一、ServletConfig
在Servlet的配置文件中,可以使用init-param标签为Servlet配置一些初始化参数,这些参数可以包括字符集编码,数据库连接信息等。这些配置信息我们可以使用ServletConfig对象来获取。
获取ServletConfig的方法:
(1)在类中重写方法init,并创建一个ServletConfig类型的成员变量,将init方法得到的ServletConfig对象赋值给成员变量
private ServletConfig config;
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
}
(2)直接在doGet方法中调用getServletConfig方法获得ServletConfig的对象
ServletConfig config = getServletConfig();
示例:
web.xml配置文件中的设置
//init-param标签是Servlet标签的子标签
Demo1
Demo1
com.demo.Demo1
username
zhangsan
password
123456
通过ServletConfig对象获得配置信息
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletConfig config = getServletConfig();
String username = config.getInitParameter("username");
String password = config.getInitParameter("password");
response.getWriter().println(username);
response.getWriter().println(password);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
二、ServletContext
1、概述
当WEB服务器启动的时候,会为每个WEB应用程序创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,他代表了当前的WEB应用,也称之为是WEB应用的上下文,被整个WEB程序所共享,是WEB应用的域对象。
域对象:有范围的Map,让数据在整个应用所共享。
2、功能
(1)获取WEB应用的初始化参数
ServletContext获取WEB应用的初始化参数的方法与ServletConfig相似,配置信息都在web.xml文件中,通过context-param便签设置WEB应用的初始化信息,context-param便签是web-app的子标签,获取方法是getServletContext。
示例:
配置信息:
username
lisi
获取初始化参数
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
String username = context.getInitParameter("username");
response.getWriter().println(username);
(2)实现数据的共享
由于ServletContext对象是WEB应用的域对象,能够被所有的Servlet所共享,所以能够实现数据的共享。
示例:
首先我们在Demo1中设置WEB应用的属性值,并获取输出
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
context.setAttribute("username", "wangwu");
Object username = context.getAttribute("username");
response.getWriter().println(username);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
然后我们在Demo3中获取属性值,我们发现可以获得相同的属性值
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
Object username = context.getAttribute("username");
response.getWriter().println(username);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
(3)获取当前WEB应用的绝对路径
示例:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo4 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
String path = context.getRealPath("/");//"/"代表当前web应用的根路径
response.getWriter().println(path);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
(4)请求转发和包含
Servlet的service()方法是Servlet容器来调用的,用户不能在一个Servlet对象中直接调用另外一个Servlet的service方法,所以需要多个Servlet协同处理。Servlet规范提供了2个途径:
- 请求转发
Servlet1先对用户的请求做一些预处理,然后把请求转发给Servlet2完成响应
示例:
将Demo5的请求转发到Demo6中
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo5 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().println("hello");
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
RequestDispatcher rd = context.getRequestDispatcher("/Demo6");
rd.forward(request, response);
response.getWriter().println("hello");
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo6 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
context.setAttribute("username", "zhaoliu");
Object username = context.getAttribute("username");
response.getWriter().println(username);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
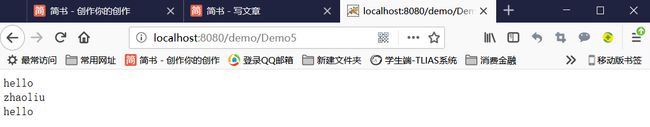
在浏览器中访问Demo5,得到结果:
- 请求响应
Servlet1把Servlet2生成的响应结果包含到自身的响应结果里面,完成响应
示例:
修改Demo5的代码,将Demo5的请求包含到Demo6中
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Demo5 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().println("hello");
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
RequestDispatcher rd = context.getRequestDispatcher("/Demo6");
rd.include(request, response);
response.getWriter().println("hello");
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
对比两个结果,我们发现在转发之后响应的内容会被取消,包含前后可以继续响应其他内容,同时地址栏中的路径都不会发生变化,二者共享一个请求响应对象,实现时需要依赖RequestDispatcher接口(请求分发器)。
注意:
1、forward()方法先清空用于存放响应正文数据的缓冲区,然后在把请求转发给Servlet2完成响应,只有Servlet2响应的结果才会发送到浏览器
2、这两个必须在服务器内部进行操作,并且以绝对路径开头