java基础复习之《异常体系》
基础复习之Java异常
Throwable
|-Error
|-Exception
|-RuntimeException
自定义异常
package com.jingfeng.test;
class NoArgException extends RuntimeException {
public NoArgException(){
super();
}
public NoArgException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
class Person{
int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(int age){
if(age<0 || age>200){
throw new NoArgException("非法参数");
}
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class ExceptionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person(-4);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
RuntimeException的源码,基本上没做什么。照样调用父类的构造函数。
public class RuntimeException extends Exception {
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897190745766939L;
/** Constructs a new runtime exception with {@code null} as its
* detail message. The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be
* initialized by a call to {@link #initCause}.
*/
public RuntimeException() {
super();
}
/** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message.
* The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a
* call to {@link #initCause}.
*
* @param message the detail message. The detail message is saved for
* later retrieval by the {@link #getMessage()} method.
*/
public RuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
/**
* Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message and
* cause. Note that the detail message associated with
* {@code cause} is not automatically incorporated in
* this runtime exception's detail message.
*
* @param message the detail message (which is saved for later retrieval
* by the {@link #getMessage()} method).
* @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the
* {@link #getCause()} method). (A null value is
* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or
* unknown.)
* @since 1.4
*/
public RuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
/** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified cause and a
* detail message of (cause==null ? null : cause.toString())
* (which typically contains the class and detail message of
* cause). This constructor is useful for runtime exceptions
* that are little more than wrappers for other throwables.
*
* @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the
* {@link #getCause()} method). (A null value is
* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or
* unknown.)
* @since 1.4
*/
public RuntimeException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
/**
* Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail
* message, cause, suppression enabled or disabled, and writable
* stack trace enabled or disabled.
*
* @param message the detail message.
* @param cause the cause. (A {@code null} value is permitted,
* and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or unknown.)
* @param enableSuppression whether or not suppression is enabled
* or disabled
* @param writableStackTrace whether or not the stack trace should
* be writable
*
* @since 1.7
*/
protected RuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
*继承Exception和继承RuntimeException的区别为什么那么大呢?
(1)继承Exception,程序编译错误,语法错误。java程序认为这个程序存在隐患,需要声明出来,要么把问题处理,让调用者知道。
(2)继承RuntimeException,编译正常,指的是运行时异常。
*异常分为俩种:
(1),编译时异常:编译器会检测的异常。需要声明。
(2),运行时异常:编译器不会检测的异常。不需要声明。(声明出来也没错)如果声明了,就是让调用者给出处理方式。(可以不处理,可以不用try...catch)。
*常见的运行时异常:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException - 数组越界访问
ClassCastException - 类型转换异常
IllegalArgumentException - 方法的参数无效
NullPointerException - 试图访问一空对象的变量、方法或空数组的元素
NumberFormatException - 数据格式异常,试图把一字符串非法转换成数值(或相反)
OutOfMemoryException - 内存不足,通常发生于创建对象之时
NoClassDefFoundException - JAVA运行时系统找不到所引用的类
*异常的声明
package com.jingfeng.test;
public class ExceptionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Person1 person = new Person1("rose");
person.show();
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
class Person1{
private String name;
public Person1(){
super();
}
public Person1(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void show() throws Exception{
throw new Exception();
}
}
因为show方法用throw抛出了一个编译时异常,所以,这个异常需要声明或者捕获处理。
声明异常用关键字throws,声明了异常,让调用者捕获处理。
主函数调用了show方法,所以主函数就要处理这个异常,如果不处理,则继续往上抛,即抛给了虚拟机,虚拟机将异常直接打印控制台。
可以声明多个异常,用逗号隔开。
*异常的捕获处理
可以使用多个catch进行捕获
try{
}catch(NoAgeException e){
}catch(Exception e){
...临时解决方案
throw new NoNameException();//异常转换,对象本身处理不了。
}finally{
}
当catch捕获的异常存在父子类关系时,父类放在后面。否则会报错
比如Exception放在第一位,其他的异常就捕获不了了。
*throw和throws的区别
(1)throw用在函数内。
throws用在函数名上。(位置不同)
(2)throw抛出的是异常对象。
throws用于对异常类的声明,后面可以有多个异常类,用逗号隔开。(作用不同)
*finally的使用
package com.jingfeng.test;
public class ExceptionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Person2 person = new Person2();
try{
person.show(-1);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
return;//返回之前执行finally代码块中的代码
//有一种情况,连finally也不执行,即退出JVM
//System.exit(0);
}finally{
System.out.println("hello");
}
System.out.println("over");
}
}
class Person2{
public void show(int x) throws Exception{
if(x<0){
throw new Exception();
}
System.out.println(x+"...show running");
}
}
首先person对象调用的show方法发生了异常,catch捕获以后对其进行了处理,处理完以后返回,结束程序。但是finally无论发生什么情况都会执行,所以return之前,应该执行fnally代码块中的代码。
*案例
package com.jingfeng.test;
public class ExceptionDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Test test = new Test();
int x = test.show(-11);
System.out.println(x);
}
}
class Test{
public int show(int x){
try{
if(x<0){
throw new Exception();
}
return 1;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
return 2;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally run");
return 3;
}
}
}
问发生异常和没有发生异常的输出值是多少?
答案:都是3.
因为return之前都要执行finally中的代码,finally中又有return语句,所以永远都是返回finally中的值。所以是3。
* try,catch,finally的组合方式
(1)
try{
}catch(){
}
检测异常,并捕获处理。
(2)
try{
}finally{
}
检测异常,不进行处理。(释放资源)
(3)
try{
}catch(){
}finally{
}
检测异常,捕获处理,释放资源。
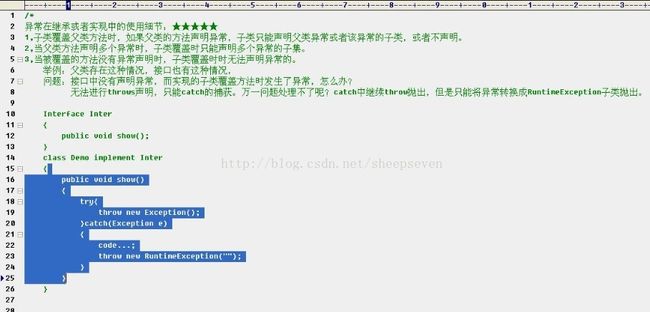
*异常在类继承和实现中的使用细节