在uboot中使用UDP协议实现UDP通信
本文所讲的uboot是基于海思芯片的uboot(如HI3520D)。因为TFTP协议是基于UDP协议,所以本文大部分代码是直接使用TFTP的。在写代码之前复习一下TFTP报文和UDP报文的结构。
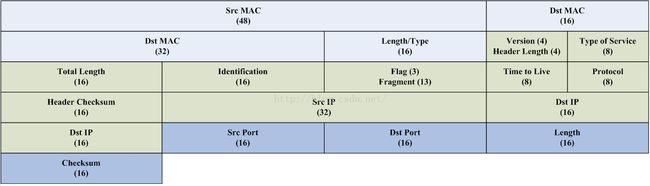
每行占64位(bit),共8字节(byte)。
UDP报文:太网包头+IP包头+UDP包头+数据
TFTP报文:太网包头+IP包头+UDP包头+TFTP包头+数据
填充太网包头+IP包头+UDP包头的话直接调用TFTP报文的就可以了。
步骤:
一、像TFTP命令一样写一个UDP命令
我直接在cmd_net.c中添加如下代码(当然也可以新建一个cmd_udp.c,那样的话要在u-boot-2010.06/include/configs/hi3520d.h文件里面添加
#define CONFIG_CMD_UDP,,并且在common目录的Makefile里面添加COBJS-$(CONFIG_CMD_UDP) += cmd_udp.o):
在下面实现netboot_UDP_TCP 函数,记得定义一下这个函数。
static int netboot_UDP_TCP (proto_t proto, cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int argc, char *argv[])
{
extern ulong upload_addr;
extern ulong upload_size;
char *s;
char *end;
int rcode = 0;
int size;
ulong addr;
/* pre-set load_addr */
if ((s = getenv("loadaddr")) != NULL) {
load_addr = simple_strtoul(s, NULL, 16);
}
switch (argc) {
case 1:
break;
case 2:
pkt_data = argv[1];
break;
default: cmd_usage(cmdtp);
show_boot_progress (-80);
return 1;
}
show_boot_progress (80);
if ((size = NetLoop(proto)) < 0) {
show_boot_progress (-81);
return 1;
}
show_boot_progress (81);
/* NetLoop ok, update environment */
netboot_update_env();
/* done if no file was loaded (no errors though) */
if (size == 0) {
show_boot_progress (-82);
return 0;
}
/* Loading ok, check if we should attempt an auto-start */
if (((s = getenv("autostart")) != NULL) && (strcmp(s,"yes") == 0)) {
char *local_args[2];
local_args[0] = argv[0];
local_args[1] = NULL;
printf ("Automatic boot of image at addr 0x%08lX ...\n",
load_addr);
show_boot_progress (82);
rcode = do_bootm (cmdtp, 0, 1, local_args);
}
if (rcode < 0)
show_boot_progress (-83);
else
show_boot_progress (84);
return rcode;
}二、为了清楚一点我在net目录下touch一个udp.c和udp.h文件
第一步之后会跳到net目录下的net.c的NetLoop函数,但是在switch(protocol)里面添加
case UDP:
UdpStart();
break;
UDP协议在net.h里面添加
![]()
Udpstart函数在udp.c里面实现,所以接下来会跳到net目录下的udp.c文件里面,udp.c和udp.h代码如下:
udp.c(主要是发送已经填充好的报文,这里发送函数直接调用TFTP协议使用的发送函数):
#include
#include
#include
#include "tftp.h"
#include "bootp.h"
#include "udp.h"
#define TIMEOUT 1000 /* Seconds to timeout for a lost pkt */
#ifndef CONFIG_NET_RETRY_COUNT
# define TIMEOUT_COUNT 10 /* # of timeouts before giving up */
#else
# define TIMEOUT_COUNT (CONFIG_NET_RETRY_COUNT * 2)
#endif
static ulong UdpTimeoutMSecs = TIMEOUT;
static int UdpTimeoutCountMax = TIMEOUT_COUNT;
/*
* These globals govern the timeout behavior when attempting a connection to a
* TFTP server. UdpRRQTimeoutMSecs specifies the number of milliseconds to
* wait for the server to respond to initial connection. Second global,
* UdpRRQTimeoutCountMax, gives the number of such connection retries.
* UdpRRQTimeoutCountMax must be non-negative and UdpRRQTimeoutMSecs must be
* positive. The globals are meant to be set (and restored) by code needing
* non-standard timeout behavior when initiating a TFTP transfer.
*/
ulong UdpRRQTimeoutMSecs = TIMEOUT;
int UdpRRQTimeoutCountMax = TIMEOUT_COUNT;
static IPaddr_t UdpServerIP;
static int UdpServerPort; /* The UDP port at their end */
static int UdpOurPort; /* The UDP port at our end */
static int UdpTimeoutCount;
static void UdpSend (void);
static void UdpTimeout (void);
/**********************************************************************/
static void
UdpSend (void)
{
volatile uchar * pkt;
volatile uchar * xp;
int len = 0;
int uplen=0;
volatile ushort *s;
/*
* We will always be sending some sort of packet, so
* cobble together the packet headers now.
*/
pkt = NetTxPacket + NetEthHdrSize() + IP_HDR_SIZE;
len = strlen(pkt_data);
memcpy(pkt, pkt_data, len);
printf("pkt_data=%s,len=%d\n", pkt_data,len);
NetSendUDPPacket(NetServerEther, UdpServerIP, UdpServerPort, UdpOurPort, len);
}
static void
UdpHandler (uchar * pkt, unsigned dest, unsigned src, unsigned len)
{
ushort proto;
ushort *s;
int i;
printf("receive udp packet\n");
s = (uchar *)pkt;
printf("len=%d\n",len);
printf("%.*s\n", len, s);
}
static void
UdpTimeout (void)
{
if (++UdpTimeoutCount > UdpTimeoutCountMax) {
puts ("\nRetry count exceeded; starting again\n");
NetStartAgain ();
} else {
puts ("T ");
NetSetTimeout (UdpTimeoutMSecs * CFG_HZ, UdpTimeout);
UdpSend ();
}
}
void
UdpStart (void)
{
char *ep; /* Environment pointer */
/*
* Allow the user to choose UDP blocksize and timeout.
* UDP protocol has a minimal timeout of 1 second.
*/
if ((ep = getenv("udptimeout")) != NULL)
UdpTimeoutMSecs = simple_strtol(ep, NULL, 10);
if (UdpTimeoutMSecs < 1000) {
printf("UDP timeout (%ld ms) too low, "
"set minimum = 1000 ms\n",
UdpTimeoutMSecs);
UdpTimeoutMSecs = 1000;
}
UdpServerIP = NetServerIP;
#if defined(CONFIG_NET_MULTI)
printf ("Using %s device\n", eth_get_name());
#endif
UdpTimeoutCountMax = UdpRRQTimeoutCountMax;
NetSetTimeout (UdpTimeoutMSecs * CFG_HZ, UdpTimeout);
NetSetHandler (UdpHandler);
UdpServerPort = 75;//WELL_KNOWN_PORT;
UdpTimeoutCount = 0;
UdpOurPort = 1024;
UdpPktLen = 0;
/* zero out server ether in case the server ip has changed */
memset(NetServerEther, 0, 6);
UdpSend ();
udp.h:
#ifndef __UDP_H__
#define __UDP_H__
extern void UdpStart (void);
#endif
三、代码基本实现完了,最后是测试
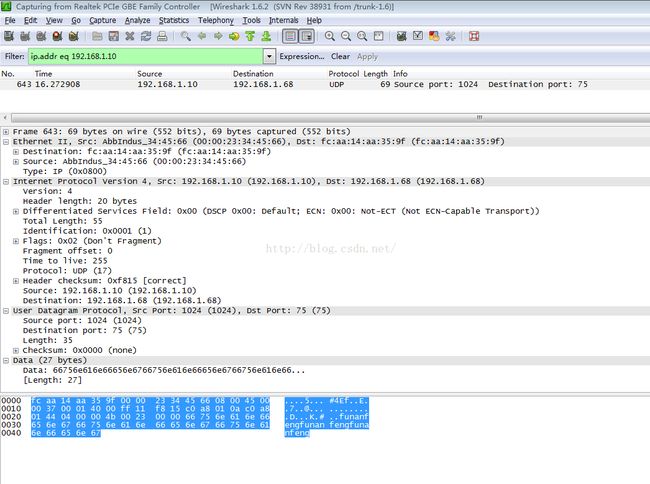
在这里千万别像TFTP命令一样用69端口和TFTP服务器测试UDP协议。否则Wireshark抓到的包是TFTP协议的包,因为TFTP服务器把收到的UDP包当成是TFTP包了,并且TFTP包都会有一个操作选项(已经定义好的),所以抓到是unknown的包。
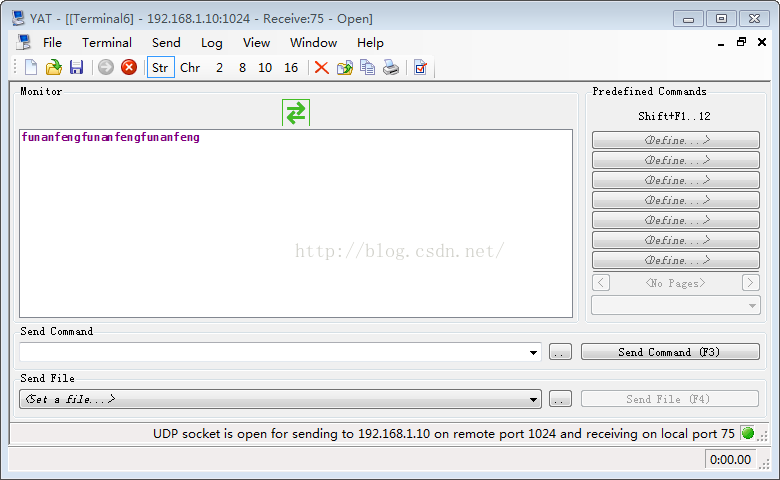
这里最好是使用能接收UDP包的工具当服务器,比如在绿软家园里面下载的YAT、TCP&UDP测试工具 V1.02等等。这次测试使用的是YAT,打开YAT并设置uboot的IP、端口号1024、服务器端口号75
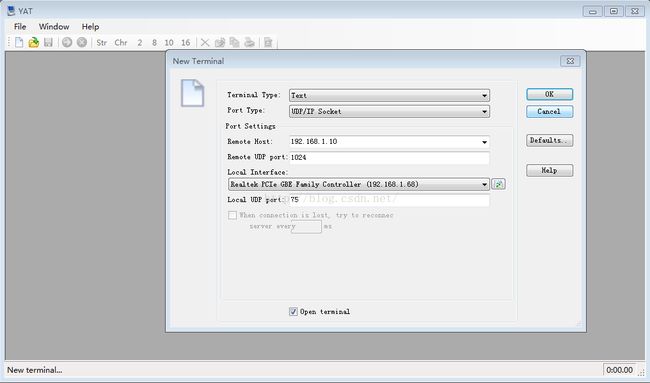
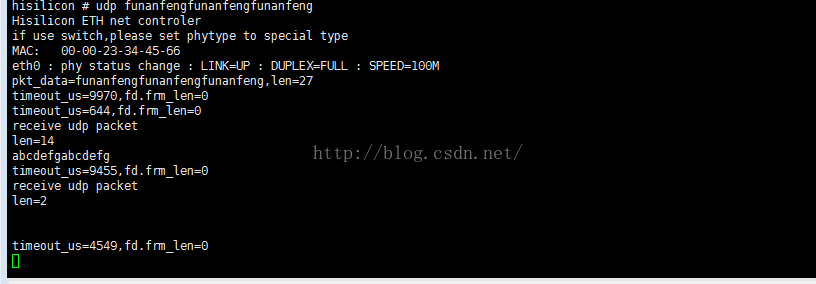
现在在uboot中开始发包,数据为字符串:funanfengfunanfengfunanfeng
Wireshark抓到的包:
YAT服务器端收到的数据:
现在测试在uboot里面接收服务器发过来的数据:
从服务器向uboot发一个字符串:abcdefgabcdefg
Wireshark抓到的包:
在uboot中收到接收到服务器发过来的字符串,但是不知为什么发完数据包之后还发过来一个空包,在其他的测试工具就没这种现象,有待解决。