CentOS7上安装并配置Nginx、PHP、MySql
一、Nginx
1、安装nginx
yum install nginx2、启动nginx
systemctl start nginx除了systemctl start nginx之外,常用的相关命令还有systemctl stop nginx、systemctl restart nginx、systemctl status nginx
3、测试nginx是否安装成功
浏览器输入ip地址或者域名(已经解析过的域名),如下图所示,则安装成功。
4,配置Nginx支持PHP解析
编辑/etc/nginx/nginx.conf,蓝色字体处为新加内容
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
location ~ .php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
}
二、PHP
1,安装PHP
yum install php php-mysql php-fpm安装过程中经常会见到如下问题:
2:postfix-2.10.1-6.el7.x86_64 有缺少的需求 libmysqlclient.so.18()(64bit)
2:postfix-2.10.1-6.el7.x86_64 有缺少的需求 libmysqlclient.so.18(libmysqlclient_18)(64bit)
解决方法:
把php-mysql换成php-mysqlnd
即执行
yum install php php-mysqlnd php-fpm2、编辑PHP的配置文件,/etc/php.ini,注意去掉分号注释
vim /etc/php.ini将 ;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1 改为 cgi.fix_pathinfo=0
3、编辑PHP-FPM配置文件
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf 将
user = nobody
group = nobody
改为
user = nginx
group = nginx
前提是已经创建了nginx用户和nginx组。如果没有创建方法:
1 groupadd -r nginx
2 useradd -r -g nginx nginx4、启动PHP—FPM
systemctl start php-fpm5、设置开机启动
systemctl enable php-fpm6,确保Nginx配置文件修该之后,重启Nginx
systemctl restart nginx7、在/usr/share/nginx/html/目录下创建phpinfo.php
内容如下:
查看php进程:ps aux | grep php 查看端口占用:netstat -ano|grep 80
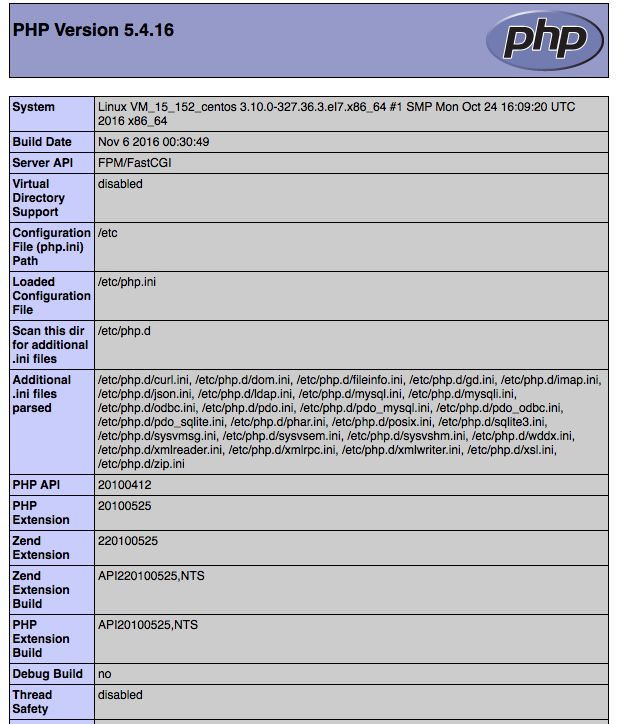
8、浏览器上输入ip/phpinfo.php,如果出现如下界面,说明PHP和Nginx均安装和配置成功。
三、MySql
CentOS 7的yum源中貌似没有正常安装mysql时的mysql-sever文件,需要去官网上下载
1、补充yum源(1)
wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm2、补充yum源(2)
rpm -ivh mysql-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm3、安装mysql
yum install mysql-community-server4、成功安装之后重启mysql服务
systemctl start mysqld初次安装mysql是root账户是没有密码的
设置密码的方法
1 mysql -uroot
2 mysql> set password for ‘root’@‘localhost’ = password('mypasswd');
3 mysql> exit
mysql -u root -p
输入密码之后,错误提示如下:ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES),意思是root的密码不正确。
解决办法如下:
a.sudo mysqld_safe --user=root --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
输入命令之后,如果提示信息为:
mysqld_safe A mysqld process already exists
表示mysqld_safe进程存在,可以通过
ps -A|grep mysql 查看mysqld_safe进程ID
kill -9 -xxxx 终结ID为xxxx的进程
重置密码方法还可以如下:
方法一、
Js代码
![]()
# /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
# mysqld_safe --user=mysql --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
# mysql -u root mysql
mysql> UPDATE user SET Password=PASSWORD('newpassword') where USER='root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> quit
# /etc/init.d/mysql restart
# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: <输入新设的密码newpassword>
mysql> ![]()
方法二、
Js代码
直接使用/etc/mysql/debian.cnf文件中[client]节提供的用户名和密码:
![]()
# mysql -udebian-sys-maint -p
Enter password: <输入[client]节的密码>
mysql> UPDATE user SET Password=PASSWORD('newpassword') where USER='root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> quit
# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: <输入新设的密码newpassword>
mysql> ![]()
支持远程访问:
mysql>use mysql;
mysql>update user set host = '%' where user = 'root'; --%可以改成ip或者其他
mysql>select host, user from user;
重启数据库
另你处引用内容如下:
1、首先停止正在运行的MySQL进程
Linux下,运行
1 killall -TERM mysqld
Windows下,如果写成服务的 可以运行:
1 net stop mysql
,如未加载为服务,可直接在进程管理器中进行关闭。
2、以安全模式启动MySQL
Linux下,运行
1 mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
Windows下,在命令行下运行
1 X:/MySQL/bin/mysqld-nt.exe --skip-grant-tables
3、完成以后就可以不用密码进入MySQL了
Linux下,运行
1 mysql -u root -p
进入
Windows下,运行
1 X:/MySQL/bin/mysql -u root -p
进入
4、更改密码
123 >use mysql
>update user set password=password("新密码") where user="root";
>flush privileges;
注意:>update mysql.user set password=password('1234') where user='root';
如果实在不行可以用root账号看下 查看information_schema库的user_privileges 表 看下他对每个账号分配的权限。
使用mysql -uroot -p,然后输入密码登录mysql时,出现了如下错误:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
一般这个错误是由密码错误引起,解决的办法自然就是重置密码
解决方案如下:
1.停止mysql数据库:systemctl stop mysqld
2.用以下命令启动MySQL,以不检查权限的方式启动:
mysqld --skip-grant-tables &
此时又报了一个错误:2018-02-01T02:52:55.093724Z 0 [ERROR] Fatal error: Please read "Security" section of the manual to find out how to run mysqld as root!
执行命令:mysqld --user=root --skip-grant-tables &
3.登录mysql:mysql -uroot或mysql
4.更新root密码
mysql5.7以下版本:UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('123456') where USER='root';
mysql5.7版本:UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD('123456') where USER='root';
5.刷新权限:flush privileges;
6.退出mysql:exit或quit
7.使用root用户重新登录mysql
mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:<输入新设的密码123456>
4.MySQL数据库远程访问权限如何打开(两种方法)
在我们使用mysql数据库时,有时我们的程序与数据库不在同一机器上或者有时候我们需要通过自己电脑用可视化sqlyog,或者navicat图形化来操作一下数据库,这时我们需要远程访问数据库。缺省状态下,mysql的用户没有远程访问的权限。
下面介绍两种方法,解决这一问题。
1、改表法
可能是你的帐号不允许从远程登陆,只能在localhost。这个时候只要在localhost的那台服务器,登入mysql后,更改 "mysql" 数据库里的 "user" 表里的 "host" 项,从"localhost"改称"%"就能远程访问了!
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p mysql>use mysql; mysql>update user set host = '%' where user = 'root'; mysql>select host, user from user; mysql>flush privileges;
2、授权法
在安装mysql的服务器上面执行:
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -h localhost -u root
#进入mysql服务以后输入下面命令对root用户远程授权
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%'WITH GRANT OPTION
#赋予任何主机访问数据的权限
##如果你想Juser用户使用Jpassword密码从任何主机连接到mysql服务器的话。
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'Juser'@'%'IDENTIFIED BY 'Jpassword' WITH GRANT OPTION;
如果你想允许用户Juser从ip为192.168.0.100的主机连接到mysql服务器,并使用Jpassword作为密码
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'Juser'@'192.168.0.100'IDENTIFIED BY 'Jpassword' WITH GRANT OPTION;
#重新加载权限语句让权限生效
mysql>FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
#退出MySQL服务器,这样就可以在其它任何的主机上以root身份登录
mysql>exit