中心:管理配置,动态更新
- 链路追踪:分析调用链路耗时
- 负载均衡器:分发负载
- 熔断:保护自己和被调用方
1.2常见的微服务
- dubbo:zookeeper+dubbo+springmvc/springboot
- 通信方式:RPC(远程过程调用协议,通俗的描述:客户端在不知道调用细节的情况下,调用存在于远程计算机上的某个对象)
- 注册中心:zookeper/redis
- 配置中心:diamond
-
springcloud:全家桶+嵌入第三方组件(Netflix)
- 通讯方式:http restful
- 注册中心:eruka/consul
- 配置中心:config
- 网关:zuul
- 分布式追踪系统:sleuth+zipkin
consumer:调用方
provider:被调用方
一个接口一般会充当两个角色(不是同时充当)
1.3微服务下电商项目基础模块设计
简介:微服务下电商项目基础模块设计,分离几个模块,课程围绕这个基础项目进行学习
- 用户服务
- 用户信息接口
- 登录接口
- 商品服务
- 商品列表
- 商品详情
- 订单服务
- 我的订单
- 下单接口
2什么是微服务的注册中心
2.1什么是微服务的注册中心
微服务注册中心:主要用于服务管理,以及动态维护服务注册表。
服务提供者(provider):启动的时候向注册中心上报自己的网络信息
服务消费者(consumer):启动的时候向注册中心上报自己的网络信息,拉取provider的相关网络信息
下面通过一张图来理解微服务注册中心的运行流程:
假定项目有两个微服务,分别为商品服务和订单服务,其中商品服务包含两个接口(商品列表、商品详情),订单服务包含两个接口(下单接口、我的订单)。
以上两个服务启动后会将其中的接口信息发送到注册中心,注册中心中有一张维护服务列表,该列表记录了所有服务接口的信息。
同时服务列表中有一种动态维护机制(心跳机制)保证每个服务接口都是可用的。例如商品服务,作为一个电商项目,会利用集群部署,即很多台服务器上都在运行同一个服务,这时候就需要保证注册列表中的接口都是可用的(对应的服务器正常运行),心跳机制就是每台服务器定时向注册中心发送心跳包,告诉注册中心,我还活着,让我保留在服务列表中。
通过注册中心,对各个服务之间进行了解耦。例如但订单服务需要访问商品服务时,它不直接访问配置文件,而是从注册中心拉取对应的信息,再进行访问。
为什么要用注册中心:
因为服务应用和机器越来越多,调用方需要知道接口的网络地址,如果靠配置文件的方式去控制网络地址,对于动态新增机器、维护带来很大的问题。
主流的注册中心:
zookeeper、Eureka、consul、etcd等
分布式应用知识CAP理论知识
CAP定理:
指的是在一个分布式系统中,Consistency(一致性)、Availability(可用性)、Partition tolerance(分区容错性),三者不可同时获得
- 一致性C:在分布式系统中的所有数据备份,在同一时刻是否同样的值。(所有节点在同一时间的数据完全一致,越多节点,数据同步越耗时)
- 可用性A:负载过大后,集群整体是否还能响应客户端到的读写请求。(服务一直可用,而且是正常响应时间)
- 分区容错性P:分区容忍性,就是高可用性,一个节点崩了,并不影响其他节点(100个节点,挂了几个,不影响服务,越多机器越好)
CAP理论就是说在分布式存储系统中,最多只能实现上面的两点。而由于当前的网络硬件肯定会出现延迟丢包等问题,所以分区容错性是我们必须需要实现的。所以我们只能在一致性和可用性之间进行权衡。
2.2服务注册和发现Eureka Server搭建实战
2.2.1第一步:创建项目
按照以上步骤点击Finish后,喝杯咖啡,等待maven配置环境…
初始化工程目录:
初始化启动文件:
需要添加依赖(按照以上步骤创建,IDEA自动配置好):
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-serverartifactId> dependency>
2.2.2第二步:添加注解@EnableEurekaServer
2.2.3第三步:设置配置文件
关于配置文件application.yml和application.properties都是可以的
application.properties:
server.port=8761
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
eureka.client.service-url.http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
application.yml:
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
yml中注意空格:yml文件中,每个字段的冒号(:)后面都需要加空格,否则无法提取字段
2.2.4第四步:访问注册中心页面
需要根据Maven配置大量环境,建议Maven设置为国内阿里云镜像
Spring官方文档:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-netflix/reference/html/#netflix-eureka-client-starter
2.3服务注册和发现之 Eureka Client搭建商品服务实战
创建一个SpringBoot应用,增加服务器注册和发现依赖
模拟商品信息,存储在内存中,开发商品列表接口,商品详情接口
创建工程目录,结构为下图所示的三层结构
/*ProductController.java*/
package net.xdclass.product_service.controller;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import net.xdclass.product_service.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Api(tags = "搭建商品服务实战")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
/**
* 获取所有商品列表
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "获取商品清单")
@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Object list() {
return productService.listProduct();
}
/**
* 根据id查找商品详情
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "根据编码获取商品信息")
@RequestMapping(value = "/find", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Object findById(@RequestParam("id") Integer id) {
return productService.findById(id);
}
}
/*Product.java*/
package net.xdclass.product_service.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Product implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2646223751221766417L;
/*编号*/
private Integer id;
/*名称*/
private String name;
/*价格*/
private Integer price;
/*库存*/
private Integer store;
public Product() {
}
public Product(Integer id, String name, Integer price, Integer store) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.store = store;
}
/*省略get和set方法*/
}
/*ProductService.java*/
package net.xdclass.product_service.service;
import net.xdclass.product_service.domain.Product;
import java.util.List;
public interface ProductService {
List<Product> listProduct();
Product findById(Integer id);
}
/*ProductServiceImpl.java*/
package net.xdclass.product_service.service.impl;
import net.xdclass.product_service.domain.Product;
import net.xdclass.product_service.service.ProductService;
import org.omg.PortableInterceptor.AdapterManagerIdHelper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.*;
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2432700951541406918L;
private static Map<Integer, Product> daoMap = new HashMap<>();
/*使用静态加载模拟内存中的数据*/
static {
Product p1 = new Product(1, "iphonex", 9999, 10);
Product p2 = new Product(2, "冰箱", 999, 100);
Product p3 = new Product(3, "洗衣机", 99, 101);
Product p4 = new Product(4, "电话", 9, 110);
Product p5 = new Product(5, "汽车", 11, 130);
Product p6 = new Product(6, "椅子", 22, 140);
Product p7 = new Product(7, "书", 33, 160);
daoMap.put(p1.getId(), p1);
daoMap.put(p2.getId(), p2);
daoMap.put(p3.getId(), p3);
daoMap.put(p4.getId(), p4);
daoMap.put(p5.getId(), p5);
daoMap.put(p6.getId(), p6);
daoMap.put(p7.getId(), p7);
}
@Override
public List<Product> listProduct() {
return new ArrayList<>(daoMap.values());
}
@Override
public Product findById(Integer id) {
return daoMap.get(id);
}
}
配置文件加入注册中心地址
.properties文件
#配置端口
server.port=8771
#配置当前微服务名称
eureka.instance.appname=product-service
#eureka.instance.app-group-name=product
#配置到注册中心
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true
eureka.client.service-url.http://localhost:8761/eureka/
.yml文件
server:
prot: 8771
#指定注册中心
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
#服务器名称
spring:
appliaction:
name: product-service
启动注册中心,并将商品服务注册到erueka
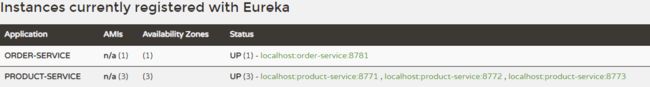
下图所示,即注册成功
下面进行同个服务多端口注册:
第一步:打开配置中心
第二步:端口设置
如下图步骤三,输入
-Dserver.port=端口号
点击ok
第三步:重新启动微服务,注册新端口到eurake
![]()
如图所示,表示两个端口成功注册到eurake
当然你可以再次注册多个不同的端口,只需要重复上述步骤即可。
第四步:测试不同端口的服务功能
利用postman分别对两个端口的服务进行测试:
2.4Eurake服务注册中心配置控制台问题处理
问题一:
去除图中警告只需要在注册中心配置文件中进行配置即可(将自我保护模式关闭)
.properties文件
eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false
.yml文件
eureka:
server:
enable-self-preservation: false
问题二:
只需要添加一个注册地址就可以进行注册,而不需要在启动类上添加注解@EnableEurakeClient
官方文档:
Note that the preceding example shows a normal Spring Boot application. By having spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client on the classpath, your application automatically registers with the Eureka Server. Configuration is required to locate the Eureka server, as shown in the following example:
翻译:
注意,前面的示例显示了一个普通的Spring启动应用程序。通过在类路径上拥有spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client,您的应用程序将自动向Eureka服务器注册。配置需要找到Eureka服务器,如下例所示:
即只需要在配置文件中配置注册路径即可
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
3服务消费者ribbon和feign实战和注册中心高可用
3.1常用的服务间隔调用方式
RPC:
远程过程调用,像本地服务(方法)一样调用服务器的服务
支持同步、异步调用
客户端和服务器之间建立TCP连接,可以一次建立一个,也可以多个调用复用一次连接
通讯层协议为protobuf、thrift、avro,直接采用二进制的形式。
Rest(Http):
http请求,支持多种协议和功能
开发方便成本低
3.2微服务调用方式之ribbon实战,订单调用商品服务
简洁:实战电商项目 订单服务 调用商品服务获取商品信息
3.2.1创建order_service项目
3.2.2使用Ribbon开发伪下单接口
/*OrderController.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.controller;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import net.xdclass.order_service.service.ProductOrderService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Api(tags = "商品订单")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/order")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private ProductOrderService productOrderService;
@ApiOperation(value = "保存订单信息")
@RequestMapping(value = "/save", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Object save(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId, @RequestParam("productId") Integer productId) {
return productOrderService.save(userId, productId);
}
}
/*ProductOrder.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
@Api("商品订单实体类")
public class ProductOrder implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6799431680127887373L;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "订单ID", name = "id")
private Integer id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "商品名称", name = "productName")
private String productName;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "订单流水号", name = "tredeNo")
private String tredeNo;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "订单价格", name = "price")
private Integer price;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8")
@ApiModelProperty(value = "订单创建时间", name = "createTime")
private Date createTime;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID", name = "userId")
private Integer userId;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名称", name = "userName")
private String userName;
/*省略set和get方法*/
}
/*ProductOrderImpl.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.service.impl;
import net.xdclass.order_service.domain.ProductOrder;
import net.xdclass.order_service.service.ProductOrderService;
import net.xdclass.product_service.domain.Product;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
@Service
public class ProductOrderImpl implements ProductOrderService {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Override
public ProductOrder save(Integer userId, Integer productId) {
//获取商品详情
Product object = restTemplate.getForObject(
"http://product-service/api/v1/product/find?id=" + productId, Product.class);
ProductOrder productOrder = new ProductOrder();
if (null != object) {
System.out.println(object);
productOrder.setId(object.getId());
productOrder.setProductName(object.getName());
productOrder.setPrice(object.getPrice());
productOrder.setUserName(port);
productOrder.setCreateTime(new Date());
productOrder.setUserId(userId);
productOrder.setTredeNo(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
}
return productOrder;
}
}
/*ProductOrderService.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.service;
import net.xdclass.order_service.domain.ProductOrder;
public interface ProductOrderService {
public ProductOrder save(Integer userId, Integer productId);
}
启动类中添加一下代码,生成RestTemplate对象用于自动注入
@Bean
@LoadBalanced//使用负载均衡器Ribbon
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
3.2.3根据名称进行调用商品,获取商品详情
启动多个product-service服务端口
如下图可以看出,ribbon自动将访问请求分配到了不同端口的服务上,实现负载均衡
4高级篇幅之Ribbon负载均衡源码分析实战
另一种ribbon的实现
官方文档:
You can also use the LoadBalancerClient directly, as shown in the following example:
public class MyClass {
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
public void doStuff() {
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.choose("stores");
URI storesUri = URI.create(String.format("http://%s:%s", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()));
// ... do something with the URI
}
}
public class MyClass {
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
public void doStuff() {
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.choose("stores");
String url = String.format("http://%s:%s", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort());
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
// ... do something with the restTemplate
//Object object = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Object.class);
}
}
该种方式下不再需要在启动类中添加
@Bean
@LoadBalanced//使用负载均衡器Ribbon
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
而是哪里需要配哪里即可
@Service
public class ProductOrderImpl implements ProductOrderService {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
@Override
public ProductOrder save(Integer userId, Integer productId) {
/*关键代码*/
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.choose("product-service");
String url = String.format("http://%s:%s/api/v1/product/find?id=" + productId, instance.getHost(), instance.getPort());
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
//获取商品详情
Product object = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Product.class);
ProductOrder productOrder = new ProductOrder();
if (null != object) {
System.out.println(object);
productOrder.setId(object.getId());
productOrder.setProductName(object.getName());
productOrder.setPrice(object.getPrice());
productOrder.setUserName(port);
productOrder.setCreateTime(new Date());
productOrder.setUserId(userId);
productOrder.setTredeNo(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
}
return productOrder;
}
}
@LoadBalanced:
- 首先从注册中心获取provider的列表
- 通过一定的策略选择其中一个节点
- 再返回给restTemplate调用
5微服务调用方式之feign 实战 订单调用商品服务
简洁:改造电商项目 订单服务 调用商品服务获取商品信息
Fegin:伪RPC客户端(本质还是用http)
-
使用feign步骤讲解
加入依赖(新旧版本依赖名称不一样)
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId> dependency> -
代码实战
这里的代码在order-service实现ribbon负载均衡上修改而得
/*OrderServiceApplication.java*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableSwagger2
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
创建Feign接口
/*Feign.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.service;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@FeignClient(name = "product-service")
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/api/v1/product/find")
String findById(@RequestParam(value = "id") Integer id);
}
注意:
@FeignClient(name = “”)中name指定的服务名称必须同生产者的服务名称一致
@GetMapping("")中指定的路径必须与调用生产者服务的访问请求路径保持一致
消费者业务逻辑实现类
/*ProductOrderImpl.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.service.impl;
@Service
public class ProductOrderImpl implements ProductOrderService {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@Override
public ProductOrder save(Integer userId, Integer productId) {
/*关键代码*/
String response = productClient.findById(productId);
JsonNode jsonNode = JsonUtils.strTOJsonNode(response);
ProductOrder productOrder = new ProductOrder();
if (null != jsonNode) {
System.out.println(jsonNode);
productOrder.setId(Integer.parseInt(jsonNode.get("id").toString()));
productOrder.setProductName(jsonNode.get("name").toString());
productOrder.setPrice(Integer.parseInt(jsonNode.get("price").toString()));
productOrder.setUserName(port);
productOrder.setCreateTime(new Date());
productOrder.setUserId(userId);
productOrder.setTredeNo(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
}
return productOrder;
}
}
Json工具类
/*JsonUtils.java*/
package net.xdclass.order_service.utils;
public class JsonUtils {
private static final ObjectMapper OBJECT_MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
public static JsonNode strTOJsonNode(String str) {
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.readTree(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
}
注意点:
- 路径
- Http方法必须对应
- 使用@requestBady,应该使用POSTMAPPING
- 多个参数的时候,通过添加@RequestParam
官方文档:
How to Include Feign
To include Feign in your project use the starter with group
org.springframework.cloudand artifact idspring-cloud-starter-openfeign. See the Spring Cloud Project page for details on setting up your build system with the current Spring Cloud Release Train.Example spring boot app
@SpringBootApplication @EnableFeignClients public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }StoreClient.java.
@FeignClient("stores") public interface StoreClient { @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/stores") ListgetStores(); @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/stores/{storeId}", consumes = "application/json") Store update(@PathVariable("storeId") Long storeId, Store store); } In the
@FeignClientannotation the String value (“stores” above) is an arbitrary client name, which is used to create a Ribbon load balancer (see below for details of Ribbon support). You can also specify a URL using theurlattribute (absolute value or just a hostname). The name of the bean in the application context is the fully qualified name of the interface. To specify your own alias value you can use thequalifiervalue of the@FeignClientannotation.The Ribbon client above will want to discover the physical addresses for the “stores” service. If your application is a Eureka client then it will resolve the service in the Eureka service registry. If you don’t want to use Eureka, you can simply configure a list of servers in your external configuration (see above for example).
6Feign核心代码解读和服务调用方式Ribbon和Feign选择
-
Ribbon和Feign的选择使用
一般选择Feign,因为Feign默认集成了Ribbon,代码编写方式更加清晰和方便采用注解方式进行配置,配置熔断等方式方便。
-
负载均衡策略设定
Feign中包含了Ribbon和Hystrix,因此可以直接设置Ribbon改变均衡策略。
以下配置代码表示:将product-service应用的均衡策略配置为随机分配,默认情况下是以轮询的方式进行分配(即每个人一次,依次循环分配)
product-service.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule -
Feign超时配置
在开发过程中每个微服务的响应时间都是不一样的,可以配置超时时间:
- readtimeout:读取超时时间(这个时间是指消费者调用生产者方法到返回响应结果之间的时间段)
- connecttimeout:连接超时时间()
配置语法:
#properties feign.client.config.default.connect-timeout=2000 feign.client.config.default.read-timeout=2000 #yml feign: client: config: default: connectTimeout: 2000 readTimeout: 2000注意:配置语句中的
default为假名,表示配置默认的超时设置,即@FeignClient下的所有接口都将设置为该超时设置默认设置readtimeout为60s,但是由于Hystrix默认是1s超时时间,spring优先以1s超时时间为准
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c0ecf01a8f054cfda1786514d84f9c01.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/775bef4d528945a896519590e3cf36da.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f43955ac6edc4e03b70a1759920de235.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a815aac04ca744c7a1fdbaef8f651fcd.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e5fa57116dd0445db9225772162f9967.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/057578f743a0463dbf1a7dee22de8c0b.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fe3783b59c264a6b95461680fa5780df.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/34b88c26c4ac4c85bd8f893a6ab6a72c.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4fe265bfd916401c8f00ab729d6db72b.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d93be825a7b34f01a8a3e372a1f51668.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/96bf88036e4c48bba7fc9894f2e8152a.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/43bd02358bb944d982e6f6999b6fe03f.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1740ce2237a54cdbb8f14f0de07db9ff.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/07706536e812431794189f8b72ad70a3.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4f5b747713754bbea0ab5dfbc1076903.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第16张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a3a7f7950ca04f7a835a616de98b51eb.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第17张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/410bc9e55fdd4336828ea99d2dc7c3ba.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第18张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b81768c9813849ef9ba4284045c410e6.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第19张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e37b45a4d6044310bf0293d267bf9ff3.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第20张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/af6d70afffac46fa87b236fe1bc17b47.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第21张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1cd998582eed48709cc6ff9ffeb70418.jpg)

![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第22张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c93b5f68747c4cb4b650977b2b317a17.jpg)

![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第23张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ea0309a055a04a249a398616fbac0974.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第24张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/86b188a89016471b9ab7fd646eee3de8.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第25张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b0720b75a3464a768f175b9d0301afb5.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第26张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/06fd3a10a1914dc4b5b037911833b6e7.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第27张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/bb54135f04b44ee99549feaa8802e62c.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第28张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b4a765d625d24db597e65a85e8ec5f38.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第29张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c90e97664d1c47f2881f691142baf476.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第30张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ae36d6f8b01d4b04b6d0e10675fbef5e.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第31张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/441eeb94c2aa4d62b46a9177fe4483f2.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第32张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6c0a7d3fbd674810bd2e81710434416a.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第33张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51005e1718b54fa394db0b50a875d17d.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第34张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/15b7f091cc244e9ab83459a3d98aa68b.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第35张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2fe9186656854022be29dc02040bd15c.jpg)
![[一]SpringCloud微服务入门_第36张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5a9837f6c7a945d98a9f2b3172285b29.jpg)