用Assimp模型加载库加载一个Crytek的游戏孤岛危机(Crysis)中的原版纳米装(Nanosuit)
用这个例子来对GitHub上的LearnOpenGL教程前四个单元用到的所有自定义或者引入的各种头文件和资源进行一个总结,不得不说这个教程简直太美妙了。
这个模型是来自对GitHub上的LearnOpenGL的一个例子:
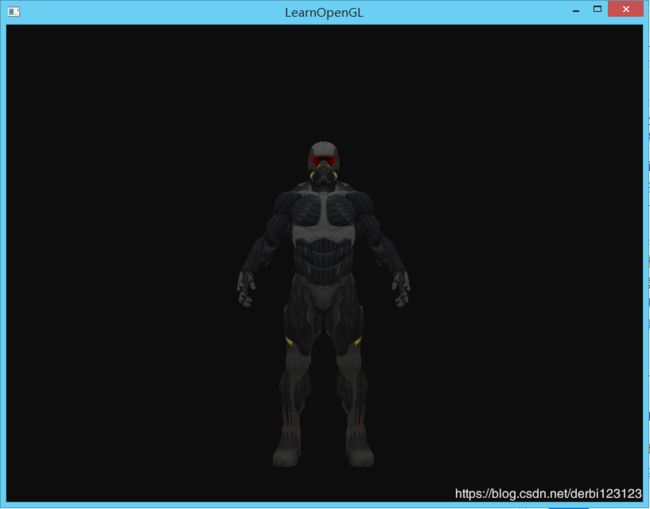
准备工作:
-
用的是OpenGL和glfw,glfw安装配置可见:
https://blog.csdn.net/derbi123123/article/details/104350624 -
还有要用到的数学库glm的配置:
https://blog.csdn.net/derbi123123/article/details/105611148 -
Assimp模型加载库的下载、编译、配置的教学可见:
https://blog.csdn.net/derbi123123/article/details/105783048 -
模型的下载地址:
https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/data/nanosuit.rar
下面给出各部分的源码:
(1)顶点着色器和片段着色器:
当然着色器部分只是对于这个例子而言的,它有自己固定的一套流程,可以让我们随心所欲的改变绘制的效果。
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;
out vec2 TexCoords;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
}
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1;
void main()
{
FragColor = texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoords);
}
(2)头文件mesh.h:
网格(Mesh)代表的是单个的可绘制实体,我们现在先来定义一个我们自己的网格类。
网格:
当使用建模工具对物体建模的时候,艺术家通常不会用单个形状创建出整个模型。通常每个模型都由几个子模型/形状组合而成。组合模型的每个单独的形状就叫做一个网格(Mesh)。比如说有一个人形的角色:艺术家通常会将头部、四肢、衣服、武器建模为分开的组件,并将这些网格组合而成的结果表现为最终的模型。一个网格是我们在OpenGL中绘制物体所需的最小单位(顶点数据、索引和材质属性)。一个模型(通常)会包括多个网格。
#ifndef MESH_H
#define MESH_H
#include (3)头文件camera.h:
为了在OpenGL中模拟出摄像机,产生一种我们在移动的感觉,而不是场景在移动。
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include (4)头文件model.h:
创建另一个类来完整地表示一个模型。
#ifndef MODEL_H
#define MODEL_H
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include (5)头文件Shader.h:
为了便于简化我们的主程序,我们把shader的配置、链接放到一个类中
#ifndef SHADER_H
#define SHADER_H
#include (6)头文件stb_image.h:
stb_image.h是Sean Barrett的一个非常流行的单头文件图像加载库,它能够加载大部分流行的文件格式,并且能够很简单得整合到你的工程之中。其下载和配置可见:
https://blog.csdn.net/derbi123123/article/details/105610298
最后就是我们的主程序了:
#include